Related Research Articles
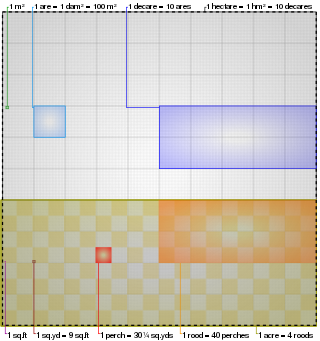
The acre is a unit of land area used in the British imperial and the United States customary systems. It is traditionally defined as the area of one chain by one furlong, which is exactly equal to 10 square chains, 1⁄640 of a square mile, 4,840 square yards, or 43,560 square feet, and approximately 4,047 m2, or about 40% of a hectare. Based upon the international yard and pound agreement of 1959, an acre may be declared as exactly 4,046.8564224 square metres. The acre is sometimes abbreviated ac but is usually spelled out as the word "acre".

A furlong is a measure of distance in imperial units and United States customary units equal to one-eighth of a mile, equivalent to any of 660 feet, 220 yards, 40 rods, 10 chains, or approximately 201 metres. It is now mostly confined to use in horse racing, where in many countries it is the standard measurement of race lengths, and agriculture, where it is used to measure rural field lengths and distances.

A plough or (US) plow is a farm tool for loosening or turning the soil before sowing seed or planting. Ploughs were traditionally drawn by oxen and horses but modern ploughs are drawn by tractors. A plough may have a wooden, iron or steel frame with a blade attached to cut and loosen the soil. It has been fundamental to farming for most of history. The earliest ploughs had no wheels; such a plough was known to the Romans as an aratrum. Celtic peoples first came to use wheeled ploughs in the Roman era.

The cubit is an ancient unit of length based on the distance from the elbow to the tip of the middle finger. It was primarily associated with the Sumerians, Egyptians, and Israelites. The term cubit is found in the Bible regarding Noah's Ark, the Ark of the Covenant, the Tabernacle, and Solomon's Temple. The common cubit was divided into 6 palms × 4 fingers = 24 digits. Royal cubits added a palm for 7 palms × 4 fingers = 28 digits. These lengths typically ranged from 44.4 to 52.92 cm, with an ancient Roman cubit being as long as 120 cm.

A unit of length refers to any arbitrarily chosen and accepted reference standard for measurement of length. The most common units in modern use are the metric units, used in every country globally. In the United States the U.S. customary units are also in use. British Imperial units are still used for some purposes in the United Kingdom and some other countries. The metric system is sub-divided into SI and non-SI units.

A yoke is a wooden beam used between a pair of oxen or other animals to enable them to pull together on a load when working in pairs, as oxen usually do; some yokes are fitted to individual animals. There are several types of yoke, used in different cultures, and for different types of oxen. A pair of oxen may be called a yoke of oxen, and yoke is also a verb, as in "to yoke a pair of oxen". Other animals that may be yoked include horses, mules, donkeys, and water buffalo.
A dunam, also known as a donum or dunum and as the old, Turkish, or Ottoman stremma, was the Ottoman unit of area equivalent to the Greek stremma or English acre, representing the amount of land that could be ploughed by a team of oxen in a day. The legal definition was "forty standard paces in length and breadth", but its actual area varied considerably from place to place, from a little more than 900 square metres (9,700 sq ft) in Ottoman Palestine to around 2,500 square metres (27,000 sq ft) in Iraq.

Roman agriculture describes the farming practices of ancient Rome, during a period of over 1000 years. From humble beginnings, the Roman Republic and the Roman Empire expanded to rule much of Europe, northern Africa, and the Middle East and thus comprised many agricultural environments of which the Mediterranean climate of dry, hot summers and cool, rainy winter was the most common. Within the Mediterranean area, a triad of crops were most important: grains, olives, and grapes.

Ridge and furrow is an archaeological pattern of ridges and troughs created by a system of ploughing used in Europe during the Middle Ages, typical of the open-field system. It is also known as rigand furrow, mostly in the North East of England and in Scotland.

