The 27th century BC was a century that lasted from the year 2700 BC to 2601 BC.

Djoser was an ancient Egyptian pharaoh of the 3rd Dynasty during the Old Kingdom, and was the founder of that epoch. He is also known by his Hellenized names Tosorthros and Sesorthos. He was the son of King Khasekhemwy and Queen Nimaathap, but whether he was also the direct successor to their throne is unclear. Most Ramesside king lists identify a king named Nebka as preceding him, but there are difficulties in connecting that name with contemporary Horus names, so some Egyptologists question the received throne sequence. Djoser is known for his step pyramid, which is the earliest colossal stone building in ancient Egypt.
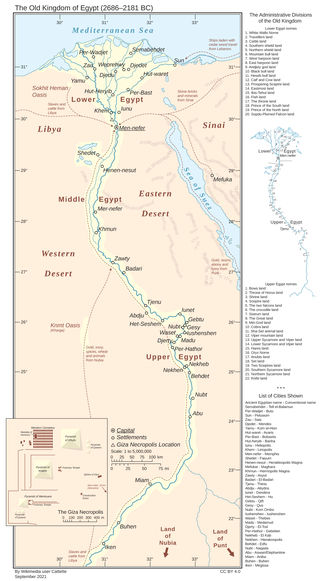
In ancient Egyptian history, the Old Kingdom is the period spanning c. 2700–2200 BC. It is also known as the "Age of the Pyramids" or the "Age of the Pyramid Builders", as it encompasses the reigns of the great pyramid-builders of the Fourth Dynasty, such as King Sneferu, who perfected the art of pyramid-building, and the kings Khufu, Khafre and Menkaure, who constructed the pyramids at Giza. Egypt attained its first sustained peak of civilization during the Old Kingdom, the first of three so-called "Kingdom" periods, which mark the high points of civilization in the lower Nile Valley.

The Egyptian pyramids are ancient masonry structures located in Egypt. Sources cite at least 118 identified "Egyptian" pyramids. Approximately 80 pyramids were built within the Kingdom of Kush, now located in the modern country of Sudan. Of those located in modern Egypt, most were built as tombs for the country's pharaohs and their consorts during the Old and Middle Kingdom periods.

Hetepheres II was a queen of ancient Egypt during the 4th Dynasty.
Hetepheres is the name of several queens, princesses and noble women from the Fourth dynasty of Egypt.

The Fourth Dynasty of ancient Egypt is characterized as a "golden age" of the Old Kingdom of Egypt. Dynasty IV lasted from c. 2613 to 2494 BC. It was a time of peace and prosperity as well as one during which trade with other countries is documented.

Nubkaure Amenemhat II, also known as Amenemhet II, was the third pharaoh of the 12th Dynasty of ancient Egypt. Although he ruled for at least 35 years, his reign is rather obscure, as well as his family relationships.
Hetepheres I was a queen of Egypt during the Fourth Dynasty of Egypt who was a wife of one king, the mother of the next king, the grandmother of two more kings, and the figure who tied together two dynasties.

Nimaathap was an ancient Egyptian queen consort at the transition time from 2nd Dynasty to 3rd Dynasty. Nimaathap may have acted as regent for her son Djoser.

Ankhhaf was an Egyptian prince and served as an overseer during the reign of the Pharaoh Khufu, who is thought to have been Ankhhaf's half-brother. One of Ankhaf's titles is also as a vizier, but it is unknown under which pharaoh he would have held this title. He lived during Egypt's 4th Dynasty.

Sneferu, well known under his Hellenized name Soris, was the founding pharaoh of the Fourth Dynasty of Egypt during the Old Kingdom. Estimates of his reign vary, with for instance The Oxford History of Ancient Egypt suggesting a reign from around 2613 to 2589 BC, a reign of 24 years, while Rolf Krauss suggests a 30-year reign, and Rainer Stadelmann a 48-year reign. He built at least three pyramids that survive to this day and introduced major innovations in the design and construction of pyramids.

Rahotep was a prince in ancient Egypt during the 4th Dynasty. He was probably a son of Pharaoh Sneferu and his first wife, although Zahi Hawass suggests his father was Huni.

Ranefer was a prince of ancient Egypt during the 4th Dynasty.

Meresankh II was a queen consort of Egypt who lived during 4th Dynasty.
Kagemni I was an ancient Egyptian who lived from the end of the 3rd Dynasty to the beginning of the 4th Dynasty. He was a vizier to both Pharaoh Huni and Pharaoh Sneferu.
Princess Hetepheres was an Egyptian princess who lived during the 4th Dynasty. Hetepheres was the daughter of King Sneferu and the wife of vizier Ankhhaf.

The Eighteenth Dynasty of Egypt is classified as the first dynasty of the New Kingdom of Egypt, the era in which ancient Egypt achieved the peak of its power. The Eighteenth Dynasty spanned the period from 1550/1549 to 1292 BC. This dynasty is also known as the Thutmoside Dynasty) for the four pharaohs named Thutmose.
This page list topics related to ancient Egypt.

Metjen was an ancient Egyptian high official at the transition time from 3rd Dynasty to 4th Dynasty. He is famous for his tomb inscription, which states that he worked and lived under the kings (pharaohs) Huni and Sneferu.















