Related Research Articles

Rigging comprises the system of ropes, cables and chains, which support and control a sailing ship or sail boat's masts and sails. Standing rigging is the fixed rigging that supports masts including shrouds and stays. Running rigging is rigging which adjusts the position of the vessel's sails and spars including halyards, braces, sheets and vangs.

A brig is a type of sailing vessel defined by its rig: two masts which are both square-rigged. Brigs originated in the second half of the 18th century and were a common type of smaller merchant vessel or warship from then until the latter part of the 19th century. In commercial use, they were gradually replaced by fore-and-aft rigged vessels such as schooners, as owners sought to reduce crew costs by having rigs that could be handled by fewer men. In Royal Navy use, brigs were retained for training use when the battle fleets consisted almost entirely of iron-hulled steamships.

The French ironclad Gloire was the first ocean-going ironclad, launched in 1859. She was developed after the Crimean War, in response to new developments of naval gun technology, especially the Paixhans guns and rifled guns, which used explosive shells with increased destructive power against wooden ships. Her design was also influenced by the Anglo-French development of ironclad floating batteries to bombard Russian forts during the same war.

A studding sail, or stun'sl is an extra sail on a square rigged vessel for use in fair weather. It is set outside the square sails, using stun'sl booms which run out along the yards. They came into use some time in the middle of the 17th century and by the beginning of the 19th century were usual on all square rigged sailing vessels. They started to become less common in the last quarter of the 19th century, as the economies of smaller crews and avoidance of damage to the ship's gear became more important than a fast voyage.

Takao (高雄) was an unprotected cruiser of the Imperial Japanese Navy. The name Takao comes from the Mount Takao, near Kyoto. Takao was used by the Imperial Japanese Navy primarily as an aviso or dispatch boat, for scouting, reconnaissance and the conveying of important messages.

Rurik was an armoured cruiser built for the Imperial Russian Navy in the early 1890s. She was named in honour of Rurik, the semi-legendary founder of ancient Russia. She was sunk at the Battle of Ulsan in the Russo-Japanese War of 1904–05.

John Tradescant the Elder, father of John Tradescant the Younger, was an English naturalist, gardener, collector and traveller.
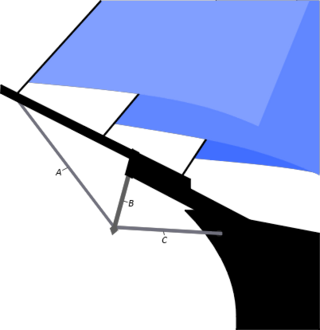
A dolphin striker is a small vertical or near vertical ancillary spar spanning between the bowsprit and martingale thereby redirecting the tension in the forward end of the martingale slightly more vertically. This vertical component is necessary to more effectively oppose the forestays' mostly upward tension on the forward end of the bowsprit than would be the case in the absence of the dolphin striker.
HMS Dragon was a Banshee-class destroyer of the Royal Navy.

The Durandal class was a group of four destroyers built for the French Navy between 1896 and 1900, used during the First World War. These vessels were France's first true destroyers rather than torpedo boats. Two units were launched in 1899 while another two followed in 1900. Another four destroyers of the similar Samsun class were laid down in 1906 and completed in 1907 for the Ottoman Navy, they also served in the First World War.
Brian Lavery, is a British naval historian, author, and Curator Emeritus at the National Maritime Museum, Greenwich, London, England.
Conway Publishing, formerly Conway Maritime Press, is an imprint of Bloomsbury Publishing. It is best known for its publications dealing with nautical subjects.
Karl Heinz Marquardt was a German-born marine modeller, artist and author.

A jibboom is a spar used to extend the length of a bowsprit on sailing ships. It can itself be extended further by a flying jib-boom. The heel end of the flying jib-boom is attached to the jib-boom, and the heel of the jib-boom to the bowsprit. The point of the flying jib-boom is generally the fore-most extent of a ship. The jib- and flying jib- booms carry the tacks of the jib and flying jib sails, respectively, and the stay for the fore topgallant mast and the royal stay.

The Arab-class gunvessels were a pair of composite gunboats built for the Royal Navy in the mid-1870s.

HMS Arab was an Arab-class composite gunvessel built for the Royal Navy in 1874. She served in the East Indies and was sold in 1889.

HMS Lily was an Arab-class composite gunvessel built for the Royal Navy. She was launched in 1874, saw service in Chinese and North American waters, and was wrecked on the coast of Labrador on 16 September 1889.

HMS Ettrick was a River-class destroyer ordered by the Royal Navy under the 1901 – 1902 Naval Estimates. Named after Ettrick Water in the Scottish Borders area south of Edinburgh, she was the first ship to carry this name in the Royal Navy. She was launched in 1903 and served during World War I. She was torpedoed by UC-61 in 1917.
Roger Charles Anderson was an independently-wealthy English maritime historian, collector, and a leading figure in the early years of the Society for Nautical Research and of the Navy Records Society. Four times editor of the Mariner's Mirror, Anderson was also a founder trustee, and later chairman of the board of trustees, of the National Maritime Museum, Greenwich. He was a Fellow of the Royal Historical Society, a Fellow of the Society of Antiquaries of London, and held the higher Doctor of Letters degree. In 2005, the Swedish naval historian Jan Glete characterised Anderson as "one of the most important naval historians of the twentieth century. He mainly wrote about early modern warship technology and used his linguistic skills to write books and essays based on the literature from several countries."
References
- 1 2 "The Masting and Rigging of English Ships of War 1625-1860". Camberpete's Naval Book Site. Archived from the original on 11 September 2011. Retrieved 17 June 2011.
- ↑ Savours, Anne (1993). "Shackleton, James Caird, and Discovery". Polar Record . 29 (171): 343. doi: 10.1017/S0032247400024165 .
- ↑ "Warship (1588); Galleon; Spanish (SLR0359)". National Maritime Museum . Retrieved 17 June 2011.[ permanent dead link ]
- ↑ "The Catalogue: Model Ship". The Tradescant Collection. Ashmolean Museum. Retrieved 17 June 2011.
- ↑ Czytko, Michael. "Literature and links, museums, historic ships and replicas". Finemodelships.com. Retrieved 17 June 2011.