The University of Georgia is a public land-grant research university with its main campus in Athens, Georgia. Chartered in 1785, it is one of the oldest public universities in the United States. It is the flagship school of the University System of Georgia.

Georgia State University is a public research university in Atlanta, Georgia. Founded in 1913, it is one of the University System of Georgia's four research universities. It is also the largest institution of higher education by enrollment based in Georgia and is in the top 10 in the nation in number of students with a diverse majority-minority student population of around 54,000 students, including approximately 33,000 undergraduate and graduate students at the main campus downtown.

Clark Atlanta University is a private, Methodist, historically black research university in Atlanta, Georgia. Clark Atlanta is the first Historically Black College or University (HBCU) in the Southern United States. Founded on September 19, 1865 as Atlanta University, it consolidated with Clark College to form Clark Atlanta University in 1988. It is classified among "R2: Doctoral Universities – High research activity".

Robert Arthur Morton Stern, usually credited as Robert A. M. Stern, is a New York City–based architect, educator, and author. He is the founding partner of the architecture firm, Robert A.M. Stern Architects, also known as RAMSA. From 1998 to 2016, he was the Dean of the Yale School of Architecture.

The architecture of Atlanta is marked by a confluence of classical, modernist, post-modernist, and contemporary architectural styles. Due to the Battle of Atlanta and the subsequent fire in 1864, the city's architecture retains almost no traces of its Antebellum past. Instead, Atlanta's status as a largely post-modern American city is reflected in its architecture, as the city has often been the earliest, if not the first, to showcase new architectural concepts. However, Atlanta's embrace of modernism has translated into an ambivalence toward architectural preservation, resulting in the destruction of architectural masterpieces, including the Commercial-style Equitable Building, the Beaux-Arts style Terminal Station, and the Classical Carnegie Library. The city's cultural icon, the Neo-Moorish Fox Theatre, would have met the same fate had it not been for a grassroots effort to save it in the mid-1970s.

Joseph Neel Reid, also referred to as Neel Reid, was a prominent architect in Atlanta, Georgia, in the early 20th century as a partner in his firm Hentz, Reid and Adler.
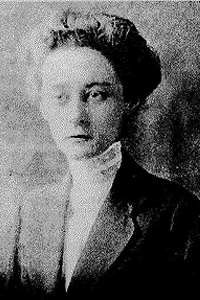
Leila Ross Wilburn (1885–1967) was an early 20th-century architect, one of the first women in Georgia to enter that profession.

The Andrew Young School of Policy Studies at Georgia State University houses the Criminal Justice & Criminology, Economics, School of Social Work, Urban Studies and Public Management & Policy departments. Georgia State University is the largest university in the state of Georgia.

The Georgia Institute of Technology is a public research university and institute of technology in Atlanta, Georgia. Established in 1885, it is part of the University System of Georgia and has satellite campuses in Savannah, Georgia; Metz, France; Shenzhen, China; and Singapore.

Albert Randolph Ross was an American architect. Born in Westfield, Massachusetts, he was a son of architect John W. Ross.

Bruce & Morgan was an American architectural firm based in Atlanta. It was established in 1882 as the partnership of architects Alexander Campbell Bruce (1835-1927) and Thomas Henry Morgan (1857-1940).

Walter T. Downing (1865-1918) was an American architect in Atlanta, Georgia. Several of his works are listed on the National Register of Historic Places.

Morgan & Dillon was a major architectural firm of Atlanta, Georgia, USA. It later became Morgan, Dillon & Lewis.
African-American architects are those in the architectural profession who are members of the African diaspora in the United States.

The architecture of Jacksonville is a combination of historic and modern styles reflecting the city's early position as a regional center of business. According to the National Trust for Historic Preservation, there are more buildings built before 1967 in Jacksonville than any other city in Florida, though few structures in the city center predate the Great Fire of 1901. Numerous buildings in the city have held state height records, dating as far back as 1902, and last holding a record in 1981.

Ellamae Ellis League, was an American architect, the fourth woman registered architect in Georgia and "one of Georgia and the South's most prominent female architects." She practiced for over 50 years, 41 of them from her own firm. From a family of architects, she was the first woman elected a Fellow of the American Institute of Architects (FAIA) in Georgia and only the eighth woman nationwide. Several buildings she designed are listed on the National Register of Historic Places (NRHP). In 2016 she was posthumously named a Georgia Woman of Achievement.

The Carnegie Building is a historic building located at 141 Carnegie Way in downtown Atlanta, Georgia, United States. Built in 1925 as the Wynne-Claughton Building, the 12-story building was designed by architect G. Lloyd Preacher. It was designated an Atlanta Historic Building in 1990 and was added to the National Register of Historic Places in 2012.

All Saints' Episcopal Church is an Episcopal church in Atlanta, Georgia. The church was founded in 1903, with the current building constructed in 1906.
Abraham Thomas Bradbury was an American architect best known for his work in Atlanta during the mid-1900s. During this time, he designed many buildings for the government of Georgia around the Georgia State Capitol. His most famous work is arguably the Georgia Governor's Mansion, located in the Buckhead district of the city. While many of his works tended to be in the modernist style, the mansion is a noted example of Greek Revival architecture in Georgia. According to the New Georgia Encyclopedia, he was "perhaps the most prominent architect of government buildings in the mid-twentieth century".

William Henry Parkins was an American architect best known for his work in Atlanta during the late 1800s.