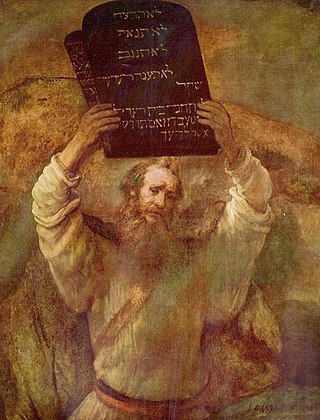The Sinai Peninsula, or simply Sinai, is a peninsula in Egypt, and the only part of the country located in Asia. It is between the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Red Sea to the south, and is a land bridge between Asia and Africa. Sinai has a land area of about 60,000 km2 (23,000 sq mi) and a population of approximately 600,000 people. Administratively, the vast majority of the area of the Sinai Peninsula is divided into two governorates: the South Sinai Governorate and the North Sinai Governorate. Three other governorates span the Suez Canal, crossing into African Egypt: Suez Governorate on the southern end of the Suez Canal, Ismailia Governorate in the center, and Port Said Governorate in the north.

Mount Sinai, also known as Jabal Musa, is a mountain on the Sinai Peninsula of Egypt. It is one of several locations claimed to be the biblical Mount Sinai, the place where, according to the Torah, Bible, and Quran, Moses received the Ten Commandments.
Holy Mountain may refer to:

Mount Hor is the name given in the Hebrew Bible to two distinct mountains. One borders the land of Edom in the area south of the Dead Sea, and the other is by the Mediterranean Sea at the Northern border of Israel. The first Mount Hor is especially significant to the Israelites, as Aaron the high priest, brother of Moses, died there.
Charles Tilstone Beke was an English traveller, geographer and Biblical critic.
Kibroth Hattaavah or Kibroth-hattaavah is one of the locations which the Israelites passed through during their Exodus journey, recorded in the Book of Numbers. It was at this place, according to the biblical narrative, that the Israelites loudly complained about constantly eating only manna, and that they had enjoyed a much more varied diet, of fish, vegetables, fruit and meat, when they lived in Egypt; the text states that this led Moses, in despair, to cry out to Yahweh, who then promised them so much meat that 'they would vomit it through their nostrils'. The narrative goes on to tell of a huge number of quails brought by the winds to both sides of the Israelite encampment, which the people gathered. Modern translations imply that Yahweh sent the plague as they were chewing the first meat that fell.

Mount Sinai is the mountain at which the Ten Commandments were given to Moses by God, according to the Book of Exodus in the Hebrew Bible. In the Book of Deuteronomy, these events are described as having transpired at Mount Horeb. "Sinai" and "Horeb" are generally considered by scholars to refer to the same place.
Jebel Musa, Jabal Moussa or Gebel Musa may refer to:
Gabal Sin Bishar is a mountain located in west-central Sinai. It was proposed to be the biblical Mount Sinai by Menashe Har-El, a biblical geographer at Tel Aviv University in his book The Sinai Journeys: The Route of the Exodus. This location was used for Zondervan's NIV Atlas of the Bible.

Mount Serbal is a mountain located in Wadi Feiran in southern Sinai. At 2,070 metres (6,791 ft) high, it is the fifth highest mountain in Egypt. It is part of the St. Catherine National Park. It is thought by some to be the Biblical Mount Sinai. Among others this was claimed by Ludwig Schneller, because it fits best with the biblical tradition taking into account the route and speed of the Israelites and the surroundings of the mountain, as Rephidim is identified with Wadi Feiran.

Jebel al-Madhbah is a mountain at Petra, Jordan, at whose peak there is a large Nabataean ritual site centered around an altar.
According to the Book of Numbers, Taberah is one of the locations which the Israelites passed through during their Exodus journey. The biblical narrative states that the place received its name, which means the pӀace of burning, because the fire of the LORD had burned there in anger because of their continued complaints. The text states that the fire first burned at the outskirts of the Israelite camp, killing some of those who lived on the edge of the group, but it was extinguished when Moses prayed on the people's behalf.
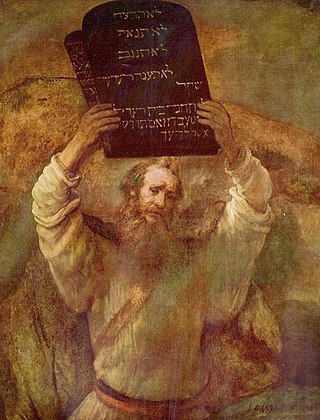
Mount Horeb is the mountain at which the Ten Commandments were given to Moses by God, according to the Book of Deuteronomy in the Hebrew Bible. It is described in two places as הַר הָאֱלֹהִים the "Mountain of Elohim". The mountain is also called the Mountain of YHWH.

Saint Catherine is a town located in the South Sinai Governorate of Egypt, situated at the foot of Mount Sinai. The city is the site of Saint Catherine's Monastery.
The Capture of Jericho occurred between 19 and 21 February 1918 to the east of Jerusalem beginning the Occupation of the Jordan Valley during the Sinai and Palestine Campaign of the First World War. Fighting took place in an area bordered by the Bethlehem–Nablus road in the west, the Jordan River in the east, and north of a line from Jerusalem to the Dead Sea. Here a British Empire force attacked Ottoman positions, forcing them back to Jericho and eventually across the Jordan River.

Wadi Feiran or Wadi Faran is Sinai's largest and widest wadi. It is an intermittent stream and rises from the mountains around Saint Catherine's Monastery, at 2500 m above sea level.

Willow Peak or Ras es-Safsafeh is a mountain in the Sinai Peninsula. The mountain peak overlooks Saint Catherine's Monastery, and is situated approximately 1km to the west.

Catherine of Alexandria is a tempera painting created by Ieremias Palladas. Palladas was a monk associated with Saint Catherine's sacred monastery in Egypt also known as Mount Sinai. He was a painter and teacher. His nephew became the Patriarch of Alexandria. His name was Gerasimos Palladas. Ieremias was a Sinaitic monk because of his association with Saint Catherine's monastery on Mount Sinai. The monastery encloses the site where it is assumed by Christians that Moses saw the burning bush. Ieremias was one of the most influential figures of his time. The Patriarch of Jerusalem Nectarius wrote about the painter in his archives.