Related Research Articles

The centromere links a pair of sister chromatids together during cell division. This constricted region of chromosome connects the sister chromatids, creating a short arm (p) and a long arm (q) on the chromatids. During mitosis, spindle fibers attach to the centromere via the kinetochore.
Molecular biology is a branch of biology that seeks to understand the molecular basis of biological activity in and between cells, including biomolecular synthesis, modification, mechanisms, and interactions.

Schizosaccharomyces pombe, also called "fission yeast", is a species of yeast used in traditional brewing and as a model organism in molecular and cell biology. It is a unicellular eukaryote, whose cells are rod-shaped. Cells typically measure 3 to 4 micrometres in diameter and 7 to 14 micrometres in length. Its genome, which is approximately 14.1 million base pairs, is estimated to contain 4,970 protein-coding genes and at least 450 non-coding RNAs.

Yeast artificial chromosomes (YACs) are genetically engineered chromosomes derived from the DNA of the yeast, Saccharomyces cerevisiae, which is then ligated into a bacterial plasmid. By inserting large fragments of DNA, from 100–1000 kb, the inserted sequences can be cloned and physically mapped using a process called chromosome walking. This is the process that was initially used for the Human Genome Project, however due to stability issues, YACs were abandoned for the use of bacterial artificial chromosome

In molecular biology, a library is a collection of genetic material fragments that are stored and propagated in a population of microbes through the process of molecular cloning. There are different types of DNA libraries, including cDNA libraries, genomic libraries and randomized mutant libraries. DNA library technology is a mainstay of current molecular biology, genetic engineering, and protein engineering, and the applications of these libraries depend on the source of the original DNA fragments. There are differences in the cloning vectors and techniques used in library preparation, but in general each DNA fragment is uniquely inserted into a cloning vector and the pool of recombinant DNA molecules is then transferred into a population of bacteria or yeast such that each organism contains on average one construct. As the population of organisms is grown in culture, the DNA molecules contained within them are copied and propagated.
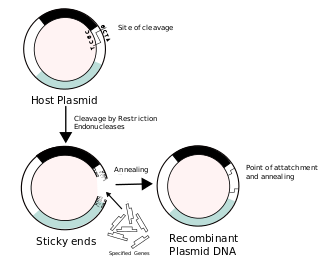
Recombinant DNA (rDNA) molecules are DNA molecules formed by laboratory methods of genetic recombination that bring together genetic material from multiple sources, creating sequences that would not otherwise be found in the genome.
Tom Maniatis, is an American professor of molecular and cellular biology. He is a professor at Columbia University, and serves as the Scientific Director and CEO of the New York Genome Center.

Kim Ashley Nasmyth is an English geneticist, the Whitley Professor of Biochemistry at the University of Oxford, a Fellow of Trinity College, Oxford, former scientific director of the Research Institute of Molecular Pathology (IMP), and former head of the Department of Biochemistry, University of Oxford. He is best known for his work on the segregation of chromosomes during cell division.
A genomic library is a collection of overlapping DNA fragments that together make up the total genomic DNA of a single organism. The DNA is stored in a population of identical vectors, each containing a different insert of DNA. In order to construct a genomic library, the organism's DNA is extracted from cells and then digested with a restriction enzyme to cut the DNA into fragments of a specific size. The fragments are then inserted into the vector using DNA ligase. Next, the vector DNA can be taken up by a host organism - commonly a population of Escherichia coli or yeast - with each cell containing only one vector molecule. Using a host cell to carry the vector allows for easy amplification and retrieval of specific clones from the library for analysis.
Jeffrey Lynn Bennetzen is an American geneticist on the faculty of the University of Georgia (UGA). Bennetzen is known for his work describing codon usage bias in yeast, and E. coli; being the first to clone and sequence an active transposon in plants, discovering that most of the DNA in plant genomes was a particular class of mobile DNA (LTR-retrotransposons); solving the C-value paradox; proposing sorghum and Setaria as model grasses; showing that rice centromeres were hotspots for recombination, but not crossovers; and developing a technique to date polyploidization events. He is an author, with Sarah Hake of the book "Handbook of Maize." Bennetzen was elected to the US National Academy of Sciences in 2004.

Joachim Wilhelm "Jo" Messing was a German-American biologist who was a professor of molecular biology and the fourth director of the Waksman Institute of Microbiology at Rutgers University.
The history of genetics can be represented on a timeline of events from the earliest work in the 1850s, to the DNA era starting in the 1940s, and the genomics era beginning in the 1970s.