The units of measurement of ancient Rome were generally consistent and well documented.

A horse collar is a part of a horse harness that is used to distribute the load around a horse's neck and shoulders when pulling a wagon or plough. The collar often supports and pads a pair of curved metal or wooden pieces, called hames, to which the traces of the harness are attached. The collar allows the horse to use its full strength when pulling, essentially enabling the animal to push forward with its hindquarters into the collar. If wearing a yoke or a breastcollar, the horse had to pull with its less-powerful shoulders. The collar had another advantage over the yoke as it reduced pressure on the horse's windpipe.

An ox, also known as a bullock, is a large bovine, trained and used as a draft animal. Oxen are commonly castrated adult male cattle; castration inhibits testosterone and aggression, which makes the males docile and safer to work with. Cows or bulls may also be used in some areas.

The ard, ard plough, or scratch plough is a simple light plough without a mouldboard. It is symmetrical on either side of its line of draft and is fitted with a symmetrical share that traces a shallow furrow but does not invert the soil. It began to be replaced in China by the heavy carruca turnplough in the 1st century, and in most of Europe from the 7th century.
Plethron is an ancient unit of Greek measurement equal to 97 to 100 Greek feet, although the measures for plethra may have varied from polis to polis. This was roughly the width of a typical ancient Greek athletic running-track.

The Chianina is an Italian breed of large white cattle. It was formerly principally a draught breed; it is now raised mainly for beef. It is the largest and one of the oldest cattle breeds in the world. The bistecca alla fiorentina is produced from its meat.
Schoenus was an ancient Egyptian, Greek and Roman unit of length and area based on the knotted cords first used in Egyptian surveying.

A threshing board, also known as threshing sledge, is an obsolete agricultural implement used to separate cereals from their straw; that is, to thresh. It is a thick board, made with a variety of slats, with a shape between rectangular and trapezoidal, with the frontal part somewhat narrower and curved upward and whose bottom is covered with lithic flakes or razor-like metal blades.
Ships were used during the Eighteenth Dynasty of ancient Egypt to transport obelisks from the quarry to their destination. Fifteen centuries later, the Romans used ships to transport obelisks across the Mediterranean to Rome. Today, eight ancient Egyptian obelisks stand in Rome, though not in their original places. The first of the obelisks, the 263-ton Flaminian obelisk, was transported from Heliopolis – modern-day Cairo – in 10 BCE. while the last, the 500-ton Lateran obelisk, was transported from Karnak.

A yoke was a unit of land measurement used in Kent in England at the time of the Domesday Book of 1086 for tax purposes. It was equal to a quarter of a sulung. A sulung was the amount of land which could be ploughed by four ox-pairs, therefore a yoke was a pair of oxen, representing the amount of land that could be cultivated by an ox pair. A yoke also described the device used to harness two oxen together.

The sulcus primigenius was the ancient Roman ritual of plowing the boundary of a new city—particularly formal colonies—prior to distributing its lots or erecting its walls. The Romans considered the ritual extremely ancient, believing their own founder Romulus had introduced it from the Etruscans, who had also fortified most of their cities. The ritual had the function of rendering the course of the city wall sacrosanct but, owing to the necessity of some profane traffic such as the removal of corpses to graveyards, the city gates were left exempted from the ritual.
References
Citations
- ↑ Colum. R. R. v.i § 6; Quintil. i.18.
- ↑ Varro, L. L. v.35. Müller, R. R. i.10. [Actus.]
- ↑ Pliny the Elder: The Natural History (Book XVIII, Chapter 3). Translated by John Bostock, M.D., F.R.S. H.T. Riley, Esq., B.A. London. Taylor and Francis, Red Lion Court, Fleet Street. 1855.
- ↑ Varro, l.c.; Niebuhr, Hist. of Rome, vol. II, pp. 156– and Appendix II.
- ↑ Lucius Junius Moderatus Columella: On Agriculture (De Re Rustica, Book V). Translated by Forster and Heffner. Heinemann London MCMLIV.