Related Research Articles
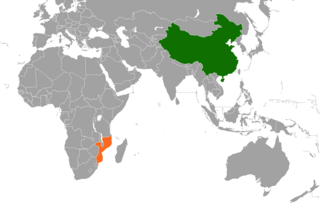
China–Mozambique relations date back to the 1960s, when China began to support the struggle of Mozambique's Marxist-oriented FRELIMO party against Portuguese colonialism. Diplomatic relations were formally established on 25 June 1975, soon after Mozambique gained independence from Portugal. In November 2006, Mozambique became the thirteenth African country to be added to China's official list of tourism destinations.
The China–Peru Free Trade Agreement is a bilateral free trade agreement designed to eliminate obstacles to trade and investment between China and Peru. The two sides concluded talks in November 2008 and signed the agreement in April 2009. The agreement was officially ratified by both countries governments on December 6, 2009, and came into effect on March 1, 2010.

Governmental relations between the People's Republic of China (PRC) and the Republic of Namibia were first established the day after Namibia's independence, but relations with Namibian independence movements date back to the 1960s.

Cape Verde–People's Republic of China relations refers to the current and historical relationship between the People's Republic of China and Cape Verde. The two states established bilateral relations on April 25, 1976, shortly after Cape Verde gained independence from the Portuguese Empire. Cape Verde is an adherent to PR China's One China Policy. In the mid-1990s, a number of Chinese capitalists began investing in the island nation and relations grew during the 2000s as a result.
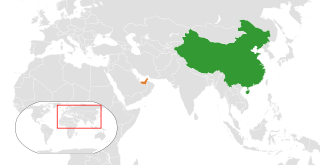
China – United Arab Emirates relations refer to the diplomatic relations between the People's Republic of China and the United Arab Emirates. Diplomatic ties were first established in 1984. The UAE maintains an embassy in Beijing and a consulate-general in Hong Kong while China has an embassy in Abu Dhabi and consulate-general in Dubai. The UAE and China have been strong international allies, with significant cooperation across economic, political and cultural aspects.

Bolivia–China relations are foreign relations between the Plurinational State of Bolivia and People's Republic of China. Relations between both nations officially began on July 9, 1985. Both nations are members of the United Nations.
Heriberto Araújo Rodríguez is a Spanish journalist and writer.

Juan José Omella y Omella is a Spanish prelate of the Roman Catholic Church. He has been serving as the archbishop of Barcelona since his installation on 26 December 2015 and as a cardinal since 28 June 2017. He was the president of the Episcopal Conference of Spain from 2020 to 2024. He previously served as auxiliary bishop of Zaragoza (1996-1999) and bishop of Barbastro-Monzón (1999–2004) and Calahorra y La Calzada-Logroño (2004-2015). He is a member of the Council of Cardinals.
Miguel Holguín y Figueroa, also written as Miguel Holguín de Figueroa, was a Spanish conquistador. He took part in the expeditions of conquest of the Chitarero, Motilon, U'wa and Lache peoples led by Nikolaus Federmann. Holguín y Figueroa later settled in Tunja, where he protested the rapacious activities of Hernán Pérez de Quesada, governor of Bogotá.
Bartolomé Camacho Zambrano was a Spanish conquistador who took part in the expedition of the Spanish conquest of the Muisca led by Gonzalo Jiménez de Quesada. He accompanied Gonzalo Suárez Rendón in the foundation of Tunja on August 6, 1539, and settled in the city. In 1583, Bartolomé Camacho Zambrano was mayor of Tunja together with Francisco de Avendaño.
Juan de Sanct Martín, also known as Juan de San Martín, was a Spanish conquistador. Little is known about De Sanct Martín, apart from a passage in El Carnero (1638) by Juan Rodríguez Freyle and Epítome de la conquista del Nuevo Reino de Granada, a work of uncertain authorship. He took part in the expedition from Santa Marta into the Eastern Ranges of the Colombian Andes led by Gonzalo Jiménez de Quesada and founded Cuítiva, Boyacá in 1550. Juan de Sanct Martín headed the left flank of the Spanish troops in the Battle of Tocarema against the Panche on August 20, 1538, while his fellow conquistador Juan de Céspedes commanded the right flank. In this battle, Juan de Sanct Martín killed the cacique of the Panche and was hurt himself. Juan de Sanct Martín had confronted the Panche the year before, when he was sent to the west while De Céspedes went south. Due to the resistance of the bellicose Panche, De Sanct Martín returned to the Spanish camp.

Ortún Velázquez de Velasco was a Spanish conquistador. He is known as the co-founder and first governor of Pamplona in the Norte de Santander department of Colombia, which borders Venezuela.

Juan Friede Alter was a Ukrainian-Colombian historian of Jewish descent who is recognised as one of the most important writers about Colombian history, the Spanish conquests and a proponent of indigenism; the defense of the rights and descriptions of the oppression of indigenous people.

Juan de(l) Junco was a Spanish conquistador who participated in the Spanish conquest of the Muisca people. Del Junco started his career as a conquistador in the 1526 expedition led by Sebastian Cabot exploring the Río de la Plata in present-day Argentina. In 1535, he arrived in Santa Marta on the Colombian Caribbean coast from where the expedition in search of El Dorado set off in April 1536.
Juan Tafur was a Spanish conquistador who participated in the Spanish conquest of the Muisca people. He was a cousin of fellow conquistadors Martín Yañéz Tafur, Hernán Venegas Carrillo and Pedro Fernández de Valenzuela. Juan Tafur was five times encomendero (mayor) of Santa Fe de Bogotá. He also received the encomiendas of Pasca, Chipaque and Usaquén. The encomienda of Suesca was shared between Tafur and Gonzalo García Zorro.
Gonzalo García Zorro was a Spanish conquistador who participated in the Spanish conquest of the Muisca people. García Zorro was encomendero (mayor) of Santa Fe de Bogotá for seven terms, and received the encomiendas of Fusagasugá and Fosca.
Antonio Díaz de Cardoso was a Portuguese conquistador who participated in the Spanish conquest of the Muisca people.

Juan de Albarracín was a Spanish conquistador who participated in the Spanish conquest of the Muisca and Panche people. He was captain of the brigs which sailed up the Magdalena River from the Caribbean coast in 1536 and later discovered the high quality salt that lead the Spanish conquistadors along the Camino de la Sal up the slopes of the eastern ranges of the Colombian Andes towards the Muisca Confederation.

Antonio de Lebrija (1507–1540) was a Spanish conquistador who participated in the Spanish conquest of the Muisca and the Chimila peoples. He was the treasurer of the conquest expedition which left Santa Marta in April 1536 following the high quality salt trail, the Camino de la Sal, along the Suárez River up the slopes of the Eastern Ranges of the Colombian Andes towards the Muisca Confederation.
References
- ↑ Bio of Juan P. Cardenal Archived 2013-12-03 at the Wayback Machine (in Spanish)
- ↑ "The Silent Chinese Conquest". Americas Quarterly . Retrieved 25 November 2013.
- ↑ La silenciosa conquista china