Bruce William Stillman is a biochemist and cancer researcher who has served as the Director of Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory (CSHL) since 1994 and President since 2003. He also served as the Director of its NCI-designated Cancer Center for 25 years from 1992 to 2016. During his leadership, CSHL has been ranked as the No. 1 institution in molecular biology and genetics research by Thomson Reuters. Stillman's research focuses on how chromosomes are duplicated in human cells and in yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae; the mechanisms that ensure accurate inheritance of genetic material from one generation to the next; and how missteps in this process lead to cancer. For his accomplishments, Stillman has received numerous awards, including the Alfred P. Sloan, Jr. Prize in 2004 and the 2010 Louisa Gross Horwitz Prize, both of which he shared with Thomas J. Kelly of Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center, as well as the 2019 Canada Gairdner International Award for biomedical research, which he shared with John Diffley.
Junhyong Kim is the Edmund J. and Louise W. Kahn Term Endowed Professor of Biology at the University of Pennsylvania and the author of over eighty published scientific papers.

Roger Brent is an American biologist known for his work on gene regulation and systems biology. He studies the quantitative behaviors of cell signaling systems and the origins and consequences of variation in them. He is Full Member in the Division of Basic Sciences at the Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center and an Affiliate Professor of Genome Sciences at the University of Washington.
Synthetic genome is a synthetically built genome whose formation involves either genetic modification on pre-existing life forms or artificial gene synthesis to create new DNA or entire lifeforms. The field that studies synthetic genomes is called synthetic genomics.
William Charles Earnshaw is an American biologist who is Professor of Chromosome Dynamics at the University of Edinburgh, where he has been a Wellcome Trust Principal Research Fellow since 1996.

Kaustuv Sanyal is an Indian molecular biologist, mycologist and Director of Bose Institute in Kolkata. He is a professor at the Molecular Biology and Genetics Unit of the Jawaharlal Nehru Centre for Advanced Scientific Research (JNCASR). He is known for his molecular and genetic studies of pathogenic yeasts such as Candida and Cryptococcus). An alumnus of Bidhan Chandra Krishi Viswavidyalaya and Madurai Kamaraj University from where he earned a BSc in agriculture and MSc in biotechnology respectively, Sanyal did his doctoral studies at Bose Institute to secure a PhD in Yeast genetics. He moved to the University of California, Santa Barbara, USA to work in the laboratory of John Carbon on the discovery of centromeres in Candida albicans. He joined JNCASR in 2005. He is a member of the Faculty of 1000 in the disciplines of Microbial Evolution and Genomics and has delivered invited speeches which include the Gordon Research Conference, EMBO conferences on comparative genomics and kinetochores. The Department of Biotechnology of the Government of India awarded him the National Bioscience Award for Career Development, one of the highest Indian science awards, for his contributions to biosciences, in 2012. He has also been awarded with the prestigious Tata Innovation Fellowship in 2017. The National Academy of Sciences, India elected him as a fellow in 2014. He is also an elected fellow of Indian Academy of Sciences (2017), and the Indian National Science Academy (2018). In 2019, he has been elected to Fellowship in the American Academy of Microbiology (AAM), the honorific leadership group within the American Society for Microbiology. He was awarded the J.C. Bose National Fellowship in 2020.

Tim J. Yen is an American molecular biologist and cancer biologist. Yen held the rank of Professor and in 2023, became Emeritus at Fox Chase Cancer Center in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. Yen is known for pioneering work in the field of mitosis.
Teresa Shu-Fong Wang is an American biochemist. She is a professor emeritus at Stanford University, and the K. Bensch Endowed Chair Professor in Experimental Pathology of Department of Pathology at the Stanford University School of Medicine. Her scientific pursuit focuses on the biochemical mechanisms of chromosome replication proteins, and molecular mechanisms of their involvement in maintaining genome integrity during chromosome replication.
References
- ↑ Bloom, K. (29 April 2015). "Anniversary of the discovery/isolation of the yeast centromere by Clarke and Carbon". Molecular Biology of the Cell. 26 (9): 1575–1577. doi:10.1091/mbc.E14-11-1512. PMC 4436770 . PMID 25926702.
- ↑ Clarke, Louise; Carbon, John (September 1976). "A colony bank containing synthetic CoI EI hybrid plasmids representative of the entire E. coli genome". Cell. 9 (1): 91–99. doi:10.1016/0092-8674(76)90055-6. PMID 788919. S2CID 2535372.