Related Research Articles

A mass driver or electromagnetic catapult is a proposed method of non-rocket spacelaunch which would use a linear motor to accelerate and catapult payloads up to high speeds. Existing and proposed mass drivers use coils of wire energized by electricity to make electromagnets, though a rotary mass driver has also been proposed. Sequential firing of a row of electromagnets accelerates the payload along a path. After leaving the path, the payload continues to move due to momentum.

A railgun or rail gun is a linear motor device, typically designed as a weapon, that uses electromagnetic force to launch high-velocity projectiles. The projectile normally does not contain explosives, instead relying on the projectile's high kinetic energy to inflict damage. The railgun uses a pair of parallel conductors (rails), along which a sliding armature is accelerated by the electromagnetic effects of a current that flows down one rail, into the armature and then back along the other rail. It is based on principles similar to those of the homopolar motor.
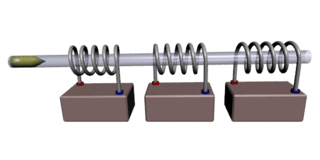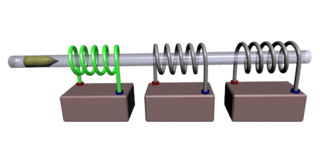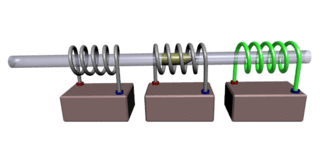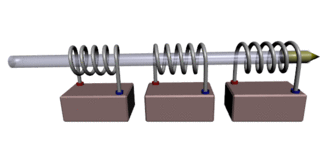
A coilgun is a type of mass driver consisting of one or more coils used as electromagnets in the configuration of a linear motor that accelerate a ferromagnetic or conducting projectile to high velocity. In almost all coilgun configurations, the coils and the gun barrel are arranged on a common axis. A coilgun is not a rifle as the barrel is smoothbore.
Francis Bitter was an American physicist.
Electromagnetic propulsion (EMP) is the principle of accelerating an object by the utilization of a flowing electrical current and magnetic fields. The electrical current is used to either create an opposing magnetic field, or to charge a field, which can then be repelled. When a current flows through a conductor in a magnetic field, an electromagnetic force known as a Lorentz force, pushes the conductor in a direction perpendicular to the conductor and the magnetic field. This repulsing force is what causes propulsion in a system designed to take advantage of the phenomenon. The term electromagnetic propulsion (EMP) can be described by its individual components: electromagnetic – using electricity to create a magnetic field, and propulsion – the process of propelling something. When a fluid is employed as the moving conductor, the propulsion may be termed magnetohydrodynamic drive. One key difference between EMP and propulsion achieved by electric motors is that the electrical energy used for EMP is not used to produce rotational energy for motion; though both use magnetic fields and a flowing electrical current.
Ames National Laboratory, formerly Ames Laboratory, is a United States Department of Energy national laboratory located in Ames, Iowa, and affiliated with Iowa State University. It is a top-level national laboratory for research on national security, energy, and the environment. The laboratory conducts research into areas of national concern, including the synthesis and study of new materials, energy resources, high-speed computer design, and environmental cleanup and restoration. It is located on the campus of Iowa State University.

Sir Richard Henry Friend is a British physicist who was the Cavendish Professor of Physics at the University of Cambridge from 1995 until 2020 and is Tan Chin Tuan Centennial Professor at the National University of Singapore. Friend's research concerns the physics and engineering of carbon-based semiconductors. He also serves as Chairman of the Scientific Advisory Board of the National Research Foundation (NRF) of Singapore.
Stuart Stephen Papworth Parkin is an experimental physicist, Managing Director at the Max Planck Institute of Microstructure Physics in Halle and an Alexander von Humboldt Professor at the Institute of Physics of the Martin-Luther-University Halle-Wittenberg.

