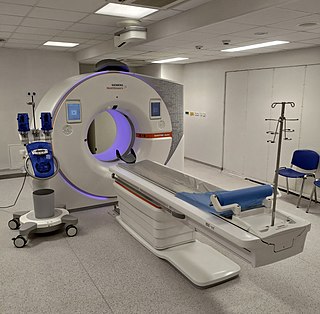
A computed tomography scan is a medical imaging technique used to obtain detailed internal images of the body. The personnel that perform CT scans are called radiographers or radiology technologists.

Radiology is the medical discipline that uses medical imaging to diagnose diseases and guide their treatment, within the bodies of humans and other animals. It began with radiography, but today it includes all imaging modalities, including those that use no electromagnetic radiation, as well as others that do, such as computed tomography (CT), fluoroscopy, and nuclear medicine including positron emission tomography (PET). Interventional radiology is the performance of usually minimally invasive medical procedures with the guidance of imaging technologies such as those mentioned above.

Mammography is the process of using low-energy X-rays to examine the human breast for diagnosis and screening. The goal of mammography is the early detection of breast cancer, typically through detection of characteristic masses or microcalcifications.
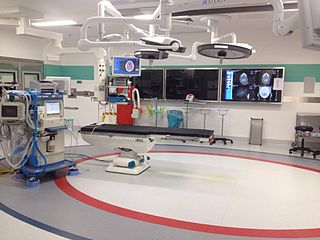
Interventional radiology (IR) is a medical specialty that performs various minimally-invasive procedures using medical imaging guidance, such as x-ray fluoroscopy, computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging, or ultrasound. IR performs both diagnostic and therapeutic procedures through very small incisions or body orifices. Diagnostic IR procedures are those intended to help make a diagnosis or guide further medical treatment, and include image-guided biopsy of a tumor or injection of an imaging contrast agent into a hollow structure, such as a blood vessel or a duct. By contrast, therapeutic IR procedures provide direct treatment—they include catheter-based medicine delivery, medical device placement, and angioplasty of narrowed structures.
In medical or research imaging, an incidental imaging finding is an unanticipated finding which is not related to the original diagnostic inquiry. As with other types of incidental medical findings, they may represent a diagnostic, ethical, and philosophical dilemma because their significance is unclear. While some coincidental findings may lead to beneficial diagnoses, others may lead to overdiagnosis that results in unnecessary testing and treatment, sometimes called the "cascade effect".
Overdiagnosis is the diagnosis of disease that will never cause symptoms or death during a patient's ordinarily expected lifetime and thus presents no practical threat regardless of being pathologic. Overdiagnosis is a side effect of screening for early forms of disease. Although screening saves lives in some cases, in others it may turn people into patients unnecessarily and may lead to treatments that do no good and perhaps do harm. Given the tremendous variability that is normal in biology, it is inherent that the more one screens, the more incidental findings will generally be found. For a large percentage of them, the most appropriate medical response is to recognize them as something that does not require intervention; but determining which action a particular finding warrants can be very difficult, whether because the differential diagnosis is uncertain or because the risk ratio is uncertain.
The American College of Radiology (ACR), founded in 1923, is a professional medical society representing nearly 40,000 diagnostic radiologists, radiation oncologists, interventional radiologists, nuclear medicine physicians and medical physicists.

Omental cake is a radiologic sign indicative of an abnormally thickened greater omentum. It refers to infiltration of the normal omental structure by other types of soft-tissue or chronic inflammation resulting in a thickened, or cake-like appearance.

Computer-aided detection (CADe), also called computer-aided diagnosis (CADx), are systems that assist doctors in the interpretation of medical images. Imaging techniques in X-ray, MRI, Endoscopy, and ultrasound diagnostics yield a great deal of information that the radiologist or other medical professional has to analyze and evaluate comprehensively in a short time. CAD systems process digital images or videos for typical appearances and to highlight conspicuous sections, such as possible diseases, in order to offer input to support a decision taken by the professional.

A CT pulmonary angiogram (CTPA) is a medical diagnostic test that employs computed tomography (CT) angiography to obtain an image of the pulmonary arteries. Its main use is to diagnose pulmonary embolism (PE). It is a preferred choice of imaging in the diagnosis of PE due to its minimally invasive nature for the patient, whose only requirement for the scan is an intravenous line.
Professor Dame Janet Elizabeth Husband is Emeritus Professor of Radiology at the Institute of Cancer Research. She had a career in diagnostic radiology that spanned nearly 40 years, using scanning technology to diagnose, stage, and follow-up cancer. She continues to support medicine and research as a board member and advisor for various organisations.
Paediatric radiology is a subspecialty of radiology involving the imaging of fetuses, infants, children, adolescents and young adults. Many paediatric radiologists practice at children's hospitals.
The National Lung Screening Trial was a United States-based clinical trial which recruited research participants between 2002 and 2004. It was sponsored by the National Cancer Institute and conducted by the American College of Radiology Imaging Network and the Lung Screening Study Group. The major objective of the trial was to compare the efficacy of low-dose helical computed tomography and standard chest X-ray as methods of lung cancer screening. The primary study ended in 2010, and the initial findings were published in November 2010, with the main results published in 2011 in the New England Journal of Medicine.

OpenNotes is a research initiative and international movement located at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center.
Dr. Joann G. Elmore is a professor of medicine at the David Geffen School of Medicine, professor of Health Policy and Management at the UCLA Fielding School of Public Health Director of the UCLA National Clinician Scholars Program, the endowed chair in Health Care Delivery for The Rosalind and Arthur Gilbert Foundation, and a practicing physician . She publishes studies on diagnostic accuracy of cancer screening and medical tests in addition to AI/machine learning, using computer-aided tools to aid in the early detection process of high-risk cancers Previously, she held faculty and leadership positions at the University of Washington, Fred Hutchinson Research Center, Group Health Research Institute, Yale University and was the Associate Director and member of the National Advisory Committee for the Robert Wood Johnson Clinical Scholars Program at Yale and University of Washington. Elmore received her medical degree from the Stanford University School of Medicine, residency training in internal medicine at Yale-New Haven Hospital, with advanced epidemiology training from the Yale School of Epidemiology and Public Health and the RWJF Clinical Scholars Program. In addition, she was a RWJF generalist physician faculty scholar. Elmore is board certified in internal medicine and serves on many national and international committees. She is Editor in Chief for Adult Primary Care at Up-To-Date and enjoys seeing patients as a primary care internist and teaching clinical medicine to students and residents.
Elliot K. Fishman is an American diagnostic radiologist, currently the director of diagnostic imaging and body CT and professor of radiology and radiological science at Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine.
HB 2102, also known as "Henda's Law", is a breast density (BD) notification law approved in 2011 by the FDA that mammography patients be provided educational materials on dense breast tissue can hide abnormalities, including breast cancer, from traditional screening. Henda's Law aims to promote patient doctor discussion as well as reduce the rate of false negatives, as mammography may not detect abnormalities in dense breasts.
Sahar Saleem is a professor of radiology at Cairo University where she specialises in paleoradiology, the use of radiology to study mummies. She discovered the knife wound in the throat of Ramesses III, which was most likely the cause of his death.
Denise R. Aberle is an American radiologist and oncologist. As a professor of radiology in the David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA and a professor of bioengineering in the UCLA Henry Samueli School of Engineering and Applied Science, Aberle was elected a member of the National Academy of Medicine and Fellow of the American Institute for Medical and Biological Engineering.







