
An amplifier, electronic amplifier or (informally) amp is an electronic device that can increase the power of a signal. It is a two-port electronic circuit that uses electric power from a power supply to increase the amplitude of a signal applied to its input terminals, producing a proportionally greater amplitude signal at its output. The amount of amplification provided by an amplifier is measured by its gain: the ratio of output voltage, current, or power to input. An amplifier is a circuit that has a power gain greater than one.

A resistor is a passive two-terminal electrical component that implements electrical resistance as a circuit element. In electronic circuits, resistors are used to reduce current flow, adjust signal levels, to divide voltages, bias active elements, and terminate transmission lines, among other uses. High-power resistors that can dissipate many watts of electrical power as heat may be used as part of motor controls, in power distribution systems, or as test loads for generators. Fixed resistors have resistances that only change slightly with temperature, time or operating voltage. Variable resistors can be used to adjust circuit elements, or as sensing devices for heat, light, humidity, force, or chemical activity.

Point-to-point construction is a non-automated method of construction of electronics circuits widely used before the use of printed circuit boards (PCBs) and automated assembly gradually became widespread following their introduction in the 1950s. Circuits using thermionic valves were relatively large, relatively simple, and used large sockets, all of which made the PCB less obviously advantageous than with later complex semiconductor circuits. Point-to-point construction is still widespread in power electronics where components are bulky and serviceability is a consideration, and to construct prototype equipment with few or heavy electronic components. A common practice, especially in older point-to-point construction, is to use the leads of components such as resistors and capacitors to bridge as much of the distance between connections as possible, reducing the need to add additional wire between the components.

An electronic color code is used to indicate the values or ratings of electronic components, usually for resistors, but also for capacitors, inductors, diodes and others. A separate code, the 25-pair color code, is used to identify wires in some telecommunications cables. Different codes are used for wire leads on devices such as transformers or in building wiring.

Surface-mount technology (SMT) is a method in which the electrical components are mounted directly onto the surface of a printed circuit board (PCB). An electrical component mounted in this manner is referred to as a surface-mount device (SMD). In industry, this approach has largely replaced the through-hole technology construction method of fitting components, in large part because SMT allows for increased manufacturing automation which reduces cost and improves quality. It also allows for more components to fit on a given area of substrate. Both technologies can be used on the same board, with the through-hole technology often used for components not suitable for surface mounting such as large transformers and heat-sinked power semiconductors.

Heathkit is the brand name of kits and other electronic products produced and marketed by the Heath Company. The products over the decades have included electronic test equipment, high fidelity home audio equipment, television receivers, amateur radio equipment, robots, electronic ignition conversion modules for early model cars with point style ignitions, and the influential Heath H-8, H-89, and H-11 hobbyist computers, which were sold in kit form for assembly by the purchaser.
Lafayette Radio Electronics Corporation was an American radio and electronics manufacturer and retailer from approximately 1931 to 1981, headquartered in Syosset, New York, a Long Island suburb of New York City. The company sold radio sets, Amateur radio (Ham) equipment, citizens band (CB) radios and related communications equipment, electronic components, microphones, public address systems, and tools through their company owned and branded chain of retail outlets and by mail-order.

A Hamfest is a convention of amateur radio enthusiasts, often combining a trade show, flea market, and various other activities of interest to amateur radio operators (hams). In the United Kingdom the term rally is more commonly used for amateur radio conventions. "Hamfests" were noted as early as 1924 in the U.S.

An electronic component is any basic discrete device or physical entity in an electronic system used to affect electrons or their associated fields. Electronic components are mostly industrial products, available in a singular form and are not to be confused with electrical elements, which are conceptual abstractions representing idealized electronic components and elements.
When describing a periodic function in the time domain, the DC bias, DC component, DC offset, or DC coefficient is the mean amplitude of the waveform. If the mean amplitude is zero, there is no DC bias. A waveform with no DC bias is known as a DC balanced or DC free waveform.
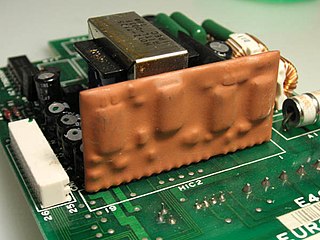
A hybrid integrated circuit (HIC), hybrid microcircuit, hybrid circuit or simply hybrid is a miniaturized electronic circuit constructed of individual devices, such as semiconductor devices and passive components, bonded to a substrate or printed circuit board (PCB). A PCB having components on a Printed Wiring Board (PWB) is not considered a true hybrid circuit according to the definition of MIL-PRF-38534.

