Related Research Articles

The Firth of Forth is the estuary, or firth, of several Scottish rivers including the River Forth. It meets the North Sea with Fife to its north and Lothian to its south.

Fishery can mean either the enterprise of raising or harvesting fish and other aquatic life or, more commonly, the site where such enterprise takes place. Commercial fisheries include wild fisheries and fish farms, both in freshwater waterbodies and the oceans. About 500 million people worldwide are economically dependent on fisheries. 171 million tonnes of fish were produced in 2016, but overfishing is an increasing problem, causing declines in some populations.

An aquatic animal is any animal, whether vertebrate or invertebrate, that lives in bodies of water for all or most of its lifetime. Aquatic animals generally conduct gas exchange in water by extracting dissolved oxygen via specialised respiratory organs called gills, through the skin or across enteral mucosae, although some are evolved from terrestrial ancestors that re-adapted to aquatic environments, in which case they actually use lungs to breathe air and are essentially holding their breath when living in water. Some species of gastropod mollusc, such as the eastern emerald sea slug, are even capable of kleptoplastic photosynthesis via endosymbiosis with ingested yellow-green algae.

Sand eel or sandeel is the common name used for a considerable number of species of fish. While they are not true eels, they are eel-like in their appearance and can grow up to 30 cm (12 in) in length. Many species are found off the western coasts of Europe from Spain to Scotland, and in the Mediterranean and Baltic Seas.

Heriot-Watt University is a public research university based in Edinburgh, Scotland. It was established in 1821 as the School of Arts of Edinburgh, the world's first mechanics' institute, and was subsequently granted university status by royal charter in 1966. It is the eighth-oldest higher education institution in the United Kingdom. The name Heriot-Watt was taken from Scottish inventor James Watt and Scottish philanthropist and goldsmith George Heriot.
Freshwater ecosystems are a subset of Earth's aquatic ecosystems. They include lakes, ponds, rivers, streams, springs, bogs, and wetlands. They can be contrasted with marine ecosystems, which have a larger salt content. Freshwater habitats can be classified by different factors, including temperature, light penetration, nutrients, and vegetation. There are three basic types of freshwater ecosystems: Lentic, lotic and wetlands. Freshwater ecosystems contain 41% of the world's known fish species.

The Isle of May is located in the north of the outer Firth of Forth, approximately 8 km (5.0 mi) off the coast of mainland Scotland. It is about 1.5 kilometres long and 0.5 kilometres wide. The island is owned and managed by NatureScot as a national nature reserve. There are now no permanent residents, but the island was the site of St Adrian's Priory during the Middle Ages.

Hydrobiology is the science of life and life processes in water. Much of modern hydrobiology can be viewed as a sub-discipline of ecology but the sphere of hydrobiology includes taxonomy, economic and industrial biology, morphology, and physiology. The one distinguishing aspect is that all fields relate to aquatic organisms. Most work is related to limnology and can be divided into lotic system ecology and lentic system ecology.

The Scottish Seabird Centre is a marine conservation and education charity, that is supported by an award-winning visitor attraction in North Berwick, East Lothian, Scotland. Opened by the Duke of Rothesay in 2000 and funded by the Millennium Commission. The showpiece of the centre is the interactive live cameras out to the wildlife on the Firth of Forth islands, including Bass Rock, Isle of May, Fidra and Craigleith. The Bass Rock is the world's largest colony of Northern gannets with an estimated 150,000 birds present.

Marine ecosystems are the largest of Earth's aquatic ecosystems and exist in waters that have a high salt content. These systems contrast with freshwater ecosystems, which have a lower salt content. Marine waters cover more than 70% of the surface of the Earth and account for more than 97% of Earth's water supply and 90% of habitable space on Earth. Seawater has an average salinity of 35 parts per thousand of water. Actual salinity varies among different marine ecosystems. Marine ecosystems can be divided into many zones depending upon water depth and shoreline features. The oceanic zone is the vast open part of the ocean where animals such as whales, sharks, and tuna live. The benthic zone consists of substrates below water where many invertebrates live. The intertidal zone is the area between high and low tides. Other near-shore (neritic) zones can include mudflats, seagrass meadows, mangroves, rocky intertidal systems, salt marshes, coral reefs, lagoons. In the deep water, hydrothermal vents may occur where chemosynthetic sulfur bacteria form the base of the food web.

