
Biomedical engineering (BME) or medical engineering is the application of engineering principles and design concepts to medicine and biology for healthcare applications. BME is also traditionally logical sciences to advance health care treatment, including diagnosis, monitoring, and therapy. Also included under the scope of a biomedical engineer is the management of current medical equipment in hospitals while adhering to relevant industry standards. This involves procurement, routine testing, preventive maintenance, and making equipment recommendations, a role also known as a Biomedical Equipment Technician (BMET) or as a clinical engineer.

The Technion – Israel Institute of Technology is a public research university located in Haifa, Israel. Established in 1912 by Jews under the dominion of the Ottoman Empire, the Technion is the oldest university in the country.

Julia Elizabeth King, Baroness Brown of Cambridge, is a British engineer and a crossbench member of the House of Lords, where she chairs the Select Committee on Science and Technology. She is the incumbent chair of the Carbon Trust and the Henry Royce Institute, and was the vice-chancellor of Aston University from 2006 to 2016.

Dame Julia Stretton Higgins is a British polymer scientist. Since 1976, she has been based at the Department of Chemical Engineering at Imperial College London, where she is emeritus professor and senior research investigator.

The Academy of Medical Sciences is an organisation established in the UK in 1998. It is one of the four UK National Academies, the others being the British Academy, the Royal Academy of Engineering and the Royal Society.

Sushanta Kumar Bhattacharyya, Baron Bhattacharyya,, was a British-Indian engineer, educator and government advisor. In 1980, he became Professor of Manufacturing Systems at the University of Warwick and founded the Warwick Manufacturing Group. In 2004, he was made a life peer and became a member of the House of Lords.
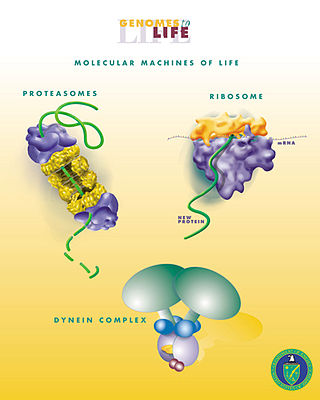
Biological engineering or bioengineering is the application of principles of biology and the tools of engineering to create usable, tangible, economically viable products. Biological engineering employs knowledge and expertise from a number of pure and applied sciences, such as mass and heat transfer, kinetics, biocatalysts, biomechanics, bioinformatics, separation and purification processes, bioreactor design, surface science, fluid mechanics, thermodynamics, and polymer science. It is used in the design of medical devices, diagnostic equipment, biocompatible materials, renewable energy, ecological engineering, agricultural engineering, process engineering and catalysis, and other areas that improve the living standards of societies.

The Institute of Physics and Engineering in Medicine (IPEM) is the United Kingdom's professional body and learned society for physicists, engineers and technologists within the field of medicine, founded in 1995, changing its name from the Institution of Physics and Engineering in Medicine and Biology (IPEMB) in 1997. The Institute is governed by an elected Board of Trustees reporting to which are the Science, Research and Innovation Council and the Professional and Standards Council. The councils have operational responsibility for scientific and professional aspects of the Institute's work, respectively. Beneath the councils is a substructure of committees, groups and panels of members, which undertake the work of the Institute.

The Department of Engineering Science is the engineering department of the University of Oxford. It is part of the university's Mathematical, Physical and Life Sciences Division. The department was ranked third best institute in the UK for engineering in the 2021 Research Excellence Framework.

The Tokyo University of Agriculture and Technology commonly known as TUAT is a national university headquartered in Fuchū, Tokyo, Japan. The university consists of two faculties that provide courses in agriculture and engineering.
Dame Lynn Faith Gladden is the Shell Professor of Chemical Engineering at the University of Cambridge. She served as Pro-vice-chancellor for research from 2010 to 2016.
The UCL Faculty of Engineering Sciences is one of the 11 constituent faculties of University College London (UCL). The Faculty, the UCL Faculty of Mathematical and Physical Sciences and the UCL Faculty of the Built Envirornment together form the UCL School of the Built Environment, Engineering and Mathematical and Physical Sciences.

Anne Neville was the Royal Academy of Engineering Chair in emerging technologies and Professor of Tribology and Surface Engineering at the University of Leeds.
Hashem Rafii-Tabar is a British-Iranian professor and scientist within computational physics and nanoscience. He is primarily known for his contribution to the computational physics of nanostructures with important applications such as Carbon Nanotubes.
Eileen Ingham is a multidisciplinary scientist specialising in biochemistry, microbiology, clinical immunology and pathogenesis. She is most recognized for her work and contribution to biocompatibility in medical implants. She is currently a professor at the University of Leeds as of 2016 when she was elected as Professor for Medical Immunology.

Ronald A. Roy is an American engineer, physicist, and academic, who is an expert in physical acoustics and its applications to ultrasonics, biomedical acoustics, acousto-optics, cavitation, and bubble swarm acoustics.
Catherine Jane Noakes is a British mechanical engineer who is Professor of Environmental Engineering for Buildings at the University of Leeds. Noakes specialises in airborne infections and the transport of airborne pathogens. During the COVID-19 pandemic, Noakes served on the Government of the United Kingdom Scientific Advisory Group for Emergencies (SAGE).

Susan Andrea Bernal López is a Colombian materials scientist who is Professor of Structural Materials at the University of Leeds. Her research considers design, development and characterisation of novel cements. She was awarded the 2020 Institute of Materials, Minerals and Mining Rosenhain Medal and Prize.
Pavlos P. Vlachos is a Greek-American engineer, scientist, academic, and entrepreneur. He is professor in Purdue’s School of Mechanical Engineering and in the Weldon School of Biomedical Engineering, and the St. Vincent Health Professor of Healthcare Engineering. He serves as the Director for the Purdue Regenstrief Center for Healthcare Engineering (RCHE).













