Mechanical advantage is a measure of the force amplification achieved by using a tool, mechanical device or machine system. The device trades off input forces against movement to obtain a desired amplification in the output force. The model for this is the law of the lever. Machine components designed to manage forces and movement in this way are called mechanisms. An ideal mechanism transmits power without adding to or subtracting from it. This means the ideal machine does not include a power source, is frictionless, and is constructed from rigid bodies that do not deflect or wear. The performance of a real system relative to this ideal is expressed in terms of efficiency factors that take into account departures from the ideal.
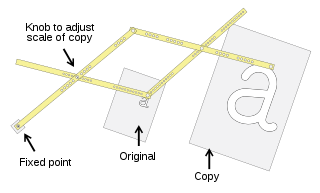
A pantograph is a mechanical linkage connected in a manner based on parallelograms so that the movement of one pen, in tracing an image, produces identical movements in a second pen. If a line drawing is traced by the first point, an identical, enlarged, or miniaturized copy will be drawn by a pen fixed to the other. Using the same principle, different kinds of pantographs are used for other forms of duplication in areas such as sculpting, minting, engraving, and milling.

A fishing reel is a hand-cranked reel used in angling to wind and stow fishing line, typically mounted onto a fishing rod, but may also be used on compound bows or crossbows to retrieve tethered arrows when bowfishing.

In mechanical engineering, a crosshead is a mechanical joint used as part of the slider-crank linkages of long reciprocating engines and reciprocating compressors to eliminate sideways force on the piston. Also, the crosshead enables the connecting rod to freely move outside the cylinder. Because of the very small bore-to-stroke ratio on such engines, the connecting rod would hit the cylinder walls and block the engine from rotating if the piston was attached directly to the connecting rod like on trunk engines. Therefore, the longitudinal dimension of the crosshead must be matched to the stroke of the engine.

A Bowden cable is a type of flexible cable used to transmit mechanical force or energy by the movement of an inner cable relative to a hollow outer cable housing. The housing is generally of composite construction, consisting of an inner lining, a longitudinally incompressible layer such as a helical winding or a sheath of steel wire, and a protective outer covering.

A torsion spring is a spring that works by twisting its end along its axis; that is, a flexible elastic object that stores mechanical energy when it is twisted. When it is twisted, it exerts a torque in the opposite direction, proportional to the amount (angle) it is twisted. There are various types:

A bimetallic strip or bimetal strip is a strip that consists of two strips of different metals which expand at different rates as they are heated. They are used to convert a temperature change into mechanical displacement. The different expansions force the flat strip to bend one way if heated, and in the opposite direction if cooled below its initial temperature. The metal with the higher coefficient of thermal expansion is on the outer side of the curve when the strip is heated and on the inner side when cooled.

A scale or balance is a device used to measure weight or mass. These are also known as mass scales, weight scales, mass balances, massometers, and weight balances.

A barrel organ is a French mechanical musical instrument consisting of bellows and one or more ranks of pipes housed in a case, usually of wood, and often highly decorated. The basic principle is the same as a traditional pipe organ, but rather than being played by an organist, the barrel organ is activated either by a person turning a crank, or by clockwork driven by weights or springs. The pieces of music are encoded onto wooden barrels, which are analogous to the keyboard of the traditional pipe organ. A person who plays a barrel organ is known as an organ grinder.
A planimeter, also known as a platometer, is a measuring instrument used to determine the area of an arbitrary two-dimensional shape.

The Mannlicher M1894 was an early blow-forward semi-automatic pistol.

In various contexts of science, technology, and manufacturing, an indicator is any of various instruments used to accurately measure small distances and angles, and amplify them to make them more obvious. The name comes from the concept of indicating to the user that which their naked eye cannot discern; such as the presence, or exact quantity, of some small distance.

