
In calculus, an antiderivative, inverse derivative, primitive function, primitive integral or indefinite integral of a function f is a differentiable function F whose derivative is equal to the original function f. This can be stated symbolically as F' = f. The process of solving for antiderivatives is called antidifferentiation, and its opposite operation is called differentiation, which is the process of finding a derivative. Antiderivatives are often denoted by capital Roman letters such as F and G.

In mathematics, an integral is the continuous analog of a sum, which is used to calculate areas, volumes, and their generalizations. Integration, the process of computing an integral, is one of the two fundamental operations of calculus, the other being differentiation. Integration was initially used to solve problems in mathematics and physics, such as finding the area under a curve, or determining displacement from velocity. Usage of integration expanded to a wide variety of scientific fields thereafter.
In mathematics, the Laplace transform, named after Pierre-Simon Laplace, is an integral transform that converts a function of a real variable to a function of a complex variable .

In the branch of mathematics known as real analysis, the Riemann integral, created by Bernhard Riemann, was the first rigorous definition of the integral of a function on an interval. It was presented to the faculty at the University of Göttingen in 1854, but not published in a journal until 1868. For many functions and practical applications, the Riemann integral can be evaluated by the fundamental theorem of calculus or approximated by numerical integration, or simulated using Monte Carlo integration.
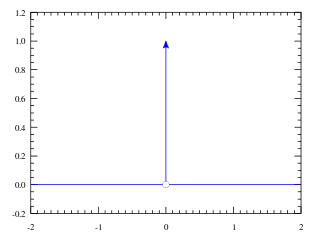
In mathematical analysis, the Dirac delta function, also known as the unit impulse, is a generalized function on the real numbers, whose value is zero everywhere except at zero, and whose integral over the entire real line is equal to one. Since there is no function having this property, modelling the delta "function" rigorously involves the use of limits or, as is common in mathematics, measure theory and the theory of distributions.

In physics, engineering and mathematics, the Fourier transform (FT) is an integral transform that takes a function as input and outputs another function that describes the extent to which various frequencies are present in the original function. The output of the transform is a complex-valued function of frequency. The term Fourier transform refers to both this complex-valued function and the mathematical operation. When a distinction needs to be made, the output of the operation is sometimes called the frequency domain representation of the original function. The Fourier transform is analogous to decomposing the sound of a musical chord into the intensities of its constituent pitches.
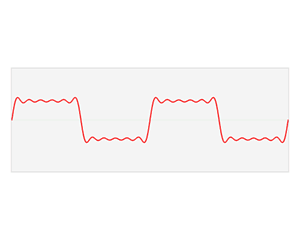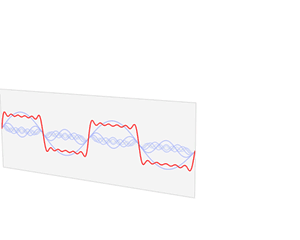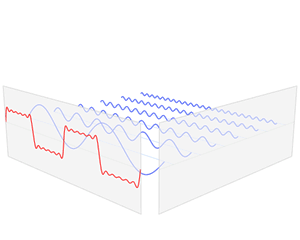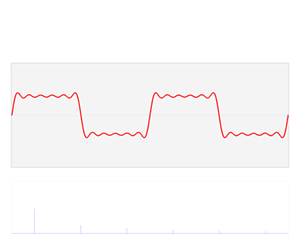
A Fourier series is an expansion of a periodic function into a sum of trigonometric functions. The Fourier series is an example of a trigonometric series, but not all trigonometric series are Fourier series. By expressing a function as a sum of sines and cosines, many problems involving the function become easier to analyze because trigonometric functions are well understood. For example, Fourier series were first used by Joseph Fourier to find solutions to the heat equation. This application is possible because the derivatives of trigonometric functions fall into simple patterns. Fourier series cannot be used to approximate arbitrary functions, because most functions have infinitely many terms in their Fourier series, and the series do not always converge. Well-behaved functions, for example smooth functions, have Fourier series that converge to the original function. The coefficients of the Fourier series are determined by integrals of the function multiplied by trigonometric functions, described in Common forms of the Fourier series below.
In mathematics, an infinite series of numbers is said to converge absolutely if the sum of the absolute values of the summands is finite. More precisely, a real or complex series is said to converge absolutely if for some real number Similarly, an improper integral of a function, is said to converge absolutely if the integral of the absolute value of the integrand is finite—that is, if A convergent series that is not absolutely convergent is called conditionally convergent.

