
The Kriegsmarine was the navy of Germany from 1935 to 1945. It superseded the Imperial German Navy of the German Empire (1871–1918) and the inter-war Reichsmarine (1919–1935) of the Weimar Republic. The Kriegsmarine was one of three official branches, along with the Heer and the Luftwaffe, of the Wehrmacht, the German armed forces from 1935 to 1945.

Subhas Chandra Bose was an Indian nationalist whose defiance of British authority in India made him a hero among many Indians, but his wartime alliances with Nazi Germany and Imperial Japan left a legacy vexed by authoritarianism, anti-Semitism, and military failure. The honorific Netaji was first applied to Bose in Germany in early 1942—by the Indian soldiers of the Indische Legion and by the German and Indian officials in the Special Bureau for India in Berlin. It is now used throughout India.

During the Second World War (1939–1945), India was a part of the British Empire. British India officially declared war on Nazi Germany in September 1939. India, as a part of the Allied Nations, sent over two and a half million soldiers to fight under British command against the Axis powers. India was also used as the base for American operations in support of China in the China Burma India Theater.
The Imperial Japanese Navy in World War II, at the beginning of the Pacific War in December 1941, was the third most powerful navy in the world, and the naval air service was one of the most potent air forces in the world. During the first six months of the war, the Imperial Japanese Navy enjoyed spectacular success inflicting heavy defeats on Allied forces, being undefeated in every battle. The attack on Pearl Harbor crippled the battleships of the US Pacific Fleet, while Allied navies were devastated during Japan's conquest of Southeast Asia. Japanese Navy aircraft operating from land bases were also responsible for the sinkings of HMS Prince of Wales and HMS Repulse which was the first time that capital ships were sunk by aerial attack while underway. In April 1942, the Indian Ocean raid drove the Royal Navy from South East Asia. After these successes, the Japanese now concentrated on the elimination and neutralization of strategic points from where the Allies could launch counteroffensives against Japan's conquests. However, at Coral Sea the Japanese were forced to abandon their attempts to isolate Australia while the defeat at Midway saw them forced on the defensive. The campaign in the Solomon Islands, in which the Japanese lost the war of attrition, was the most decisive; they had failed to commit enough forces in sufficient time.

Emilie Schenkl was an Austrian stenographer, secretary and trunk exchange operator. She was the wife or the companion of Subhas Chandra Bose, an Indian nationalist leader.
I-29, code-named Matsu, was a B1 type submarine of the Imperial Japanese Navy used during World War II on two secret missions with Germany. She was sunk while returning from the second mission.

There was considerable Axis naval activity in Australian waters during the Second World War, despite Australia being remote from the main battlefronts. German and Japanese warships and submarines entered Australian waters between 1940 and 1945 and attacked ships, ports and other targets. Among the best-known attacks are the sinking of HMAS Sydney by a German raider in November 1941, the bombing of Darwin by Japanese naval aircraft in February 1942, and the Japanese midget submarine attack on Sydney Harbour in May 1942. About 40 Allied merchant ships were damaged or sunk off the Australian coast by surface raiders, submarines and mines. Japanese submarines also shelled three Australian ports and submarine-based aircraft flew over several Australian capital cities.

The Type B1 submarine, also called I-15-class submarine was the first group of boats of the Type B cruiser submarines built for the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN) during the 1940s. In total 20 were built, starting with I-15, which gave the series their alternative name.
Imperial Japanese Navy submarines originated with the purchase of five Holland type submarines from the United States in 1904. Japanese submarine forces progressively built up strength and expertise, becoming by the beginning of World War II one of the world's most varied and powerful submarine fleets.

