Related Research Articles

Bacterial conjugation is the transfer of genetic material between bacterial cells by direct cell-to-cell contact or by a bridge-like connection between two cells. This takes place through a pilus. It is a parasexual mode of reproduction in bacteria.

Genetic engineering, also called genetic modification or genetic manipulation, is the modification and manipulation of an organism's genes using technology. It is a set of technologies used to change the genetic makeup of cells, including the transfer of genes within and across species boundaries to produce improved or novel organisms.
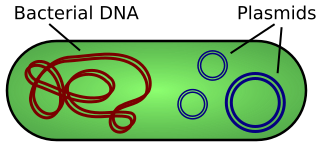
A plasmid is a small, extrachromosomal DNA molecule within a cell that is physically separated from chromosomal DNA and can replicate independently. They are most commonly found as small circular, double-stranded DNA molecules in bacteria; however, plasmids are sometimes present in archaea and eukaryotic organisms. Plasmids often carry useful genes, such as antibiotic resistance and virulence. While chromosomes are large and contain all the essential genetic information for living under normal conditions, plasmids are usually very small and contain additional genes for special circumstances.

The University of Canterbury is a public research university based in Christchurch, New Zealand. It was founded in 1873 as Canterbury College, the first constituent college of the University of New Zealand. It is New Zealand's second-oldest university, after the University of Otago, which was founded four years earlier, in 1869.
Victoria University of Wellington is a public research university in Wellington, New Zealand. It was established in 1897 by Act of Parliament, and was a constituent college of the University of New Zealand.

Lincoln University is a public university in New Zealand that was formed in 1990 when Lincoln College, Canterbury was made independent of the University of Canterbury. Founded in 1878, it is the oldest agricultural teaching institution in the Southern Hemisphere. It remains the smallest university in New Zealand and one of the eight public universities. The campus is situated on 50 ha of land located about 15 km (9 mi) outside the city of Christchurch, in Lincoln, Canterbury.

In molecular biology and genetics, transformation is the genetic alteration of a cell resulting from the direct uptake and incorporation of exogenous genetic material from its surroundings through the cell membrane(s). For transformation to take place, the recipient bacterium must be in a state of competence, which might occur in nature as a time-limited response to environmental conditions such as starvation and cell density, and may also be induced in a laboratory.

Stanley Norman Cohen is an American geneticist and the Kwoh-Ting Li Professor in the Stanford University School of Medicine. Stanley Cohen and Herbert Boyer were the first scientists to transplant genes from one living organism to another, a fundamental discovery for genetical engineering. Thousands of products have been developed on the basis of their work, including human growth hormone and hepatitis B vaccine. According to immunologist Hugh McDevitt, "Cohen's DNA cloning technology has helped biologists in virtually every field". Without it, "the face of biomedicine and biotechnology would look totally different." Boyer cofounded Genentech in 1976 based on their work together, but Cohen was a consultant for Cetus Corporation and declined to join. In 2022, Cohen was found guilty of having committed fraud in misleading investors into a biotechnology company he founded in 2016, and paid $29 million in damages.
Sir Albert William Liley was a New Zealand medical practitioner, renowned for developing techniques to improve the health of foetuses in utero.

Esther Miriam Zimmer Lederberg was an American microbiologist and a pioneer of bacterial genetics. She discovered the bacterial virus lambda phage and the bacterial fertility factor F, devised the first implementation of replica plating, and furthered the understanding of the transfer of genes between bacteria by specialized transduction.
The Marsden Medal is a yearly award given by the New Zealand Association of Scientists. It is named after Sir Ernest Marsden and honours "a lifetime of outstanding service to the cause or profession of science, in recognition of service rendered to the cause or profession of science in the widest connotation of the phrase." It rivals the Rutherford Medal from the Royal Society of New Zealand.

Dame Juliet Ann Gerrard is a New Zealand biochemistry academic. She is a professor at the University of Auckland and the New Zealand Prime Minister's Chief Science Advisor.

The New Zealand Tertiary Education Union is the main trade union in the New Zealand tertiary education sector, with over 10,000 members employed within the sector across New Zealand. Its membership includes academics, researchers, teachers and workers employed in all occupations in universities, polytechnics, institutes of technology, wānanga, other tertiary education providers and allied organisations.

Michelle Rogan-Finnemore is a New Zealand-American science administrator, and currently the Executive Secretary of the Council of Managers of National Antarctic Programmes (COMNAP) which is the international association which brings together the National Antarctic Programs that make up its members. She is also the namesake of Finnemore Peak.

Garth Alan Carnaby is a New Zealand fibre physicist and science and public administrator.

Ann Brower is an environmental geographer from New Zealand. A survivor of the 2011 Christchurch earthquake, she successfully lobbied for a law change to the Building Act, which was passed in 2016 as the Brower Amendment. Brower was promoted to full professor at the University of Canterbury in December 2021. In 2022 she won the Charles Fleming Award for Environmental Achievement.
Joanna Jean Putterill is a New Zealand molecular botanist. She is currently a full professor at the University of Auckland.

Heather Hendrickson is a microbiologist and an Associate Professor in the School of Biological Sciences at the University of Canterbury in Christchurch, New Zealand. She previously worked at Massey University, Auckland, New Zealand. Her research is focussed on the evolution of bacterial cell shape, and the discovery of bacteriophages that can attack antibiotic-resistant bacteria and the bee disease American foulbrood.

The Dodd-Walls Centre for Photonic and Quantum Technologies is a New Zealand Centre of Research Excellence, established in 2015, hosted by the University of Otago, and composed of researchers in six New Zealand universities as well as partner institutions in the US, United Kingdom, and Singapore. It does fundamental research on the quantum nature of matter, the physics and optics of light, and the manipulation of individual photons. New knowledge and applications are commercialised for industries including agritech, medicine, and civil engineering.

Rosemary Ann Du Plessis is a New Zealand academic sociologist, and is an adjunct associate professor at the University of Canterbury. In 2020 she was appointed an Officer of the New Zealand Order of Merit for services to women and education.
References
- ↑ "Jack Heinemann – The Conversation". Theconversation.com. 6 October 2011. Retrieved 9 November 2016.
- 1 2 "UC SPARK – University of Canterbury – New Zealand". Canterbury.ac.nz. Retrieved 9 November 2016.
- ↑ "About – Centre for Integrated Research on Biosafety – University of Canterbury – New Zealand". Inbi.canterbury.ac.nz. Archived from the original on 7 November 2016. Retrieved 9 November 2016.
- ↑ "FSANZ rejects scientists' concerns about the safety of GM wheat | AgScience". Agscienceblog.wordpress.com. 23 May 2013. Retrieved 9 November 2016.
- ↑ "Kiwi professor's anti-GM claims rejected | The National Business Review". Nbr.co.nz. 28 May 2013. Archived from the original on 17 April 2019. Retrieved 9 November 2016.
- ↑ "The Battle for Biodiversity: Monsanto and Farmers Clash". The Atlantic. 28 March 2011. Retrieved 9 November 2016.
- ↑ "Comparison of agriculture in North America and Europe raises questions about the value of GM | AgScience". Agscienceblog.wordpress.com. 19 June 2013. Retrieved 9 November 2016.
- ↑ "Award recipients and alumni – TEU". Teu.ac.nz. 19 February 2016. Archived from the original on 9 October 2016. Retrieved 9 November 2016.
- ↑ "Staff welcome Canterbury's academic freedom policy | Scoop News". Scoop.co.nz. 21 March 2014. Retrieved 9 November 2016.