Related Research Articles

The Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency (MHRA) is an executive agency of the Department of Health and Social Care in the United Kingdom which is responsible for ensuring that medicines and medical devices work and are acceptably safe.

KRMW is a radio station licensed to Cedarville, Arkansas, United States. It serves the Fayetteville/Fort Smith area. The station is owned by Cumulus Media.

Lateral flow tests (LFTs), also known as lateral flow immunochromatographic assays or rapid tests, are simple devices intended to detect the presence of a target substance in a liquid sample without the need for specialized and costly equipment. These tests are widely used in medical diagnostics for home testing, point of care testing, or laboratory use. For instance, the home pregnancy test is an LFT that detects a certain hormone. These tests are simple, economic and generally show results in around five to 30 minutes. Many lab-based applications increase the sensitivity of simple LFTs by employing additional dedicated equipment.
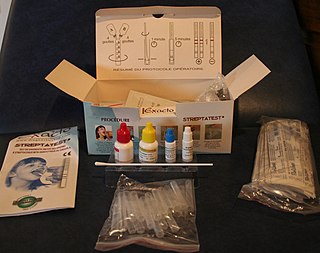
A rapid diagnostic test (RDT) is a medical diagnostic test that is quick and easy to perform. RDTs are suitable for preliminary or emergency medical screening and for use in medical facilities with limited resources. They also allow point-of-care testing in primary care for things that formerly only a laboratory test could measure. They provide same-day results within two hours, typically in approximately 20 minutes.

A rapid antigen test (RAT), or rapid test, is a rapid diagnostic test suitable for point-of-care testing that directly detects the presence or absence of an antigen. It is commonly used for the detection of SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19. Rapid tests are a type of lateral flow tests that detect protein, distinguishing it from other medical tests that detect antibodies or nucleic acid, of either laboratory or point-of-care types. Rapid tests generally give a result in 5 to 30 minutes, require minimal training or infrastructure, and have significant cost advantages.

COVID-19 testing involves analyzing samples to assess the current or past presence of SARS-CoV-2. The two main branches detect either the presence of the virus or of antibodies produced in response to infection. Molecular tests for viral presence through its molecular components are used to diagnose individual cases and to allow public health authorities to trace and contain outbreaks. Antibody tests instead show whether someone once had the disease. They are less useful for diagnosing current infections because antibodies may not develop for weeks after infection. It is used to assess disease prevalence, which aids the estimation of the infection fatality rate.

The COVID-19 pandemic in the United Kingdom is part of the worldwide pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2. The virus reached the UK in late January 2020. As of 24 March 2021, there have been 4.4 million cases confirmed and 127,543 deaths overall among people who had recently tested positive – the world's fourteenth-highest death rate by population and the highest death toll in Europe. There have been 152,919 deaths where the death certificate mentioned COVID by 7 May 2021. There has been some disparity between the outbreak's severity in each of the four countries. Health in the UK is devolved, with England, Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland each having their own publicly-funded healthcare systems and governments.

COVID-19 surveillance involves monitoring the spread of the coronavirus disease in order to establish the patterns of disease progression. The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends active surveillance, with focus of case finding, testing and contact tracing in all transmission scenarios. COVID-19 surveillance is expected to monitor epidemiological trends, rapidly detect new cases, and based on this information, provide epidemiological information to conduct risk assessment and guide disease preparedness.