Tracker action is a term used in reference to pipe organs and steam calliopes to indicate a mechanical linkage between keys or pedals pressed by the organist and the valve that allows air to flow into pipe(s) of the corresponding note. This is in contrast to "direct electric action" and "electro-pneumatic action", which connect the key to the valve through an electrical link or an electrically assisted pneumatic system respectively, or "tubular-pneumatic action" which utilizes a change of pressure within lead tubing which connects the key to the valve pneumatic.
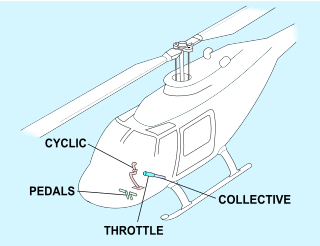
Helicopter flight controls are used to achieve and maintain controlled aerodynamic helicopter flight. Changes to the aircraft flight control system transmit mechanically to the rotor, producing aerodynamic effects on the rotor blades that make the helicopter move in a desired way. To tilt forward and back (pitch) or sideways (roll) requires that the controls alter the angle of attack of the main rotor blades cyclically during rotation, creating differing amounts of lift at different points in the cycle. To increase or decrease overall lift requires that the controls alter the angle of attack for all blades collectively by equal amounts at the same time, resulting in ascent, descent, acceleration and deceleration.
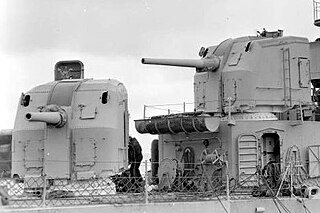
The Mark 12 5"/38-caliber gun was a United States dual-purpose naval gun, but also installed in single-purpose mounts on a handful of ships. The 38-caliber barrel was a mid-length compromise between the previous United States standard 5"/51 low-angle gun and 5"/25 anti-aircraft gun. United States naval gun terminology indicates the gun fired a projectile 5 inches (127 mm) in diameter, and the barrel was 38 calibers long. The increased barrel length provided greatly improved performance in both anti-aircraft and anti-surface roles compared to the 5"/25 gun. However, except for the barrel length and the use of semi-fixed ammunition, the 5"/38 gun was derived from the 5"/25 gun. Both weapons had power ramming, which enabled rapid fire at high angles against aircraft. The 5"/38 entered service on USS Farragut, commissioned in 1934, the first new destroyer design since the last Clemson was built in 1922. The base ring mount, which improved the effective rate of fire, entered service on USS Porter, commissioned in 1936.

A mechanical watch is a watch that uses a clockwork mechanism to measure the passage of time, as opposed to quartz watches which function using the vibration modes of a piezoelectric quartz tuning fork, or radio watches, which are quartz watches synchronized to an atomic clock via radio waves. A mechanical watch is driven by a mainspring which must be wound either periodically by hand or via a self-winding mechanism. Its force is transmitted through a series of gears to power the balance wheel, a weighted wheel which oscillates back and forth at a constant rate. A device called an escapement releases the watch's wheels to move forward a small amount with each swing of the balance wheel, moving the watch's hands forward at a constant rate. The escapement is what makes the 'ticking' sound which is heard in an operating mechanical watch. Mechanical watches evolved in Europe in the 17th century from spring powered clocks, which appeared in the 15th century.
Tyer's Electric Train Tablet system is a form of railway signalling for single line railways used in several countries; it was first devised in Great Britain by engineer Edward Tyer after the Thorpe rail accident of 1874, which left 21 people dead. It was used in New Zealand for close to 100 years until June 1994. The system used a hard disk called a tablet, a form of token.

A white light scanner (WLS) is a device for performing surface height measurements of an object using coherence scanning interferometry (CSI) with spectrally-broadband, "white light" illumination. Different configurations of scanning interferometer may be used to measure macroscopic objects with surface profiles measuring in the centimeter range, to microscopic objects with surface profiles measuring in the micrometer range. For large-scale non-interferometric measurement systems, see structured-light 3D scanner.
A pipe support or pipe hanger is a designed element that transfer the load from a pipe to the supporting structures. The load includes the weight of the pipe proper, the content that the pipe carries, all the pipe fittings attached to pipe, and the pipe covering such as insulation. The four main functions of a pipe support are to anchor, guide, absorb shock, and support a specified load. Pipe supports used in high or low temperature applications may contain insulation materials. The overall design configuration of a pipe support assembly is dependent on the loading and operating conditions.
In engineering, a solenoid is a device that converts electrical energy to mechanical energy, using an electromagnet formed from a coil of wire. The device creates a magnetic field from electric current, and uses the magnetic field to create linear motion.