Euler's constant is a mathematical constant, usually denoted by the lowercase Greek letter gamma, defined as the limiting difference between the harmonic series and the natural logarithm, denoted here by log:
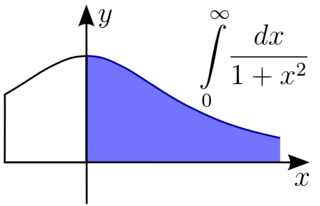
In mathematical analysis, an improper integral is an extension of the notion of a definite integral to cases that violate the usual assumptions for that kind of integral. In the context of Riemann integrals, this typically involves unboundedness, either of the set over which the integral is taken or of the integrand, or both. It may also involve bounded but not closed sets or bounded but not continuous functions. While an improper integral is typically written symbolically just like a standard definite integral, it actually represents a limit of a definite integral or a sum of such limits; thus improper integrals are said to converge or diverge. If a regular definite integral is worked out as if it is improper, the same answer will result.

In complex analysis, a branch of mathematics, Morera's theorem, named after Giacinto Morera, gives an important criterion for proving that a function is holomorphic.

The path integral formulation is a description in quantum mechanics that generalizes the stationary action principle of classical mechanics. It replaces the classical notion of a single, unique classical trajectory for a system with a sum, or functional integral, over an infinity of quantum-mechanically possible trajectories to compute a quantum amplitude.

In mathematics, the integral test for convergence is a method used to test infinite series of monotonous terms for convergence. It was developed by Colin Maclaurin and Augustin-Louis Cauchy and is sometimes known as the Maclaurin–Cauchy test.
In mathematics, the Poisson summation formula is an equation that relates the Fourier series coefficients of the periodic summation of a function to values of the function's continuous Fourier transform. Consequently, the periodic summation of a function is completely defined by discrete samples of the original function's Fourier transform. And conversely, the periodic summation of a function's Fourier transform is completely defined by discrete samples of the original function. The Poisson summation formula was discovered by Siméon Denis Poisson and is sometimes called Poisson resummation.
In mathematics, the Riemann–Liouville integral associates with a real function another function Iαf of the same kind for each value of the parameter α > 0. The integral is a manner of generalization of the repeated antiderivative of f in the sense that for positive integer values of α, Iαf is an iterated antiderivative of f of order α. The Riemann–Liouville integral is named for Bernhard Riemann and Joseph Liouville, the latter of whom was the first to consider the possibility of fractional calculus in 1832. The operator agrees with the Euler transform, after Leonhard Euler, when applied to analytic functions. It was generalized to arbitrary dimensions by Marcel Riesz, who introduced the Riesz potential.
In mathematics, the question of whether the Fourier series of a periodic function converges to a given function is researched by a field known as classical harmonic analysis, a branch of pure mathematics. Convergence is not necessarily given in the general case, and certain criteria must be met for convergence to occur.
In mathematics, the explicit formulae for L-functions are relations between sums over the complex number zeroes of an L-function and sums over prime powers, introduced by Riemann (1859) for the Riemann zeta function. Such explicit formulae have been applied also to questions on bounding the discriminant of an algebraic number field, and the conductor of a number field.
Quantum calculus, sometimes called calculus without limits, is equivalent to traditional infinitesimal calculus without the notion of limits. The two types of calculus in quantum calculus are q-calculus and h-calculus. The goal of both types is to find "analogs" of mathematical objects, where, after taking a certain limit, the original object is returned. In q-calculus, the limit as q tends to 1 is taken of the q-analog. Likewise, in h-calculus, the limit as h tends to 0 is taken of the h-analog. The parameters and can be related by the formula .

In mathematics, the integral of a non-negative function of a single variable can be regarded, in the simplest case, as the area between the graph of that function and the X axis. The Lebesgue integral, named after French mathematician Henri Lebesgue, is one way to make this concept rigorous and to extend it to more general functions.
In mathematics, differential forms on a Riemann surface are an important special case of the general theory of differential forms on smooth manifolds, distinguished by the fact that the conformal structure on the Riemann surface intrinsically defines a Hodge star operator on 1-forms without specifying a Riemannian metric. This allows the use of Hilbert space techniques for studying function theory on the Riemann surface and in particular for the construction of harmonic and holomorphic differentials with prescribed singularities. These methods were first used by Hilbert (1909) in his variational approach to the Dirichlet principle, making rigorous the arguments proposed by Riemann. Later Weyl (1940) found a direct approach using his method of orthogonal projection, a precursor of the modern theory of elliptic differential operators and Sobolev spaces. These techniques were originally applied to prove the uniformization theorem and its generalization to planar Riemann surfaces. Later they supplied the analytic foundations for the harmonic integrals of Hodge (1941). This article covers general results on differential forms on a Riemann surface that do not rely on any choice of Riemannian structure.

























