Related Research Articles

Apollonius of Tyana was a first-century Greek philosopher and religious leader from the town of Tyana, Cappadocia in Roman Anatolia, who spent his life travelling and teaching in the Middle East, North Africa and (allegedly) India. He is a central figure in Neopythagoreanism and was one of the most famous "miracle workers" of his day.
The Lesser Key of Solomon, also known by its Latin title Lemegeton Clavicula Salomonis or simply the Lemegeton, is an anonymously authored grimoire on sorcery. It was compiled in the mid-17th century, mostly from materials several centuries older. It is divided into five books: the Ars Goetia, Ars Theurgia-Goetia, Ars Paulina, Ars Almadel, and Ars Notoria. It is based on the Testament of Solomon and the ring mentioned within it that he used to seal demons.

Enochian magic is a system of Renaissance magic developed by John Dee and Edward Kelley and adopted by more modern practitioners. The origins of this esoteric tradition are rooted in documented collaborations between Dee and Kelley, encompassing the revelation of the Enochian language and script, which Dee wrote were delivered to them directly by various angels during their mystical interactions. Central to the practice is the invocation and command of various spiritual beings.

Vincent of Beauvais was a Dominican friar at the Cistercian monastery of Royaumont Abbey, France. He is known mostly for his Speculum Maius, a major work of compilation that was widely read in the Middle Ages. Often retroactively described as an encyclopedia or as a florilegium, his text exists as a core example of brief compendiums produced in medieval Europe.

The Schola Medica Salernitana was a medieval medical school, the first and most important of its kind. Situated on the Tyrrhenian Sea in the south Italian city of Salerno, it was founded in the 9th century and rose to prominence in the 10th century, becoming the most important source of medical knowledge in Western Europe at the time.
The Sworn Book of Honorius is a medieval grimoire purportedly written by Honorius of Thebes. The Latin word juratus, which is typically translated "sworn", is intended to mean "oathbound". It was allegedly the grimoire of Pope Honorius I, hence its name.
Sex magic is any type of sexual activity used in magical, ritualistic or otherwise religious and spiritual pursuits. One practice of sex magic is using sexual arousal or orgasm with visualization of a desired result. A premise posited by sex magicians is the concept that sexual energy is a potent force that can be harnessed to transcend one's normally perceived reality.

Sefer Raziel HaMalakh is a grimoire of Practical Kabbalah from the Middle Ages written primarily in Hebrew and Aramaic. Liber Razielis Archangeli, its 13th-century Latin translation produced under Alfonso X of Castile, survives.

Catherine of Bologna [Caterina de' Vigri] was an Italian Poor Clare, writer, teacher, mystic, artist, and saint. The patron saint of artists and against temptations, Catherine de' Vigri was venerated for nearly three centuries in her native Bologna before being formally canonized in 1712 by Pope Clement XI. Her feast day is 9 March.

Revelations of Divine Love is a medieval book of Christian mystical devotions. Containing 87 chapters, the work was written between the 14th and 15th centuries by Julian of Norwich, about whom almost nothing is known. It is the earliest surviving example of a book in the English language known to have been written by a woman. It is also the earliest surviving work written by an English anchorite or anchoress.

