
Java is a high-level, class-based, object-oriented programming language that is designed to have as few implementation dependencies as possible. It is a general-purpose programming language intended to let programmers write once, run anywhere (WORA), meaning that compiled Java code can run on all platforms that support Java without the need to recompile. Java applications are typically compiled to bytecode that can run on any Java virtual machine (JVM) regardless of the underlying computer architecture. The syntax of Java is similar to C and C++, but has fewer low-level facilities than either of them. The Java runtime provides dynamic capabilities that are typically not available in traditional compiled languages.

A Java virtual machine (JVM) is a virtual machine that enables a computer to run Java programs as well as programs written in other languages that are also compiled to Java bytecode. The JVM is detailed by a specification that formally describes what is required in a JVM implementation. Having a specification ensures interoperability of Java programs across different implementations so that program authors using the Java Development Kit (JDK) need not worry about idiosyncrasies of the underlying hardware platform.
Java Platform, Standard Edition is a computing platform for development and deployment of portable code for desktop and server environments. Java SE was formerly known as Java 2 Platform, Standard Edition (J2SE).
In computing, cross-platform software is computer software that is designed to work in several computing platforms. Some cross-platform software requires a separate build for each platform, but some can be directly run on any platform without special preparation, being written in an interpreted language or compiled to portable bytecode for which the interpreters or run-time packages are common or standard components of all supported platforms.
A computing platform, digital platform, or software platform is an environment in which software is executed. It may be the hardware or the operating system (OS), a web browser and associated application programming interfaces, or other underlying software, as long as the program code is executed using the services provided by the platform. Computing platforms have different abstraction levels, including a computer architecture, an OS, or runtime libraries. A computing platform is the stage on which computer programs can run.
The GNU Compiler for Java (GCJ) is a discontinued free compiler for the Java programming language. It was part of the GNU Compiler Collection.
In software design, the Java Native Interface (JNI) is a foreign function interface programming framework that enables Java code running in a Java virtual machine (JVM) to call and be called by native applications and libraries written in other languages such as C, C++ and assembly.
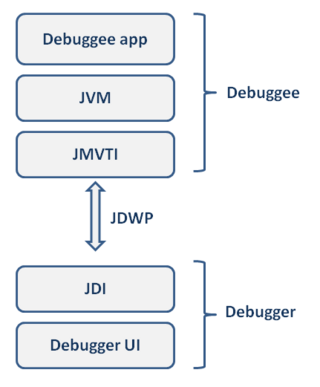
The Java Platform Debugger Architecture (JPDA) is a collection of APIs to debug Java code.
Apache Harmony is a retired open source, free Java implementation, developed by the Apache Software Foundation. It was announced in early May 2005 and on October 25, 2006, the board of directors voted to make Apache Harmony a top-level project. The Harmony project achieved 99% completeness for J2SE 5.0, and 97% for Java SE 6. The Android operating system has historically been a major user of Harmony, although since Android Nougat it increasingly relies on OpenJDK libraries.
In software engineering, profiling is a form of dynamic program analysis that measures, for example, the space (memory) or time complexity of a program, the usage of particular instructions, or the frequency and duration of function calls. Most commonly, profiling information serves to aid program optimization, and more specifically, performance engineering.
Application virtualization software refers to both application virtual machines and software responsible for implementing them. Application virtual machines are typically used to allow application bytecode to run portably on many different computer architectures and operating systems. The application is usually run on the computer using an interpreter or just-in-time compilation (JIT). There are often several implementations of a given virtual machine, each covering a different set of functions.

Java is a set of computer software and specifications that provides a software platform for developing application software and deploying it in a cross-platform computing environment. Java is used in a wide variety of computing platforms from embedded devices and mobile phones to enterprise servers and supercomputers. Java applets, which are less common than standalone Java applications, were commonly run in secure, sandboxed environments to provide many features of native applications through being embedded in HTML pages.

Google Web Toolkit, or GWT Web Toolkit, is an open-source set of tools that allows web developers to create and maintain JavaScript front-end applications in Java. It is licensed under Apache License 2.0.

Squawk is a Java micro edition virtual machine for embedded system and small devices. Most virtual machines for the Java platform are written in low level native languages such as C/C++ and assembler; what makes Squawk different is that Squawk's core is mostly written in Java. A Java implementation provides ease of portability, and integration of virtual machine and application resources such as objects, threads, and operating-system interfaces.
In software development, the programming language Java was historically considered slower than the fastest 3rd generation typed languages such as C and C++. In contrast to those languages, Java compiles by default to a Java Virtual Machine (JVM) with operations distinct from those of the actual computer hardware. Early JVM implementations were interpreters; they simulated the virtual operations one-by-one rather than translating them into machine code for direct hardware execution.
Eclipse OpenJ9 is a high performance, scalable, Java virtual machine (JVM) implementation that is fully compliant with the Java Virtual Machine Specification.
WebSphere sMash was a development and runtime environment from IBM for the creation of dynamic web applications using the scripting languages Apache Groovy and PHP. It contained a PHP runtime written in Java. Project Zero was the experimental software development community in which new versions of WebSphere sMash were incubated. WebSphere sMash was withdrawn from sale in 2012, with support discontinued in 2014.
The Java Development Kit (JDK) is a distribution of Java Technology by Oracle Corporation. It implements the Java Language Specification (JLS) and the Java Virtual Machine Specification (JVMS) and provides the Standard Edition (SE) of the Java Application Programming Interface (API). It is derivative of the community driven OpenJDK which Oracle stewards. It provides software for working with Java applications. Examples of included software are the virtual machine, a compiler, performance monitoring tools, a debugger, and other utilities that Oracle considers useful for a Java programmer.
Java bytecode is the instruction set of the Java virtual machine (JVM), crucial for executing programs written in the Java language and other JVM-compatible languages. Each bytecode operation in the JVM is represented by a single byte, hence the name "bytecode", making it a compact form of instruction. This intermediate form enables Java programs to be platform-independent, as they are compiled not to native machine code but to a universally executable format across different JVM implementations.

GraalVM is a Java Development Kit (JDK), written in Java. The open-source distribution of GraalVM is based on OpenJDK, and the enterprise distribution is based on Oracle JDK. As well as just-in-time (JIT) compilation, GraalVM can compile a Java application ahead-of-time so that it starts instantly, provides peak performance with no warmup, and uses fewer resources. It provides additional programming languages and execution modes. The first production-ready release, GraalVM 19.0, was distributed in May 2019. The most recent release is GraalVM for JDK 21, made available in September 2023.








