
The Amazon River in South America is the largest river by discharge volume of water in the world, and the disputed longest river system in the world in comparison to the Nile.

The Missouri River is the longest river in the United States. Rising in the eastern Centennial Mountains of the Bitteroot Range of the Rocky Mountains of southwestern Montana, the Missouri flows east and south for 2,341 miles (3,767 km) before entering the Mississippi River north of St. Louis, Missouri. The river drains semi-arid watershed of more than 500,000 square miles (1,300,000 km2), which includes parts of ten U.S. states and two Canadian provinces. Although a tributary of the Mississippi, the Missouri River is slightly longer and carries a comparable volume of water. When combined with the lower Mississippi River, it forms the world's fourth longest river system.

A dam is a barrier that stops or restricts the flow of surface water or underground streams. Reservoirs created by dams not only suppress floods but also provide water for activities such as irrigation, human consumption, industrial use, aquaculture, and navigability. Hydropower is often used in conjunction with dams to generate electricity. A dam can also be used to collect or store water which can be evenly distributed between locations. Dams generally serve the primary purpose of retaining water, while other structures such as floodgates or levees are used to manage or prevent water flow into specific land regions.

The Willamette River is a major tributary of the Columbia River, accounting for 12 to 15 percent of the Columbia's flow. The Willamette's main stem is 187 miles (301 km) long, lying entirely in northwestern Oregon in the United States. Flowing northward between the Oregon Coast Range and the Cascade Range, the river and its tributaries form the Willamette Valley, a basin that contains two-thirds of Oregon's population, including the state capital, Salem, and the state's largest city, Portland, which surrounds the Willamette's mouth at the Columbia.

The Batman River is a major tributary of the Tigris in southeast Turkey. The region along the Batman River is known for its oil fields.

Grand Coulee Dam is a concrete gravity dam on the Columbia River in the U.S. state of Washington, built to produce hydroelectric power and provide irrigation water. Constructed between 1933 and 1942, Grand Coulee originally had two powerhouses. The third powerhouse ("Nat"), completed in 1974 to increase energy production, makes Grand Coulee the largest power station in the United States by nameplate capacity at 6,809 MW.

Aracati is a city or municipality in the state of Ceará, in the northeast region of Brazil. The city was officially founded on April 11, 1747. It is part of the microregion of Litoral de Aracati, which is one of the four microregions that make up the macroregion of Jaguaribe. It is the birthplace of the revolutionary Eduardo Angelim, the romanticist Adolfo Caminha, the bishop Manuel do Rego Medeiros, the abolitionist Dragão do Mar, the actor Emiliano Queiroz, the classical pianist Jacques Klein and the writer Yury Teodósio.

Keystone Lake is a reservoir in northeastern Oklahoma on the Arkansas and Cimarron rivers. It is located upstream about 23 miles (37 km) from Tulsa. It was created in 1968 when the Keystone Dam was completed. The primary purposes are: flood control, hydroelectric power generation, wildlife management and recreation.

Oroville Dam is an earthfill embankment dam on the Feather River east of the city of Oroville, California, in the Sierra Nevada foothills east of the Sacramento Valley. At 770 feet (235 m) high, it is the tallest dam in the U.S. and serves mainly for water supply, hydroelectricity generation, and flood control. The dam impounds Lake Oroville, the second-largest reservoir in California, capable of storing more than 3.5 million acre-feet (1.1×10^12 US gal; 4.3×109 m3).

Pine Flat Dam is a concrete gravity dam on the Kings River in the Central Valley of Fresno County, California United States. Situated about 28 miles (45 km) east of Fresno, the dam is 440 feet (130 m) high and impounds Pine Flat Lake, in the foothills of the Sierra Nevada just outside the boundary of Kings Canyon National Park. The dam's primary purpose is flood control, with irrigation, hydroelectric power generation and recreation secondary in importance.

