Tocobaga was the name of a chiefdom of Native Americans, its chief, and its principal town during the 16th century. The chiefdom was centered around the northern end of Old Tampa Bay, the arm of Tampa Bay that extends between the present-day city of Tampa and northern Pinellas County. The exact location of the principal town is believed to be the archeological Safety Harbor site. This is the namesake for the Safety Harbor culture, of which the Tocobaga are the most well-known group.
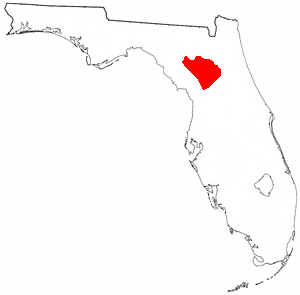
The Alachua culture is a Late Woodland Southeast period archaeological culture in north-central Florida, dating from around 600 to 1700. It is found in an area roughly corresponding to present-day Alachua County, the northern half of Marion County and the western part of Putnam County. It was preceded by the Cades Pond culture, which inhabited approximately the same area.

The Potano tribe lived in north-central Florida at the time of first European contact. Their territory included what is now Alachua County, the northern half of Marion County and the western part of Putnam County. This territory corresponds to that of the Alachua culture, which lasted from about 700 until 1700. The Potano were among the many tribes of the Timucua people, and spoke a dialect of the Timucua language.
The Glades culture is an archaeological culture in southernmost Florida that lasted from about 500 BCE until shortly after European contact. Its area included the Everglades, the Florida Keys, the Atlantic coast of Florida north through present-day Martin County and the Gulf coast north to Marco Island in Collier County. It did not include the area around Lake Okeechobee, which was part of the Belle Glade culture.
Maxine L. Margolis is an American anthropologist and an inductee of the American Academy of Arts and Sciences. She is a professor of anthropology at the University of Florida in Gainesville, and has been with the university since 1970. Margolis holds a Ph.D. in anthropology from Columbia University. Margolis received the BRASA Lifetime Contribution Award in 2014.
The Westo were an Iroquoian Native American tribe encountered in what became the Southeastern U.S. by Europeans in the 17th century. They probably spoke an Iroquoian language. The Spanish called these people Chichimeco, and Virginia colonists may have called the same people Richahecrian. Their first appearance in the historical record is as a powerful tribe in colonial Virginia who had migrated from the mountains into the region around present-day Richmond. Their population provided a force of 700–900 warriors.

The Mocama were a Native American people who lived in the coastal areas of what are now northern Florida and southeastern Georgia. A Timucua group, they spoke the dialect known as Mocama, the best-attested dialect of the Timucua language. Their heartland extended from about the Altamaha River in Georgia to south of the mouth of the St. John's River, covering the Sea Islands and the inland waterways, Intracoastal. and much of present-day Jacksonville. At the time of contact with Europeans, there were two major chiefdoms among the Mocama, the Saturiwa and the Tacatacuru, each of which evidently had authority over multiple villages. The Saturiwa controlled chiefdoms stretching to modern day St. Augustine, but the native peoples of these chiefdoms have been identified by Pareja as speaking Agua Salada, which may have been a distinct dialect.
Big Mound City (8PB48) is a prehistoric site near Canal Point, Florida, United States. It is located 10 miles east of Canal Point, off U.S. Route 98. On May 24, 1973, it was added to the U.S. National Register of Historic Places. It is located inside the J.W. Corbett Wildlife Management Area.