The South African Institute for Aquatic Biodiversity (SAIAB), is involved in research, education and in applications of its knowledge and research to African fish fauna, for either economic or conservation benefit.
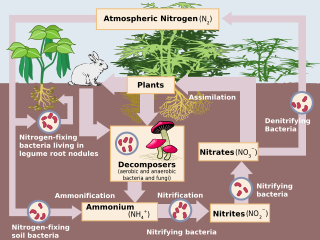
Human impact on the nitrogen cycle is diverse. Agricultural and industrial nitrogen (N) inputs to the environment currently exceed inputs from natural N fixation. As a consequence of anthropogenic inputs, the global nitrogen cycle (Fig. 1) has been significantly altered over the past century. Global atmospheric nitrous oxide (N2O) mole fractions have increased from a pre-industrial value of ~270 nmol/mol to ~319 nmol/mol in 2005. Human activities account for over one-third of N2O emissions, most of which are due to the agricultural sector. This article is intended to give a brief review of the history of anthropogenic N inputs, and reported impacts of nitrogen inputs on selected terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems.

A wild fishery is a natural body of water with a sizeable free-ranging fish or other aquatic animal population that can be harvested for its commercial value. Wild fisheries can be marine (saltwater) or lacustrine/riverine (freshwater), and rely heavily on the carrying capacity of the local aquatic ecosystem.

Loch Enoch is a multi-basin freshwater loch in Galloway, to the east of Merrick and south of Mullwharchar. The loch is situated in a granite basin and has several small islands and some beaches on its shore. The sharp granite sand of these beaches was collected and sold for sharpening knives and scythes. The catchment area's vegetation is mainly Purple Moor Grass and Heather.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to fishing:

Sir Ian Lamont Boyd, is a Scottish zoologist, environmental and polar scientist, former Chief Scientific Adviser at the Department for Environment, Food and Rural Affairs (DEFRA) and is a professor of biology at the University of St Andrews. He is Chair of the UK Research Integrity Office and President of the Royal Society of Biology.
Peter Mitchell Grant is Senior Honorary Professorial Fellow, former Regius Professor of Engineering and Head of School of Engineering and Electronics at the University of Edinburgh. In 2004 he was awarded the 82nd Faraday Medal by the Institute of Electrical Engineers for his 'outstanding contributions to signal processing'.
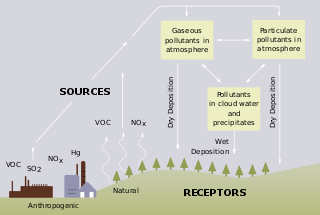
Freshwater acidification occurs when acidic inputs enter a body of fresh water through the weathering of rocks, invasion of acidifying gas, or by the reduction of acid anions, like sulfate and nitrate within a lake, pond, or reservoir. Freshwater acidification is primarily caused by sulfur oxides (SOx) and nitrogen oxides (NOx) entering the water from atmospheric depositions and soil leaching. Carbonic acid and dissolved carbon dioxide can also enter freshwaters, in a similar manner associated with runoff, through carbon dioxide-rich soils. Runoff that contains these compounds may incorporate acidifying hydrogen ions and inorganic aluminum, which can be toxic to marine organisms. Acid rain also contributes to freshwater acidification. A well-documented case of freshwater acidification in the Adirondack Lakes, New York, emerged in the 1970s, driven by acid rain from industrial sulfur dioxide (SO₂) and nitrogen oxide (NOₓ) emissions.

A marine food web is a food web of marine life. At the base of the ocean food web are single-celled algae and other plant-like organisms known as phytoplankton. The second trophic level is occupied by zooplankton which feed off the phytoplankton. Higher order consumers complete the web. There has been increasing recognition in recent years that marine microorganisms.

Human activities affect marine life and marine habitats through overfishing, habitat loss, the introduction of invasive species, ocean pollution, ocean acidification and ocean warming. These impact marine ecosystems and food webs and may result in consequences as yet unrecognised for the biodiversity and continuation of marine life forms.
References
- 1 2 3 4 "John Baxter". Heriot-Watt University. 2015. Retrieved 9 July 2015.
- ↑ "Editorial Board". Aquatic Conservation: Marine and Freshwater Ecosystems . 2015. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.454.6470 . doi:10.1002/(ISSN)1099-0755 . Retrieved 9 July 2015.
- 1 2 "John Baxter" (PDF). Ocean Acidification - International Reference User Group. 2 December 2013. p. 21. Retrieved 9 July 2015.
- ↑ "John Baxter". Scottish Seabird Centre. 2015. Archived from the original on 10 July 2015. Retrieved 9 July 2015.
- ↑ John Baxter publications indexed by Microsoft Academic
- ↑ "John M Baxter". University of St Andrews. 2014. Retrieved 9 July 2015.