I-26 was an Imperial Japanese Navy B1 type submarine commissioned in 1941. She saw service in the Pacific War theatre of World War II, patrolling off the West Coast of Canada and the United States, the east coast of Australia, and Fiji and in the Indian Ocean and taking part in Operation K, preparatory operations for the Aleutian Islands campaign, and the Guadalcanal campaign, the Marianas campaign, and the Battle of Leyte Gulf. She was the first Japanese submarine to sink an American merchant ship in the war, sank the first ship lost off the coast of State of Washington during the war, damaged the aircraft carrier USS Saratoga (CV-3), sank the light cruiser USS Juneau (CLAA-52), and was the third-highest-scoring Japanese submarine of World War II in terms of shipping tonnage sunk. Her bombardment of Vancouver Island in 1942 was the first foreign attack on Canadian soil since 1870. In 1944, I-26′s crew committed war crimes in attacking the survivors of a ship she sank. She was sunk in October 1944 during her ninth war patrol.
German submarine U-180 was a Type IXD1 transport U-boat of Nazi Germany's Kriegsmarine which served in World War II. Her keel was laid down on 25 February 1941 at the DeSchiMAG AG Weser yard in Bremen as yard number 1020. She was launched on 10 December 1941 and commissioned on 16 May 1942 under Fregattenkapitän Werner Musenberg. Stripped of torpedo armament, the Type IXD1s were designated as transport submarines, and could carry up to 252 tonnes of freight. U-180 was used primarily in clandestine operations.
Michel(HSK-9) was an auxiliary cruiser of Nazi Germany's Kriegsmarine that operated as a merchant raider during World War II. Built by Danziger Werft in Danzig 1938/39 as the freighter Bielsko for the Polish Gdynia-America-Line (GAL), she was requisitioned by the Kriegsmarine at the outbreak of World War II and converted into the hospital ship Bonn. In the summer of 1941, she was converted into the auxiliary cruiser Michel, and was commissioned on 7 September 1941. Known as Schiff 28, her Royal Navy designation was Raider H. She was the last operative German raider of World War II.

Allied submarines were used extensively during the Pacific War and were a key contributor to the defeat of the Empire of Japan.

The Gruppe Monsun or Monsoon Group was a force of German U-boats (submarines) that operated in the Pacific and Indian Oceans during World War II. Although similar naming conventions were used for temporary groupings of submarines in the Atlantic, the longer duration of Indian Ocean patrols caused the name to be permanently associated with the relatively small number of U-boats operating out of Penang. After 1944, the U-boats of the Monsun Gruppe were operationally placed under the authority of the Southeast Asia U-boat Region.

Prior to World War II, the Indian Ocean was an important maritime trade route between European nations and their colonial territories in East Africa, the Arabian Peninsula, British India, Indochina, the East Indies (Indonesia), and Australia for a long time. Naval presence was dominated by the Royal Navy Eastern Fleet and the Royal Australian Navy as World War II began, with a major portion of the Royal Netherlands Navy operating in the Dutch East Indies and the Red Sea Flotilla of the Italian Regia Marina operating from Massawa.
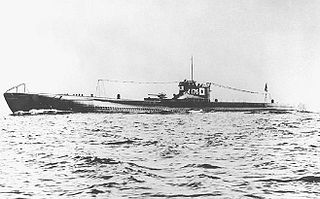
The Japanese submarine I-176 was a "Kaidai" type of cruiser submarine active in World War II. A KD7 sub-class boat, I-176 was built for the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN) in the early 1940s.
At the beginning of World War II, the Royal Navy was the strongest navy in the world, with the largest number of warships built and with naval bases across the globe. It had over 15 battleships and battlecruisers, 7 aircraft carriers, 66 cruisers, 164 destroyers and 66 submarines. With a massive merchant navy, about a third of the world total, it also dominated shipping. The Royal Navy fought in every theatre from the Atlantic, Mediterranean, freezing Northern routes to Russia and the Pacific ocean.

The 8th Submarine Squadron of the Imperial Japanese Navy was based at Swettenham Pier, Penang, Malaya, until late 1944 during World War II. Its mission was to disrupt Allied supply lines in aid of Nazi Germany.
I-66, later I-166, was a Kaidai-class cruiser submarine of the KD5 sub-class completed for the Imperial Japanese Navy in 1932. She served during World War II, supporting the Japanese invasion of Malaya and the invasion of Sarawak, taking part in the Battle of Midway, and conducting numerous war patrols in the Indian Ocean before was sunk in July 1944.

I-6 was an Imperial Japanese Navy J2 type submarine commissioned in 1935. She was a large cruiser submarine that served in the Second Sino-Japanese War and World War II. During the latter conflict she operated in support of the attack on Pearl Harbor, torpedoed the aircraft carrier USS Saratoga (CV-3), conducted anti-shipping patrols in the Indian Ocean and South Pacific Ocean, and took part in the Aleutian Islands campaign and New Guinea campaign before she was sunk in June 1944.