Tuttle Creek Lake is a reservoir on the Big Blue River 5 miles (8 km) north of Manhattan, in the Flint Hills region of northeast Kansas. It was built and is operated by the Army Corps of Engineers for the primary purpose of flood control. Secondary functions of the project include release of water stores to maintain barge traffic on the Mississippi River during seasons of drought, maintenance of a multi-use conservation pool for fish and wildlife enhancement and recreation, and release of sufficient water in droughts to maintain water quality for downstream communities.

Perry Lake is a US Army Corps of Engineers operated reservoir in northeast Kansas. Its primary purposes are flood control, water reserve for nearby areas and regional recreation. The lake is approximately 11,150 acres (45 km²) in size, with over 160 miles (260 km) of shoreline. Perry Lake's full multi-purpose pool elevation is 891.5 feet (271.7 m) above sea level. Perry Lake is located about 40 miles (64 km) west of Kansas City, just northwest of Lawrence, Kansas. Its close proximity to Kansas City, Lawrence, and the state capitol, Topeka, make it a very popular destination, with the nickname "Paradise on the Plains".
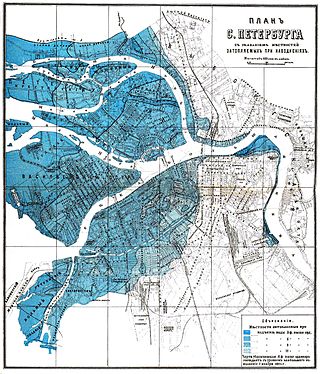
Floods in Saint Petersburg refer to a rise of water on the territory of St. Petersburg, a major city in Russia and its former capital. They are usually caused by the overflow of the delta of Neva River and surging water in the eastern part of Neva Bay but sometimes caused by melting snow. Floods are registered when the water rises above 160 cm with respect to a gauge at the Saint Petersburg Mining Institute. More than 300 floods have occurred since the city was founded in 1703.

Fort Patrick Henry Dam is a hydroelectric dam on the South Fork Holston River within the city of Kingsport, in Sullivan County in the U.S. state of Tennessee. It is the lowermost of three dams on the South Fork Holston owned and operated by the Tennessee Valley Authority, which built the dam in the early 1950s to take advantage of the hydroelectric potential created by the regulation of river flow with the completion of Watauga Dam, South Holston Dam, and Boone Dam further upstream in preceding years. The dam impounds the 872-acre (353 ha) Fort Patrick Henry Lake. While originally built for hydroelectric generation, the dam now plays an important role in the regulation of water flow and water temperature for the John Sevier Fossil Plant and other industrial plants downstream. The dam and associated infrastructure were listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 2017.
Alto Santo is a municipality in the state of Ceará in the Northeast region of Brazil.

Jaguaribe is a municipality in the state of Ceará in the Northeast region of Brazil.

Tauá is a municipality in the state of Ceará in the Northeast region of Brazil. In 2020 it had an estimated population of 59,062 people. It is one of the largest municipalities in the state, with an area of 4,018.188 square kilometres (1,551.431 sq mi).

The Três Marias Dam, also known as Bernardo Mascarenhas, is an embankment dam on the São Francisco River near Três Marias in Minas Gerais, Brazil. It was constructed for hydroelectric power production and flood control. The dam was completed in 1961 and its first generator was operational in 1962. The dam's power plant is named after Bernard Mascarenhas who in 1889, built South America's first major hydroelectric power plant in Brazil, the Marmelos Zero Power Plant.

The Orós Dam or President Juscelino Kubitschek Dam is located on the Jaguaribe River, in the northeastern Brazilian state of Ceará.

The Castanhão Dam is a dam in the state of Ceará, Brazil. It is the largest multiple use reservoir in the country, the largest on an intermittent river, and the main reservoir for the state and the metropolitan region of Fortaleza. The dam supplies drinking water, and supports industry, irrigation and fish farming. Through steady release of water the dam maintains water flow in the Jaguaribe River throughout the year. During 2012–16 Ceará experienced a prolonged drought. Water levels in the reservoir dropped to 5% of capacity and usage had to be rationed.





















