
The 1997 Asian financial crisis was a period of financial crisis that gripped much of East and Southeast Asia during the late 1990s. The crisis began in Thailand in July 1997 before spreading to several other countries with a ripple effect, raising fears of a worldwide economic meltdown due to financial contagion. However, the recovery in 1998–1999 was rapid, and worries of a meltdown quickly subsided.
A real estate investment trust is a company that owns, and in most cases operates, income-producing real estate. REITs own many types of commercial real estate, including office and apartment buildings, studios, warehouses, hospitals, shopping centers, hotels and commercial forests. Some REITs engage in financing real estate. REITs act as a bridge between the worlds of housing and urban development on one hand, and institutional investors and financial markets on the other. They are typically categorized into commercial REITs (C-REITs) and residential REITs (R-REITs), with the latter focusing on housing assets such as apartments and single-family homes.

Illegal logging is the harvest, transportation, purchase, or sale of timber in violation of laws. The harvesting procedure itself may be illegal, including using corrupt means to gain access to forests; extraction without permission, or from a protected area; the cutting down of protected species; or the extraction of timber in excess of agreed limits. Illegal logging is a driving force for a number of environmental issues such as deforestation, soil erosion and biodiversity loss which can drive larger-scale environmental crises such as climate change and other forms of environmental degradation.
An exchange-traded fund (ETF) is a type of investment fund that is also an exchange-traded product, i.e., it is traded on stock exchanges. ETFs own financial assets such as stocks, bonds, currencies, debts, futures contracts, and/or commodities such as gold bars. Many ETFs provide some level of diversification compared to owning an individual stock.
An emerging market is a market that has some characteristics of a developed market, but does not fully meet its standards. This includes markets that may become developed markets in the future or were in the past. The term "frontier market" is used for developing countries with smaller, riskier, or more illiquid capital markets than "emerging". As of 2006, the economies of China and India are considered to be the largest emerging markets. According to The Economist, many people find the term outdated, but no new term has gained traction. Emerging market hedge fund capital reached a record new level in the first quarter of 2011 of $121 billion. Emerging market economies’ share of global PPP-adjusted GDP has risen from 27 percent in 1960 to around 53 percent by 2013. The ten largest emerging economies by nominal GDP are 4 of the 9 BRICS countries along with Mexico, South Korea, Indonesia, Turkey, Saudi Arabia, and Poland. The inclusion of South Korea, Poland, and sometimes Taiwan are questionable given they are no longer considered emerging markets by the IMF and World Bank If we ignore those three, the top ten would include Argentina and Thailand.
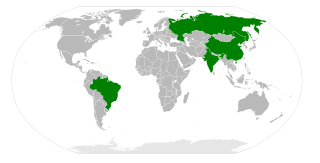
BRIC is a term describing the foreign investment strategies grouping acronym that stands for Brazil, Russia, India, and China. The separate BRICS organisation would go on to become a political and economic organization largely based on such grouping. The grouping has been rendered as "the BRICs", "the BRIC countries", "the BRIC economies", or alternatively as the "Big Four".
Russell indexes are a family of global stock market indices from FTSE Russell that allow investors to track the performance of distinct market segments worldwide. Many investors use mutual funds or exchange-traded funds based on the FTSE Russell Indexes as a way of gaining exposure to certain portions of the U.S. stock market. Additionally, many investment managers use the Russell Indexes as benchmarks to measure their own performance. Russell's index design has led to more assets benchmarked to its U.S. index family than all other U.S. equity indexes combined.

Jakarta Stock Exchange was a stock exchange based in Jakarta, Indonesia, before it merged with the Surabaya Stock Exchange to form the Indonesia Stock Exchange.

MSCI Inc. is an American finance company headquartered in New York City. MSCI is a global provider of equity, fixed income, real estate indices, multi-asset portfolio analysis tools, ESG and climate products. It operates the MSCI World, MSCI All Country World Index (ACWI) and MSCI Emerging Markets Indices among others.

Technip S.A. was a company that carried out project management, engineering and construction for the energy industry; in 2017 it completed a merger with FMC Technologies to form TechnipFMC. Its headquarters were in the 16th arrondissement of Paris. It has about 38,000 employees and operates in 48 countries.
The JPMorgan Emerging Market Bond Index (EMBI) are a set of three bond indices to track bonds in emerging markets operated by J P Morgan. The indices are the Emerging Markets Bond Index Plus, the Emerging Markets Bond Index Global and the Emerging Markets Bond Global Diversified Index.
A frontier market is a term for a type of developing country's market economy which is more developed than a least developed country's, but too small, risky, or illiquid to be generally classified as an emerging market economy. The term is an economic term which was coined by International Finance Corporation’s Farida Khambata in 1992. The term is commonly used to describe the equity markets of the smaller and less accessible, but still "investable" countries of the developing world. The frontier, or pre-emerging equity markets are typically pursued by investors seeking high, long-run return potential as well as low correlations with other markets. Some frontier market countries were emerging markets in the past, but have regressed to frontier status.
The FTSE Global Equity Index Series is a series of stock market indices provided by FTSE Group. It was launched in September 2003, and provides coverage of over 17,000 stocks in 48 countries, covering 98% of the world's investable market capitalization.

S&P Dow Jones Indices LLC is a joint venture between S&P Global, the CME Group, and News Corp that was announced in 2011 and later launched in 2012. It produces, maintains, licenses, and markets stock market indices as benchmarks and as the basis of investable products, such as exchange-traded funds (ETFs), mutual funds, and structured products. The company currently has employees in 15 cities worldwide, including New York, London, Frankfurt, Singapore, Hong Kong, Sydney, Beijing, and Dubai.

In finance, a stock index, or stock market index, is an index that measures the performance of a stock market, or of a subset of a stock market. It helps investors compare current stock price levels with past prices to calculate market performance.
ASEAN Exchanges is a collaboration of the 7 exchanges from Malaysia, Vietnam, Indonesia, Philippines, Thailand and Singapore to promote the growth of the ASEAN capital market by bringing more ASEAN investment opportunities to more investors.

The OECD Development Centre was established in 1961 as an independent platform for knowledge sharing and policy dialogue between Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) member countries and developing economies, allowing these countries to interact on an equal footing.

An emerging power or rising power is a sovereign state or union of states with significant rising influence in global affairs. Such a power aspires to have a more powerful position or role in international relations, either regionally or globally, and possess sufficient resources and levels of development that such goals are potentially achievable.









