
The North West Company was a fur trading business headquartered in Montreal from 1779 to 1821. It competed with increasing success against the Hudson's Bay Company in the regions that later became Western Canada and Northwestern Ontario. With great wealth at stake, tensions between the companies increased to the point where several minor armed skirmishes broke out, and the two companies were forced by the British government to merge.

Simon Fraser was a Canadian explorer and fur trader who charted much of what is now the Canadian province of British Columbia. He also built the first European settlement in British Columbia.

Oregon Country was a large region of the Pacific Northwest of North America that was subject to a long dispute between the United Kingdom and the United States in the early 19th century. The area, which had been demarcated by the Treaty of 1818, consisted of the land north of 42° N latitude, south of 54°40′ N latitude, and west of the Rocky Mountains down to the Pacific Ocean and east to the Continental Divide. Article III of the 1818 treaty gave joint control to both nations for ten years, allowed land to be claimed, and guaranteed free navigation to all mercantile trade. However, both countries disputed the terms of the international treaty. Oregon Country was the American name, while the British used Columbia District for the region.

The Pacific Fur Company (PFC) was an American fur trade venture wholly owned and funded by John Jacob Astor that functioned from 1810 to 1813. It was based in the Pacific Northwest, an area contested over the decades among the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, the Spanish Empire, the United States of America and the Russian Empire.

Fort Astoria was the primary fur trading post of John Jacob Astor's Pacific Fur Company (PFC). A maritime contingent of PFC staff was sent on board the Tonquin, while another party traveled overland from St. Louis. This land based group later became known as the Astor Expedition. Built at the entrance of the Columbia River in 1811, Fort Astoria was the first American-owned settlement on the Pacific coast of North America.
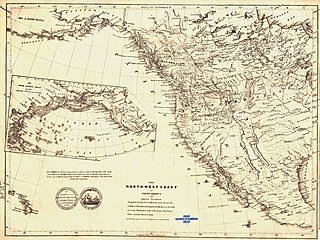
New Caledonia was a fur-trading district of the Hudson's Bay Company that comprised the territory of the north-central portions of present-day British Columbia, Canada. Though not a British colony, New Caledonia was part of the British claim to North America. Its administrative centre was Fort St. James. The rest of what is now mainland British Columbia was called the Columbia Department by the British, and the Oregon Country by the Americans. Even before the partition of the Columbia Department by the Oregon Treaty in 1846, New Caledonia was often used to describe anywhere on the mainland not in the Columbia Department, such as Fort Langley in the Fraser Valley.

Stuart Lake, or Nak'albun in the Carrier (Dakelh) language is a lake situated in the Northern Interior of British Columbia, Canada. The town of Fort St. James is situated by the lake near the outlet. Stuart Lake is 66 kilometres (41 mi) long, 10 kilometres (6.2 mi) wide and relatively shallow, with an average depth of 26 metres (85 ft). There are several privately owned islands on Stuart lake.

The Columbia District was a fur trading district in the Pacific Northwest region of British North America in the 19th century. Much of its territory overlapped with the disputed Oregon Country. It was explored by the North West Company between 1793 and 1811, and established as an operating fur district around 1810. The North West Company was absorbed into the Hudson's Bay Company in 1821 under which the Columbia District became known as the Columbia Department. The Oregon Treaty of 1846 marked the effective end of the Hudson's Bay Company's Columbia Department.

The Nechako River arises on the Nechako Plateau east of the Kitimat Ranges of the Coast Mountains of British Columbia, Canada, and flows north toward Fort Fraser, then east to Prince George where it enters the Fraser River. "Nechako" is an anglicization of netʃa koh, its name in the indigenous Carrier language which means "big river".

John Stuart was a 19th-century Scottish–Canadian explorer and fur trader. He was a partner in the North West Company and Chief Factor of the Hudson's Bay Company. Stuart is best known as Simon Fraser's lieutenant who participated in his explorations of present-day British Columbia from 1805 to 1808. Fraser named Stuart River and Stuart Lake in British Columbia for his friend. Stuart was the uncle of Lord Strathcona.
The Stuart River or Nak'alkoh is one of the largest tributaries of the Nechako River in northeastern British Columbia, Canada. The Nechako is in turn one the more important tributaries of the Fraser River. The Stuart River flows 187 kilometres (116 mi) from Stuart Lake to its junction with the Nechako River. The river drains a portion of the Nechako Plateau—a gently-rolling region characterized by small lakes and tributaries. Low but impressive ridges interact with the river, creating high bluffs and hoodoos.
Samuel Black was a Scottish fur trader and explorer, a clerk in the New North Nest Company (XYC) and Wintering Partner in the North West Company (NWC), and later clerk, chief trader, and chief factor in the Hudson's Bay Company (HBC) for the Columbia District. In 1824, he explored the Finlay River and its tributaries in present-day north-central British Columbia, Canada, including the Muskwa, Omineca and Stikine for the HBC. His journals were published by the Hudson's Bay Record Society in 1955.
John McLeod was a Scottish-born explorer of Canada, in his capacity as a fur trader with the North West Company and Hudson's Bay Company. He was born at Valtos, Lochs in the Isle of Lewis. He is remembered primarily for his explorations of several major rivers of the southwestern Northwest Territories, southern Yukon Territory, and northern British Columbia.

Oregon pioneer history (1806–1890) is the period in the history of Oregon Country and Oregon Territory, in the present day state of Oregon and Northwestern United States.

Robert Stuart was a Scottish-born, Canadian and American fur trader, best known as a member of the first European-American party to cross South Pass during an overland expedition from Fort Astoria to Saint Louis in 1811. He was a member of the North West Company (NWC) until recruited by John Jacob Astor to develop the new Pacific Fur Company, which was based at Fort Astoria, on the coast of present-day Oregon. Astor intended the venture to develop a continent-wide commercial empire in fur trading.

Frank Cyril Swannell was one of British Columbia's most famous surveyors.

This article covers the water based Canadian canoe routes used by early explorers of Canada with special emphasis on the fur trade.

Fort St. James is a district municipality and former fur trading post in northern central British Columbia, Canada. It is located on the south-eastern shore of Stuart Lake in the Omineca Country, at the northern terminus of Highway 27, which connects to Highway 16 at Vanderhoof.
Ovide de Montigny was a French-Canadian fur trapper active in the Pacific Northwest from 1811 to 1822.
David Stuart was a fur trader who worked primarily for the North West and Pacific Fur companies throughout his varied career.