Literature
Van der Aa, Biographisch Woordenboek der Nederlanden (1852)
- ↑ De Nederlandsche leeuw: Volumes 117-118
Jacob van Oudshoorn | |
|---|---|
| Bishop of Utrecht | |
| Church | Catholic Church |
| Diocese | Archdiocese of Utrecht |
| In office | 1322 |
| Personal details | |
| Died | c. 18 September 1322 |
Jacob van Oudshoorn (died c. 18 September 1322) was bishop of Utrecht in 1322.
Van Oudshoorn descended from a noble Hollandic house; he was the son of Willem and brother of Dirk van Oudshoorn (1301–1327), lords of Oudshoorn and Aarlanderveen. [1] Van Oudshoorn was deacon in Utrecht before he was elected bishop. He was consecrated by the archbishop of Cologne, Hendrik II van Virnenburg, but pope John XXII only accepted his nomination after the payment of a large amount of money, which ruined his family. Shortly after this he died, according to his own suspicions, from poison. He was called brave, learned and pious.
Van der Aa, Biographisch Woordenboek der Nederlanden (1852)
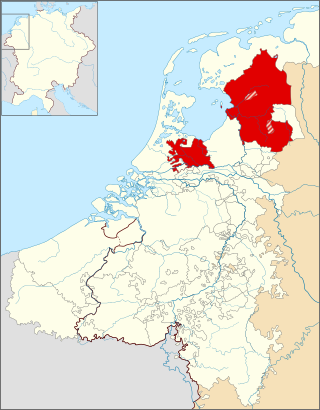
The Bishopric of Utrecht was an ecclesiastical principality of the Holy Roman Empire in the Low Countries, in the present-day Netherlands. From 1024 to 1528, as one of the prince-bishoprics of the Holy Roman Empire, it was ruled by the bishops of Utrecht. The Prince-Bishopric of Utrecht must not be confused with the Diocese of Utrecht, which extended beyond the Prince-Bishopric and over which the bishop exercised spiritual authority.

The Hook and Cod wars comprise a series of wars and battles in the County of Holland between 1350 and 1490. Most of these wars were fought over the title of count of Holland, but some have argued that the underlying reason was because of the power struggle of the bourgeois in the cities against the ruling nobility.

The Old Catholic Church of the Netherlands, sometimes Jansenist Church of Holland, is an Old Catholic jurisdiction originating from the Archdiocese of Utrecht (695–1580). The Old Catholic Church of the Netherlands is the mother church of the Old Catholic Union of Utrecht.

Saint Radbod was bishop of Utrecht from 899 to 917.

Bernardus Johannes Alfrink was a Dutch Cardinal of the Roman Catholic Church. He served as Archbishop of Utrecht from 1955 to 1975, and was elevated to the cardinalate in 1960.

Nicolaas van Nieuwland, or Nicolas Van Nienlant was a Dutch Roman Catholic prelate who served as Bishop of Haarlem and abbot of Egmond Abbey from 1562 to 1569 and as Auxiliary Bishop of Utrecht (1541–?).
Dirk VII was the count of Holland from 1190 to 1203. He was the elder son of Floris III and Ada of Huntingdon.
The Drenther Crusade was a military campaign launched against the inhabitants of Drenthe with the approval of the Papacy in 1228 and lasting until 1232. It was led by Willibrand, Bishop of Utrecht, commanding an army composed mostly of Frisian crusaders.

Saint Bernulf or Bernold of Utrecht was Bishop of Utrecht (1026/27–1054).

The Diocese of 's-Hertogenbosch is a Latin Church ecclesiastical jurisdiction or diocese of the Catholic church in the Netherlands. The modern diocese was created in 1853. It is a suffragan of the archdiocese of Utrecht. It is currently led by bishop Gerard de Korte. Its see is St John's Cathedral, 's-Hertogenbosch.

John of Nassau, German: Johann von Nassau, Dutch: Jan van Nassau was a clergyman from the House of Nassau. From 1267 to 1290 he was Bishop-Elect of the Bishopric of Utrecht as John I. He did not care much for his spiritual functions, and his government also failed due to his weak political and poor financial management. During his reign, the influence of the County of Holland in the Bishopric greatly increased. John's government was one of the worst the Bishopric had to endure; without talent and energy, slavishly surrendering to all sensual pleasures, it was never possible for him to maintain the inner peace, under which the Nedersticht in particular suffered greatly.
Frederick van Sierck was a bishop of Utrecht, in the present day Netherlands, from 1317 to 1322.
John or Jan van Diest was bishop of Utrecht from 1322 to 1340.
Frederick II, Frederik II or Friedrich II may refer to:

The Lordship of Utrecht was formed in 1528 when Charles V of Habsburg conquered the Bishopric of Utrecht, during the Guelders Wars.

Jaap van der Leck was a Dutch football manager.
The historic Diocese of Utrecht (695–1580) was a Roman Catholic diocese and archdiocese in the Low Countries before and during the Protestant Reformation.
Baron Pieter van Reedevan Oudtshoorn was a senior official and Governor designate of the Dutch Cape Colony. He was appointed Governor of the Cape Colony in 1772 to succeed the deceased Governor Ryk Tulbagh but died at sea on his way to the Cape Colony to take up his post. The Western Cape town of Oudtshoorn is named after him. He is the progenitor of the van R(h)eede van Oudtshoorn family in South Africa.

Cornelis van Steenoven was a Dutch Roman Catholic priest who later served as the seventh Old Catholic Archbishop of Utrecht from 1724 to 1725. Consecrated without the permission of the pope, Steenoven was at the center of the 18th-century controversy between national churches and what many considered to be the overreaching powers of the papacy.