The federal judiciary of the United States is one of the three branches of the federal government of the United States organized under the United States Constitution and laws of the federal government. The U.S. federal judiciary consists primarily of the U.S. Supreme Court, the U.S. Courts of Appeals, and the U.S. District Courts. It also includes a variety of other lesser federal tribunals.
The judiciary of Australia comprises judges who sit in federal courts and courts of the States and Territories of Australia. The High Court of Australia sits at the apex of the Australian court hierarchy as the ultimate court of appeal on matters of both federal and State law.

The Supreme Court of Georgia is the highest judicial authority of the U.S. state of Georgia. The court was established in 1845 as a three-member panel, increased in number to six, then to seven in 1945, and finally to nine in 2017. Since 1896, the justices have been elected by the people of the state. The justices are currently elected in statewide non-partisan elections for six-year terms, with any vacancies filled through an appointment by the Governor.
The Superior Court is the state court in the U.S. state of New Jersey, with statewide trial and appellate jurisdiction. The New Jersey Constitution of 1947 establishes the power of the New Jersey courts: under Article Six of the State Constitution, "judicial power shall be vested in a Supreme Court, a Superior Court, and other courts of limited jurisdiction." The Superior Court has three divisions: the Law Division which is the main trial court for cases of civil or criminal law, the Chancery Division, which tries equity law cases, and the Appellate Division, which is the intermediate appellate court in New Jersey. "Appeals may be taken to the Appellate Division of the Superior Court from the law and chancery divisions of the Superior Court and in such other causes as may be provided by law." Each division of the Superior Court is divided into various Parts."

The judiciary of Pakistan is the national system of courts that maintains the law and order in the Islamic Republic of Pakistan. Pakistan uses a common law system, which was introduced during the colonial era, influenced by local medieval judicial systems based on religious and cultural practices. The Constitution of Pakistan lays down the fundamentals and working of the Pakistani judiciary.

The Judiciary of Ghana comprises the Superior Courts of Judicature, established under the 1992 Constitution, and the Inferior Courts, established by Parliament. The hierarchy of courts derives largely from British juridical forms. The courts have jurisdiction over all civil and criminal matters.

The Supreme Court of Guam is the highest judicial body of the United States territory of Guam. The Court hears all appeals from the Superior Court of Guam and exercises original jurisdiction only in cases where a certified question is submitted to it by a U.S. federal court, the Governor of Guam, or the Guam Legislature. The Supreme Court of Guam is the ultimate judicial authority on local matters. In the past, appeals of questions involving the U.S. Constitution or federal laws or treaties were heard by a three-judge appellate panel of the U.S. District Court of Guam, from which appeals could be further taken to the United States Court of Appeals for the Ninth Circuit, but this is no longer the case. Since 2006, the court's decisions have only been appealable to the Supreme Court of the United States, in line with the practice regarding the highest courts of the 50 states. The Court sits in the Monessa G. Lujan Memorial Courtroom, which is on the third floor of the Guam Judicial Center in Hagatna, Guam.

The state government of Georgia is the U.S. state governmental body established by the Georgia State Constitution. It is a republican form of government with three branches: the legislature, executive, and judiciary. Through a system of separation of powers or "checks and balances", each of these branches has some authority to act on its own, some authority to regulate the other two branches, and has some of its own authority, in turn, regulated by the other branches. The seat of government for Georgia is located in Atlanta.
The Judiciary of Colorado is established and authorized by Article VI of the Colorado Constitution as well as the law of Colorado. The various courts include the Colorado Supreme Court, Colorado Court of Appeals, Colorado district courts, Colorado county courts, Colorado water courts, and municipal courts. The administration of the state judicial system is the responsibility of the Chief Justice of the Colorado Supreme Court as its executive head and is assisted by several other commissions. In Denver, the county and municipal courts are integrated and administratively separate from the state court system.

The Oregon Judicial Department (OJD) is the judicial branch of government of the state of Oregon in the United States. The chief executive of the branch is the Chief Justice of the Oregon Supreme Court. Oregon’s judiciary consists primarily of four different courts: the Oregon Supreme Court, the Oregon Tax Court, the Oregon Court of Appeals, and the Oregon circuit courts. Additionally, the OJD includes the Council on Court Procedures, the Oregon State Bar, Commission on Judicial Fitness and Disability, and the Public Defense Services Commission. Employees of the court are the largest non-union group among state workers.

The judiciary of Colombia is a branch of the State of Colombia that interprets and applies the laws of Colombia, to ensure equal justice under law, and to provide a mechanism for dispute resolution. The judiciary comprises a hierarchical system of courts presided over by judges, magistrates and other adjudicators.
The Government of Guam (GovGuam) is a presidential representative democratic system, whereby the president is the head of state and the governor is head of government, and of a multi-party system. Guam is an organized, unincorporated territory of the United States with policy relations between Guam and the US under the jurisdiction of the Office of Insular Affairs.

The Connecticut Superior Court is the state trial court of general jurisdiction. It hears all matters other than those of original jurisdiction of the Probate Court, and hears appeals from the Probate Court. The Superior Court has 13 judicial districts which have at least one courthouse and one geographical area court. Civil cases, administrative appeals, family matters, and serious criminal offenses are generally heard in a judicial district courthouse. All criminal arraignments, misdemeanors, felonies, and motor vehicle violations that require a court appearance are heard in one of the 20 geographical area courts.
The Judiciary of Vermont is the state court system of Vermont, charged with Vermont law.
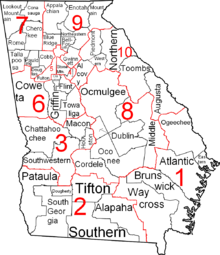
Courts of Georgia include:

The Judiciary of Spain consists of Courts and Tribunals, composed of judges and magistrates (Justices), who have the power to administer justice in the name of the King of Spain.

The judiciary of Jamaica is based on the judiciary of the United Kingdom. The courts are organized at four levels, with additional provision for appeal to the Judicial Committee of the Privy Council in London. The Court of Appeal is the highest appellate court. The Supreme Court has unlimited jurisdiction in all cases, and sits as the Circuit Court to try criminal cases. The Parish Court in each parish hears both criminal and civil cases, excluding grave offences. The Petty Sessions are held under Justices of the Peace, with power to hear minor crimes.
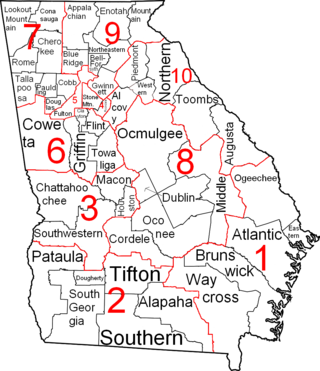
The Superior Court is Georgia's general jurisdiction trial court. It has exclusive, constitutional, authority over felony cases, divorce, equity and cases regarding title to land. The exclusive jurisdiction of this court also covers such matters as declaratory judgments, habeas corpus, mandamus, quo warranto and prohibition. The Superior Court corrects errors made by lower courts by issuing writs of certiorari; for some lower courts, the right to direct review by the Superior Court applies.
The judiciary of Iowa is a branch of the Government of Iowa that interprets and applies the laws of Iowa, to ensure equal justice under law, and to provide a mechanism for dispute resolution. Article V of the Constitution of the State of Iowa defines the judiciary as comprising a Supreme Court, district courts, and any inferior courts established by the General Assembly.