See also
- State Jewish Theater (disambiguation)
- Halachic state - a state based on halacha (Jewish religious law)
The Jewish state is a characterization of the modern-day state of Israel.
Jewish state may also refer to:

The Decapolis was a group of ten Hellenistic cities on the eastern frontier of the Roman Empire in the Southern Levant in the first centuries BC and AD. Most of the cities were located to the east of the Jordan Rift Valley, between Judaea, Iturea, Nabataea, and Syria.

Syria Palaestina was the renamed Roman province formerly known as Judaea, following the Roman suppression of the Bar Kokhba revolt, in what then became known as the Palestine region between the early 2nd and late 4th centuries AD. The provincial capital was Caesarea Maritima. It forms part of timeline of the period in the region referred to as Roman Palestine.
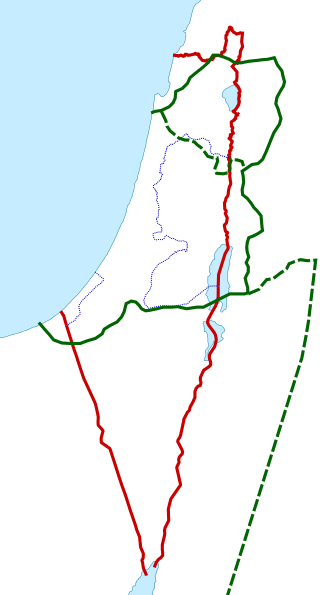
The region of Palestine, also known as historic Palestine, is a geographical area in West Asia. It includes modern-day Israel and the State of Palestine, as well as parts of northwestern Jordan in some definitions. Other names for the region include Canaan, the Promised Land, the Land of Israel, or the Holy Land.

This timeline tries to compile dates of important historical events that happened in or that led to the rise of the Middle East. The Middle East is the territory that comprises today's Egypt, the Persian Gulf states, Iran, Iraq, Israel and Palestine, Cyprus, Jordan, Lebanon, Oman, Saudi Arabia, Syria, Turkey, United Arab Emirates, and Yemen. The Middle East, with its particular characteristics, was not to emerge until the late second millennium AD. To refer to a concept similar to that of today's Middle East but earlier in time, the term ancient Near East is used.

Judaea was a Roman province from 6 to 132 AD, which incorporated the Levantine regions of Idumea, Philistia, Judea, Samaria, and Galilee, extending over parts of the former regions of the Hasmonean and Herodian kingdoms of Judea. The name Judaea was derived from the Iron Age Kingdom of Judah, that was centered predominantly in Judea.

Arrapha or Arrapkha was an ancient city in what today is northeastern Iraq, thought to be located at city of Kirkuk.
Syria is a country in the Middle East, incorporating the northern Levant.
Palaestina may refer to:
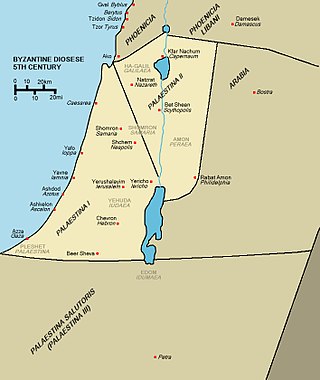
Palaestina Secunda or Palaestina II was a province of the Byzantine Empire from 390, until its conquest by the Muslim armies in 634–636. Palaestina Secunda, a part of the Diocese of the East, roughly comprised inland Galilee, the Jezreel (Yizrael) Valley, Bet Shean Valley, and the corresponding area of Transjordan, with its capital in Scythopolis. The province experienced the rise of Christianity under the Byzantines, but was also a thriving center of Judaism, after the Jews had been driven out of Judea by the Romans as a result of their 1st- and 2nd-century revolts.
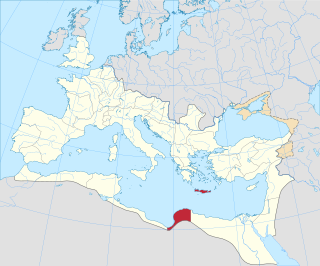
Crete and Cyrenaica was a senatorial province of the Roman Republic and later the Roman Empire, established in 67 BC, which included the island of Crete and the region of Cyrenaica in modern-day Libya. These areas were settled by Greek colonists from the eighth to sixth centuries BC. After Alexander the Great's death, his short-lived empire was partitioned between his generals during the Wars of the Diadochi. Cyrenaica ended up under Egyptian rule, except for Crete, which remained independent.

Judea or Judaea is a mountainous region of the Levant. Traditionally dominated by the city of Jerusalem, it is now part of Palestine and Israel. The name's usage is historic, having been used in antiquity and still into the present day; it originates from Yehudah, a Hebrew name. Yehudah was a son of Jacob, who was later given the name "Israel" and whose sons collectively headed the Twelve Tribes of Israel. Yehudah's progeny among the Israelites formed the Tribe of Judah, with whom the Kingdom of Judah is associated. Related nomenclature continued to be used under the rule of the Babylonians, the Persians, the Greeks, and the Romans. Under the Hasmoneans, the Herodians, and the Romans, the term was applied to an area larger than Judea of earlier periods. In 132 CE, the Roman province of Judaea was merged with Galilee to form the enlarged province of Syria Palaestina.

The history of the Jews in the Roman Empire traces the interaction of Jews and Romans during the period of the Roman Empire. A Jewish diaspora had migrated to Rome and to the territories of Roman Europe from the land of Israel, Anatolia, Babylon and Alexandria in response to economic hardship and incessant warfare over the land of Israel between the Ptolemaic and Seleucid empires from the 4th to the 1st centuries BCE. In Rome, Jewish communities thrived economically. Jews became a significant part of the Roman Empire's population in the first century CE, with some estimates as high as 7 million people; however, this estimation has been questioned.

The article deals with the biblical and historical kings of the Land of Israel—Abimelech of Sichem, the three kings of the United Kingdom of Israel and those of its successor states, Israel and Judah, followed in the Second Temple period, part of classical antiquity, by the kingdoms ruled by the Hasmonean and Herodian dynasties.

Palaestina Salutaris or Palaestina Tertia was a Byzantine province, which covered the area of the Negev, Sinai and south-west of Transjordan, south of the Dead Sea. The province, a part of the Diocese of the East, was split from Arabia Petraea during the reforms of Diocletian in c.300 CE and existed until the Muslim Arab conquests of the 7th century.
Amathus (Ancient Greek: Ἀμαθοῦς or τὰ Ἀμαθά; in Eusebius, Ἀμμαθοὺς. Hebrew: עמתו was a fortified city east of the Jordan River, in modern-day Jordan.
The administration of Judaea as a province of Rome from 6 to 135 was carried out primarily by a series of Roman Prefects, Procurators, and Legates pro praetore. These administrators coincided with the ostensible rule by Hasmonean and Herodian rulers of Judea. The Roman administrators were as follows:
This article presents a timeline of the name Judea through an incomplete list of notable historical references to the name through the various time periods of the region.