Beginning in the second half of the 16th century, the Kingdom of Spain established a number of missions throughout La Florida in order to convert the Native Americans to Roman Catholicism, to facilitate control of the area, and to obstruct regional colonization by other Protestants, particularly, those from England and France. Spanish Florida originally included much of what is now the Southeastern United States, although Spain never exercised long-term effective control over more than the northern part of what is now the State of Florida from present-day St. Augustine to the area around Tallahassee, southeastern Georgia, and some coastal settlements, such as Pensacola, Florida. A few short-lived missions were established in other locations, including Mission Santa Elena in present-day South Carolina, around the Florida peninsula, and in the interior of Georgia and Alabama.
Acuera was the name of both an indigenous town and a province or region in central Florida during the 16th and 17th centuries. The indigenous people of Acuera spoke a dialect of the Timucua language. In 1539 the town first encountered Europeans when it was raided by soldiers of Hernando de Soto's expedition. French colonists also knew this town during their brief tenure (1564–1565) in northern Florida.
John Mann Goggin was a cultural anthropologist in the southwest, southeast, Mexico, and Caribbean, primarily focusing on the ethnology, cultural history, and typology of artifacts from archaeological sites.
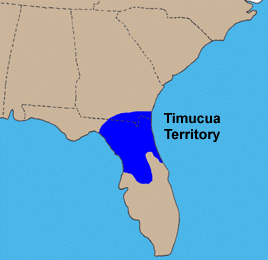
The Timucua were a Native American people who lived in Northeast and North Central Florida and southeast Georgia. They were the largest indigenous group in that area and consisted of about 35 chiefdoms, many leading thousands of people. The various groups of Timucua spoke several dialects of the Timucua language. At the time of European contact, Timucuan speakers occupied about 19,200 square miles (50,000 km2) in the present-day states of Florida and Georgia, with an estimated population of 200,000. Milanich notes that the population density calculated from those figures, 10.4 per square mile (4.0/km2) is close to the population densities calculated by other authors for the Bahamas and for Hispaniola at the time of first European contact. The territory occupied by Timucua speakers stretched from the Altamaha River and Cumberland Island in present-day Georgia as far south as Lake George in central Florida, and from the Atlantic Ocean west to the Aucilla River in the Florida Panhandle, though it reached the Gulf of Mexico at no more than a couple of points.
The Indigenous peoples of Florida lived in what is now known as Florida for more than 12,000 years before the time of first contact with Europeans. However, the indigenous Floridians living east of the Apalachicola River had largely died out by the early 18th century. Some Apalachees migrated to Louisiana, where their descendants now live; some were taken to Cuba and Mexico by the Spanish in the 18th century, and a few may have been absorbed into the Seminole and Miccosukee tribes.

Uzita (Uçita) was the name of a 16th-century native chiefdom, its chief town and its chiefs. Part of the Safety Harbor culture, it was located in present-day Florida on the south side of Tampa Bay.
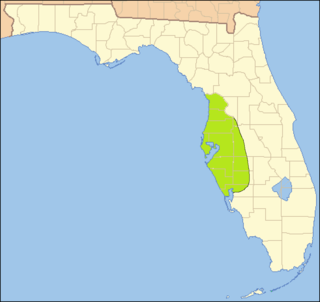
The Safety Harbor culture was an archaeological culture practiced by Native Americans living on the central Gulf coast of the Florida peninsula, from about 900 CE until after 1700. The Safety Harbor culture is defined by the presence of Safety Harbor ceramics in burial mounds. The culture is named after the Safety Harbor site, located close to the center of the culture area. The Safety Harbor site is the probable location of the chief town of the Tocobaga, the best known of the groups practicing the Safety Harbor culture.
Benito Ruíz de Salazar Vallecilla was twice governor of Spanish Florida, from 1645 to 1646 and from 1648 to 1651.
Pohoy was a chiefdom on the shores of Tampa Bay in present-day Florida in the late sixteenth century and all of the seventeenth century. Following slave-taking raids by people from the Lower Towns of the Muscogee Confederacy at the beginning of the eighteenth century, the surviving Pohoy people lived in several locations in peninsular Florida. The Pohoy disappeared from historical accounts after 1739.
Ocale was the name of a town in Florida visited by the Hernando de Soto expedition, and of a putative chiefdom of the Timucua people. The town was probably close to the Withlacoochee River at the time of de Soto's visit, and may have later been moved to the Oklawaha River.
San Buenaventura de Potano was a Spanish mission near Orange Lake in southern Alachua County or northern Marion County, Florida, located on the site where the town of Potano had been located when it was visited by Hernando de Soto in 1539. The Richardson/UF Village Site (8AL100), in southern Alachua County, has been proposed as the location of the town and mission.
Urriparacoxi, or Paracoxi, was the chief of a Native American group in central Florida at the time of Hernando de Soto's expedition through what is now the southeastern United States. "Urriparacoxi" was a title, meaning "war leader". There is no known name for the people he led, or for their territory.
 "Experts Debte(sic) Theory On Columbus"
"Experts Debte(sic) Theory On Columbus" 