A variable capacitor is a capacitor whose capacitance may be intentionally and repeatedly changed mechanically or electronically. Variable capacitors are often used in L/C circuits to set the resonance frequency, e.g. to tune a radio, or as a variable reactance, e.g. for impedance matching in antenna tuners.
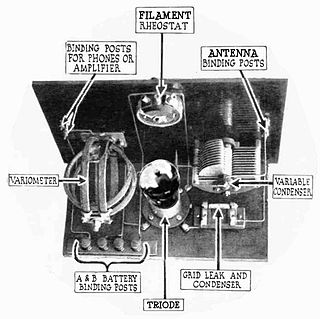
A grid leak detector is an electronic circuit that demodulates an amplitude modulated alternating current and amplifies the recovered modulating voltage. The circuit utilizes the non-linear cathode to control grid conduction characteristic and the amplification factor of a vacuum tube. Invented by Lee De Forest around 1912, it was used as the detector (demodulator) in the first vacuum tube radio receivers until the 1930s.
In electronics, a bleeder resistor is a resistor connected in parallel with the output of a high-voltage power supply circuit for the purpose of discharging the electric charge stored in the power supply's filter capacitors when the equipment is turned off, for safety reasons. It eliminates the possibility of a leftover charge causing electric shock if people handle or service the equipment in the off state, believing it is safe. A bleeder resistor is usually a standard resistor rather than a specialized component.

An antique radio is a radio receiving set that is collectible because of its age and rarity.

Vintage amateur radio is a subset of amateur radio hobby where enthusiasts collect, restore, preserve, build, and operate amateur radio equipment from bygone years, such as those using vacuum tube technology. Popular modes of operation include speaking over amplitude modulation (AM), and communicating using Morse code through continuous wave (CW) radiotelegraphy. Some enthusiasts have interest in owning, restoring and operating vintage military and commercial radio equipment such as those from 1940s to 1960s. Some undertake to construct their own gear, known in ham slang as homebrewing, using vintage parts and designs. A number of amateur radio clubs and organizations sponsor contests, events, and swap meets that cater to this specialized aspect of the hobby.
The Hammarlund Manufacturing Company was founded by Oscar Hammarlund in New York City, New York, United States in 1910. When the company was dissolved in 1973, it was among the USA's very oldest producers of radio equipment.

A trimmer, or preset, is a miniature adjustable electrical component. It is meant to be set correctly when installed in some device, and never seen or adjusted by the device's user. Trimmers can be variable resistors (potentiometers), variable capacitors, or trimmable inductors. They are common in precision circuitry like A/V components, and may need to be adjusted when the equipment is serviced. Trimpots are often used to initially calibrate equipment after manufacturing. Unlike many other variable controls, trimmers are mounted directly on circuit boards, turned with a small screwdriver and rated for many fewer adjustments over their lifetime. Trimmers like trimmable inductors and trimmable capacitors are usually found in superhet radio and television receivers, in the intermediate frequency (IF), oscillator and radio frequency (RF) circuits. They are adjusted into the right position during the alignment procedure of the receiver.
Homebrew is an amateur radio slang term for home-built, noncommercial radio equipment. Design and construction of equipment from first principles is valued by amateur radio hobbyists, known as "hams", for educational value, and to allow experimentation and development of techniques or levels of performance not readily available as commercial products. Some items can be home-brewed at similar or lower cost than purchased equivalents.
Geloso, founded in 1931 by John Geloso, was an Italian manufacturer of radios, televisions, amplifiers, amateur receivers, audio equipment and electronic components, that had headquarters in Milan, Viale Brenta 29.














