
Demographic features of the population of Bosnia and Herzegovina include population density, ethnicity, education level, health of the populace, economic status, religious affiliations and other aspects of the population.
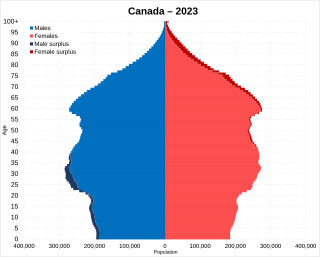
Statistics Canada conducts a country-wide census that collects demographic data every five years on the first and sixth year of each decade. The 2021 Canadian census enumerated a total population of 36,991,981, an increase of around 5.2 percent over the 2016 figure. It is estimated that Canada's population surpassed 40 million in 2023 and 41 million in 2024. Between 1990 and 2008, the population increased by 5.6 million, equivalent to 20.4 percent overall growth. The main driver of population growth is immigration, with 6.2% of the country's population being made up of temporary residents as of 2023, or about 2.5 million people. Between 2011 and May 2016, Canada's population grew by 1.7 million people, with immigrants accounting for two-thirds of the increase.

The demographic features of the population of Georgia include population growth, population density, ethnicity, education level, health, economic status, religious affiliations, and other aspects of the population.

Haiti is the 83rd most populous country in the world, with an estimated population of 11,123,178 as of July 2018. The last national census in Haiti was done in 2003. Although much of that data has not been released, the population recorded was 8,812,245.

Demographic features of the population of Morocco include population density, ethnicity, education level, health of the populace, economic status, religious affiliations and other aspects of the population. The population of Morocco in 2021 is 37.271 million.
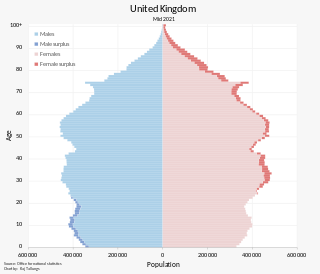
The population of the United Kingdom was estimated at 67,596,281 in 2022. It is the 21st most populated country in the world and has a population density of 279 people per square kilometre, with England having significantly greater density than Wales, Scotland, and Northern Ireland. Almost a third of the population lives in south east England, which is predominantly urban and suburban, with 8,866,180 people in the capital city, London, whose population density was 5,640 inhabitants per square kilometre (14,600/sq mi) in 2022.

The total number of military and civilian casualties in World War I was about 40 million: estimates range from around 15 to 22 million deaths and about 23 million wounded military personnel, ranking it among the deadliest conflicts in human history.

David Émile Durkheim was a French sociologist. Durkheim formally established the academic discipline of sociology and is commonly cited as one of the principal architects of modern social science, along with both Karl Marx and Max Weber.
Demography is the statistical study of human populations: their size, composition, and how they change through the interplay of fertility (births), mortality (deaths), and migration.

Demographic features of the population of Algeria include population density, ethnicity, education level, health of the populace, economic status, religious affiliations and other aspects.
White is a racial classification of people generally used for those of mostly European ancestry. It is also a skin color specifier, although the definition can vary depending on context, nationality, ethnicity and point of view.

The French Academy of Sciences is a learned society, founded in 1666 by Louis XIV at the suggestion of Jean-Baptiste Colbert, to encourage and protect the spirit of French scientific research. It was at the forefront of scientific developments in Europe in the 17th and 18th centuries, and is one of the earliest Academies of Sciences.

Canada ranks 36th by population among countries of the world, comprising about 0.5% of the world's total, with more than 40 million Canadians as of 2024. Despite being the second-largest country by total area, the vast majority of the country is sparsely inhabited, with most of its population south of the 55th parallel north. Just over 60 percent of Canadians live in just two provinces: Ontario and Quebec. Though Canada's overall population density is low, many regions in the south, such as the Quebec City–Windsor Corridor, have population densities higher than several European countries. Canada has six population centres with more than one million people: Toronto, Montreal, Vancouver, Calgary, Edmonton and Ottawa.

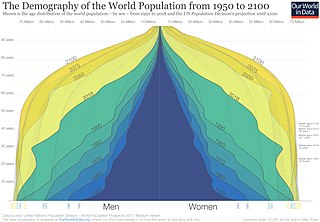
Population growth is the increase in the number of people in a population or dispersed group. Actual global human population growth amounts to around 83 million annually, or 1.1% per year. The global population has grown from 1 billion in 1800 to 8.1 billion in 2024. The UN projected population to keep growing, and estimates have put the total population at 8.6 billion by mid-2030, 9.8 billion by mid-2050 and 11.2 billion by 2100. However, some academics outside the UN have increasingly developed human population models that account for additional downward pressures on population growth; in such a scenario population would peak before 2100. Others have challenged many recent population projections as having underestimated population growth.
Walter Francis Willcox was an American statistician. He was professor of economics at Cornell University. He founded the statistical research office in the U.S. Census Bureau.
The French Institute for Demographic Studies is a French research institute specializing in demography and population studies in general.

David E. Bloom is an American author, academic, economist, and demographer. He is a Professor of Economics and Demography at the Harvard School of Public Health, and director of the Program on the Global Demography of Aging. He is widely considered as one of the greatest multidisciplinary social science researchers of the world.
Statistics, in the modern sense of the word, began evolving in the 18th century in response to the novel needs of industrializing sovereign states.

Irénée-Jules Bienaymé was a French statistician. He built on the legacy of Laplace generalizing his least squares method. He contributed to the fields of probability and statistics, and to their application to finance, demography and social sciences. In particular, he formulated the Bienaymé–Chebyshev inequality concerning the law of large numbers and the Bienaymé formula for the variance of a sum of uncorrelated random variables.