NHS Test and Trace is a government-funded service in England, established in 2020 to track and help prevent the spread of COVID-19. It is part of the UK Health Security Agency; the service and the agency are headed by Jenny Harries.
Operation Moonshot is a UK government programme to introduce same day mass testing for COVID-19 in England as a way of enabling large gatherings of people to take place in that country while maintaining control over the virus. According to the British Medical Journal, the programme aims to deliver 10 million tests per day by 2021.
Abingdon Health is a British manufacturer of lateral flow assay diagnostic tests, sometimes called rapid tests, lateral flow immunoassays (LFIA), lateral flow tests (LFT) or quick tests. Since its formation in 2008, Abingdon Health has grown to become an organisation of over 200 people and has developed and manufactured lateral flow rapid tests across multiple industries.
The AbC-19 rapid antibody test is an immunological test for COVID-19 exposure developed by the UK Rapid Test Consortium and manufactured by Abingdon Health. It uses a lateral flow test to determine whether a person has IgG antibodies to the SARS-CoV-2 virus that causes COVID-19. The test uses a single drop of blood obtained from a finger prick and yields results in 20 minutes.
The UK Rapid Test Consortium (UK-RTC) is a United Kingdom industry consortium created to produce a lateral flow rapid test for COVID-19. Rapid tests are a form of COVID-19 testing technology that was originally developed from significant investment by the United Kingdom government to develop new forms of COVID-19 testing that provided advantages over existing forms such as PCR. Its members include Abingdon Health, BBI Solutions, CIGA Healthcare, Omega Diagnostics, and Oxford University.
CIGA Healthcare is a British manufacturer of lateral flow assay diagnostic tests. It is under contract to the British government for the supply of AbC-19 rapid antibody tests, a test for the presence of IgG antibody against the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein, as part of the UK Rapid Test Consortium program.
The following is a timeline of the COVID-19 pandemic in Northern Ireland during 2021. There are significant differences in the legislation and the reporting between the countries of the UK: England, Scotland, Northern Ireland, and Wales.

Denis Francis Kinane is a Scottish immunologist, cell biologist, infection, immunity and genomics specialist. He is the author of more than 250 papers with an H-index of 82, and editor of Nature and Springer journals. Kinane has held professorial appointments in pathology, periodontology, immunology, infection and immunity at medical and dental schools in the UK, USA and Switzerland. He is a director of two large US and Chinese health companies and Scientific Director, CMO and founder of several smaller international companies.
The National Advisory Committee on Immunization is an external advisory body that provides the Public Health Agency of Canada (PHAC) "with independent, ongoing and timely medical, scientific, and public health advice in response to questions from PHAC relating to immunization." It is composed of "experts in the fields of pediatrics, infectious diseases, immunology, pharmacy, nursing, epidemiology, pharmacoeconomics, social science and public health." The Committee "reports to the Vice-President of the Infectious Disease Prevention and Control Branch" of PHAC, and "works with staff of the Centre for Immunization and Respiratory Infectious Diseases" of the PHAC "to provide ongoing and timely medical, scientific and public health advice."
Shelley Deeks is a Canadian public health expert. She was appointed to the National Advisory Committee on Immunization. Her advertised "specialities include communicable disease control, outbreak investigations, vaccine safety, epidemiology and program evaluation." She is a fellow of the Royal College of Physicians of Canada and the Australian Faculty of Public Health Medicine.
Clair Deeks is a New Zealand anti-vaccine activist who has challenged the government's response to COVID-19. She was an unsuccessful Advance NZ candidate for the country's general election in 2020, and set up the group Voices for Freedom (VFF) which was involved in the distribution of pamphlets that have been criticised by experts as containing COVID-19 misinformation about vaccines, lockdown and the wearing of masks. As a food blogger, Deeks promoted the paleo diet and "healthy" lunchboxes for children and developed a petition to stop the rating system for foods used by the NZ and Australian governments. She is a former corporate lawyer.

COVID-19 rapid antigen tests, also frequently called COVID-19 lateral flow tests, are rapid antigen tests used to detect SARS-COV-2 infection (COVID-19). They are quick to implement with minimal training, offered significant cost advantages, costing a fraction of other forms of COVID-19 testing and give users a result within 5–30 minutes. However, they have a high false negative rate. Rapid antigen tests are used in several countries as part of mass testing or population-wide screening approaches. They are thought to be valuable for identifying individuals who are asymptomatic and could potentially spread the virus to other people, who would otherwise not know they were infected. This differs from other forms of COVID-19 testing, such as PCR, that are generally seen to be a useful test for symptomatic individuals, as they have a higher sensitivity and can more accurately identify cases.
References
- ↑ Burke, Maria (18 November 2020). "Scientists urge caution on use of lateral flow tests to screen for Covid-19". Chemistry World.
- ↑ Deeks, Jon; Raffle, Angela; Gill, Mike (12 January 2021). "Covid-19: government must urgently rethink lateral flow test roll out". The BMJ Opinion.