Rajagopala Chidambaram is an Indian Physicist who is known for his integral role in India's nuclear weapons program; he coordinated test preparation for the Pokhran-I (1975) and Pokhran-II (1998).

The Electro-Magnetic Laboratory Rail Gun is a 32-megajoule electro-magnetic laboratory rail gun being evaluated by the US Office of Naval Research (ONR) Naval Air Warfare and Weapons Department. The US Navy is pursuing development of the launcher system through two industry teams – General Atomics and BAE Systems – to reduce risk in the program and to foster innovation in next-generation shipboard weapons. The same amount of energy is released by the detonation of 4.8 kg (11 lb) of C4.

The Swiss Electromagnetics Research and Engineering Centre (SEREC) is the sole organization for handling electromagnetic research and concerns in Switzerland.
Akhlesh Lakhtakia is Evan Pugh University Professor and Charles Godfrey Binder Professor of engineering science and mechanics at the Pennsylvania State University. His research focuses on electromagnetic fields in complex materials, such as sculptured thin films, chiral materials, bianisotropy and industrially scalable bioreplication, an emerging form of engineered biomimicry applied to harvesting of solar energy and pest eradication. His technique for visualization of latent fingerprints was covered in the NOVA documentary series "Forensics on Trial".

The history of metamaterials begins with artificial dielectrics in microwave engineering as it developed just after World War II. Yet, there are seminal explorations of artificial materials for manipulating electromagnetic waves at the end of the 19th century. Hence, the history of metamaterials is essentially a history of developing certain types of manufactured materials, which interact at radio frequency, microwave, and later optical frequencies.

George Albert Sawatzky is a Canadian physicist, known for his research in solid state physics and strongly correlated electron systems. He has co-developed the Cini-Sawatzky theory of the Auger effect and the ZSA (Zaanen-Sawatzky-Allen) classification of bandgaps in solids.
Bhakta B. Rath is an Indian American material physicist and head of the Materials Science and Component Technology of the United States Naval Research Laboratory (NRL), the corporate research laboratory for the United States Navy and the United States Marine Corps. He is the chief administrative officer for program planning, interdisciplinary coordination, supervision and control of research and is the associate director of research for Materials Science and Component Technology at NRL.

Kasturi Lal Chopra was an Indian materials physicist and a former director of the Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur. He was the founder of the Thin Film Laboratory at Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi and the Microscience Laboratory at IIT, Kharagpur and held several US and Indian patents for his research findings. Author of a number of books on thin film technology, he was a recipient of Shanti Swarup Bhatnagar Prize, the highest Indian award in the science and technology categories. The Government of India awarded him the fourth highest civilian honour of the Padma Shri, in 2008, for his contributions to science and engineering.
Morris Tanenbaum was an American physical chemist and executive who worked at Bell Laboratories and AT&T Corporation.
Ma Weiming is a Chinese electrical engineer. He is a professor of the PLA Naval University of Engineering. He is an academician of the Chinese Academy of Engineering and holds the military rank of rear admiral. He led the development of the electromagnetic catapult system for the Type 003 aircraft carrier and the development of electromagnetic railguns. In 2017, he was awarded the Order of August First, the highest honour of the People's Liberation Army.

James "Jim" U. Lemke was an American physicist and entrepreneur who lived in San Diego. He developed magnetic recording and internal combustion engine technologies.

Subrata Roy is an Indian-born American inventor, educator, and scientist known for his work in plasma-based flow control and plasma-based self-sterilizing technology. He is a professor of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering at the University of Florida and the founding director of the Applied Physics Research Group at the University of Florida.
References
- ↑ Bischoff, Laura (November 3, 1999), "Kettering, Ohio, Firm Develops Cutting-Edge Metal-Making Processes", Knight-Ridder .
- ↑ Gaffney, Timothy R. (July 12, 2006), "Kettering company developing electromagnetic cannon for Navy", Dayton Daily News .
- ↑ IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, January 1989, p. 7.