
John Taylor Wedgwood (christened 19 October 1782- 6 March 1856) was an English line engraver. [1] [2]

John Taylor Wedgwood (christened 19 October 1782- 6 March 1856) was an English line engraver. [1] [2]
He was the son of the potter Thomas Wedgwood II (1734-1788) and his wife Elizabeth Taylor. His elder brother was of Ralph Wedgwood, who was a pioneer of photography, and they both were cousins of Josiah Wedgwood, the industrial potter.
He worked for many years in Paris. His work focused on adapting existing paintings, mostly portraits, for printing. He used the burin technique for engraving. [2]
Wedgwood covered original works by artists such as Samuel Cooper, [3] William Johnstone White, [3] John Thurston, [3] Henry Weekes, [3] Mary Beale, [3] Titian [3] Sir Joshua Reynolds, [4] Thomas Gainsborough, [4] Eugène Devéria, [4] Salvator Rosa, [4] Antonio Correggio, [4] Henry Perronet Briggs, [4] Sir George Hayter, [4] Lemuel Francis Abbott, [4] John Singleton Copley, [4] William Behnes, [4] Miss Carmichael, [4] Achille Devéria, [4] Louis Boulanger, [4] Robert Blemmell Schnebbelie, [4] Henry Corbould, [4] Louis Boulanger, [4] George Shepherd, [4] George Robert Lewis, [4] Sir Francis Legatt Chantrey, [4] Antoine François Callet/Joseph Siffred Duplessis, [4] William Dobson, [4] Francis Parsons, [4] Sir Peter Lely, [4] Willem van de Passe, [4] Henry Perronet Briggs, [4]

Josiah Wedgwood was an English potter, entrepreneur and abolitionist. Founding the Wedgwood company in 1759, he developed improved pottery bodies by systematic experimentation, and was the leader in the industrialisation of the manufacture of European pottery.

John Flaxman was a British sculptor and draughtsman, and a leading figure in British and European Neoclassicism. Early in his career, he worked as a modeller for Josiah Wedgwood's pottery. He spent several years in Rome, where he produced his first book illustrations. He was a prolific maker of funerary monuments.

The Etruria Works was a ceramics factory opened by Josiah Wedgwood in 1769 in a district of Stoke-on-Trent, Staffordshire, England, which he named Etruria. The factory ran for 180 years, as part of the wider Wedgwood business.
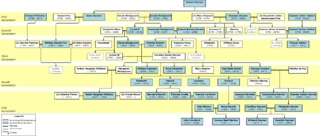
The Darwin–Wedgwood family are members of two connected families, each noted for particular prominent 18th-century figures: Erasmus Darwin, a physician and natural philosopher, and Josiah Wedgwood, a noted potter and founder of the eponymous Wedgwood and Sons pottery company. The Darwin and Wedgwood families were on friendly terms for much of their history and members intermarried, notably Charles Darwin, who married Emma Wedgwood.

Jasperware, or jasper ware, is a type of pottery first developed by Josiah Wedgwood in the 1770s. Usually described as stoneware, it has an unglazed matte "biscuit" finish and is produced in a number of different colours, of which the most common and best known is a pale blue that has become known as Wedgwood Blue. Relief decorations in contrasting colours are characteristic of jasperware, giving a cameo effect. The reliefs are produced in moulds and applied to the ware as sprigs.

Southworth & Hawes was an early photographic firm in Boston, 1843–1863. Its partners, Albert Sands Southworth (1811–1894) and Josiah Johnson Hawes (1808–1901), have been hailed as the first great American masters of photography, whose work elevated photographic portraits to the level of fine art. Their images are prominent in every major book and collection of early American photography.
Thomas Wedgwood IV was an English master potter who taught his illustrious youngest brother Josiah Wedgwood the trade. Wedgwood was the son of the potter Thomas Wedgwood III and his wife Mary Stringer. He married twice, first to Isabell Beech (1722–1750), who had five children, two of whom died in infancy.

Wedgwood is an English fine china, porcelain and luxury accessories manufacturer that was founded on 1 May 1759 by the potter and entrepreneur Josiah Wedgwood and was first incorporated in 1895 as Josiah Wedgwood and Sons Ltd. It was rapidly successful and was soon one of the largest manufacturers of Staffordshire pottery, "a firm that has done more to spread the knowledge and enhance the reputation of British ceramic art than any other manufacturer", exporting across Europe as far as Russia, and to the Americas. It was especially successful at producing fine earthenware and stoneware that were accepted as equivalent in quality to porcelain but were considerably cheaper.
Events from the year 1843 in art.
Events from the year 1769 in art.
Events from the year 1775 in art.

Louis Candide Boulanger was a French Romantic painter, pastellist, lithographer and a poet, known for his religious and allegorical subjects, portraits, genre scenes.

Eugène François Marie Joseph Devéria was a French Romantic history painter, portraitist and muralist.
Moses Wight (1827–1895) was an artist in Boston, Massachusetts and Paris in the 19th century. He painted portraits of Edward Everett, Louis Agassiz, Charles Sumner, Alexander von Humboldt, and other notables.

Henry Perronet Briggs RA was an English painter of portraits and historical scenes.

Thomas Brigstocke was a Welsh portrait painter. He studied art in London, and then spent eight years in Italy before returning to England. In the 1840s he visited Egypt, where he painted portraits of Mohammed Ali Pasha and his family.

Benjamin Smith (1754–1833) was a British engraver, printseller and publisher, active from 1786 to 1833. He was born c. 1754 in London. He worked mainly in dot or stipple engraving, producing portraits, illustrations, and allegorical and biblical subjects after prominent artists of the day.

Trump was a pug owned by English painter William Hogarth. The artist included the dog in several works, including his 1745 self-portrait Painter and his Pug, held by the Tate Gallery. In the words of the Tate's display caption, "Hogarth's pug dog, Trump, serves as an emblem of the artist's own pugnacious character."
Isaac Henry Gosset (1713–1799) was an 18th-century sculptor and wax-modeller.