Thomas of Cantimpré was a Flemish Catholic medieval writer, preacher, theologian and a friar belonging to the Dominican Order. He is best known for his encyclopedic work on nature De natura rerum, for the moral text Bonum universale de Apibus and for his hagiographical writings.
Shem HaMephorash, meaning "the explicit name," is originally a Tannaitic term describing the Tetragrammaton. In Kabbalah, it may refer to a name of God composed of either 4, 12, 22, 42, or 72 letters, the latter version being the most common.
The Glossa Ordinaria, which is Latin for "Ordinary [i.e. in a standard form] Gloss", is a collection of biblical commentaries in the form of glosses. The glosses are drawn mostly from the Church Fathers, but the text was arranged by scholars during the twelfth century. The Gloss is called "ordinary" to distinguish it from other gloss commentaries. In origin, it is not a single coherent work, but a collection of independent commentaries which were revised over time. The Glossa ordinaria was a standard reference work into the Early Modern period, although it was supplemented by the Postills attributed to Hugh of St Cher and the commentaries of Nicholas of Lyra.
The Medicina Plinii or Medical Pliny is an anonymous Latin compilation of medical remedies dating to the early 4th century AD. The excerptor, saying that he speaks from experience, offers the work as a compact resource for travelers in dealing with hucksters who sell worthless drugs at exorbitant prices or with know-nothings only interested in profit. The material is presented in three books in the conventional order a capite ad calcem, the first dealing with treatments pertaining to the head and throat, the second the torso and lower extremities, and the third systemic ailments, skin diseases, and poisons.
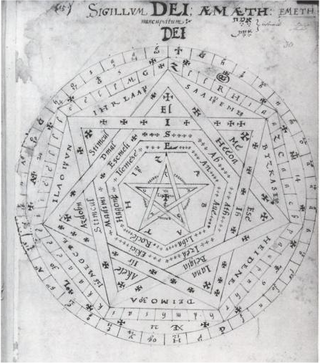
The Sigillum Dei is a magical diagram, composed of two circles, a pentagram, two heptagons, and one heptagram, and is labeled with the names of God and its angels. It is an angelic magic seal with the magical function that, according to one of the oldest sources, allowed a destined intended magician to have the power to possess the Spirit of God and when activated can become the 'Living' God; or The Lord God itself; amongst humanity and all creation itself, communicate with spirits as well as angels and archangels, control all elements, control every creature's holy spirit on the planet including the Spirit of God itself; all except for the Archangels, and to control light itself. The intended user also possesses the true benefic vision of God.

Agostino Paravicini Bagliani is an Italian historian, specializing in the history of the papacy, cultural anthropology, and in the history of the body and the relationship between nature and society during the Middle Ages.

Trota of Salerno was a medical practitioner and writer in the southern Italian coastal town of Salerno who lived in the early or middle decades of the 12th century. Her fame spread as far as France and England in the 12th and 13th centuries. A Latin text that gathered some of her therapies was incorporated into an ensemble of treatises on women's medicine that came to be known as the Trotula, "the little book [called] 'Trotula'". Gradually, readers became unaware that this was the work of three different authors. They were also unaware of name of the historical writer, which was "Trota" and not "Trotula". The latter was thenceforth misunderstood as the author of the whole compendium. These misconceptions about the author of Trotula contributed to the erasure or modification of her name, gender, level of education, medical knowledge, or the time period in which the texts were written; this trend often resulted from the biases of later scholars. Trota's authentic work was forgotten until it was rediscovered in the late 20th century.
Liber Officiorum Spirituum was a goetic grimoire and a major source for Johann Weyer's Pseudomonarchia Daemonum and the Ars Goetia. The original work has not been located, but some derived texts bearing the title have been found, some in the Sloane manuscripts, some in the Folger Shakespeare Library. Each version bears many similarities to each other and to the Pseudomonarchia Daemonum and the Ars Goetia, though they are far from identical.

Stephen Skinner is an Australian author, editor, publisher and lecturer. He is known for authoring books on magic, feng shui, sacred geometry and alchemy. He has published more than 46 books in more than 20 languages.
The Ars Notoria is a 13th-century Latin textbook of magic from Northern Italy. It claims to grant its practitioner an enhancement of their mental faculties, the ability to communicate with angels, and earthly and heavenly knowledge through ritual magic. The magical ritual that it describes expresses both religious orthodoxy and esoteric elements. These, besides its promise of a fast track to gaining knowledge rapidly, captivated young boys, university students, and clerics.
References
- ↑ For John's biography, see Watson's Introduction A, in Claire Fanger and Nicholas Watson, The Flowers of Heavenly Teaching (Toronto: Pontifical Institute Press, 2015)
- ↑ On the Ars notoria see Julien Véronèse, L'Ars notoria au Moyen Age. Introduction et édition critique (Florence: Sismel - Edizioni del Galluzzo, 2007).
- ↑ The Book of Visions was translated by Claire Fanger and Nicholas Watson in 2001 as "The Prologue of John of Morigny's Liber Visionum: Translation"
- ↑ See Claire Fanger, Rewriting Magic (University Park: Penn State University Press, 2015), chapter 4.
- ↑ Claire Fanger and Nicholas Watson, "The Prologue of John of Morigny's Liber Visionum: Introduction"
- ↑ "Manuscripts and manuscript catalogues with entries for Liber florum" (PDF).
- ↑ See Fanger's Introduction B in Fanger and Watson, eds., The Flowers of Heavenly Teaching.