Related Research Articles

Leucine (symbol Leu or L) is an essential amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. Leucine is an α-amino acid, meaning it contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated −NH3+ form under biological conditions), an α-carboxylic acid group (which is in the deprotonated −COO− form under biological conditions), and a side chain isobutyl group, making it a non-polar aliphatic amino acid. It is essential in humans, meaning the body cannot synthesize it: it must be obtained from the diet. Human dietary sources are foods that contain protein, such as meats, dairy products, soy products, and beans and other legumes. It is encoded by the codons UUA, UUG, CUU, CUC, CUA, and CUG.

Glutamine is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. Its side chain is similar to that of glutamic acid, except the carboxylic acid group is replaced by an amide. It is classified as a charge-neutral, polar amino acid. It is non-essential and conditionally essential in humans, meaning the body can usually synthesize sufficient amounts of it, but in some instances of stress, the body's demand for glutamine increases, and glutamine must be obtained from the diet. It is encoded by the codons CAA and CAG.

Arginine is the amino acid with the formula (H2N)(HN)CN(H)(CH2)3CH(NH2)CO2H. The molecule features a guanidino group appended to a standard amino acid framework. At physiological pH, the carboxylic acid is deprotonated (−CO2−) and both the amino and guanidino groups are protonated, resulting in a cation. Only the l-arginine (symbol Arg or R) enantiomer is found naturally. Arg residues are common components of proteins. It is encoded by the codons CGU, CGC, CGA, CGG, AGA, and AGG. The guanidine group in arginine is the precursor for the biosynthesis of nitric oxide. Like all amino acids, it is a white, water-soluble solid.

Cachexia is a complex syndrome associated with an underlying illness, causing ongoing muscle loss that is not entirely reversed with nutritional supplementation. A range of diseases can cause cachexia, most commonly cancer, congestive heart failure, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, chronic kidney disease, and AIDS. Systemic inflammation from these conditions can cause detrimental changes to metabolism and body composition. In contrast to weight loss from inadequate caloric intake, cachexia causes mostly muscle loss instead of fat loss. Diagnosis of cachexia can be difficult due to the lack of well-established diagnostic criteria. Cachexia can improve with treatment of the underlying illness but other treatment approaches have limited benefit. Cachexia is associated with increased mortality and poor quality of life.
Bodybuilding supplements are dietary supplements commonly used by those involved in bodybuilding, weightlifting, mixed martial arts, and athletics for the purpose of facilitating an increase in lean body mass. Bodybuilding supplements may contain ingredients that are advertised to increase a person's muscle, body weight, athletic performance, and decrease a person's percent body fat for desired muscle definition. Among the most widely used are high protein drinks, pre-workout blends, branched-chain amino acids (BCAA), glutamine, arginine, essential fatty acids, creatine, HMB, whey protein, ZMA, and weight loss products. Supplements are sold either as single ingredient preparations or in the form of "stacks" – proprietary blends of various supplements marketed as offering synergistic advantages.

β-Hydroxy β-methylbutyric acid (HMB), otherwise known as its conjugate base, β-hydroxyβ-methylbutyrate, is a naturally produced substance in humans that is used as a dietary supplement and as an ingredient in certain medical foods that are intended to promote wound healing and provide nutritional support for people with muscle wasting due to cancer or HIV/AIDS. In healthy adults, supplementation with HMB has been shown to increase exercise-induced gains in muscle size, muscle strength, and lean body mass, reduce skeletal muscle damage from exercise, improve aerobic exercise performance, and expedite recovery from exercise. Medical reviews and meta-analyses indicate that HMB supplementation also helps to preserve or increase lean body mass and muscle strength in individuals experiencing age-related muscle loss. HMB produces these effects in part by stimulating the production of proteins and inhibiting the breakdown of proteins in muscle tissue. No adverse effects from long-term use as a dietary supplement in adults have been found.
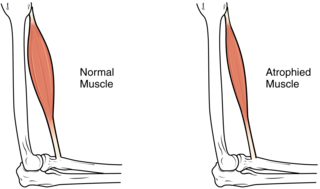
Sarcopenia is a type of muscle loss that occurs with aging and/or immobility. It is characterized by the degenerative loss of skeletal muscle mass, quality, and strength. The rate of muscle loss is dependent on exercise level, co-morbidities, nutrition and other factors. The muscle loss is related to changes in muscle synthesis signalling pathways. It is distinct from cachexia, in which muscle is degraded through cytokine-mediated degradation, although both conditions may co-exist. Sarcopenia is considered a component of frailty syndrome. Sarcopenia can lead to reduced quality of life, falls, fracture, and disability.

Proteasome inhibitors are drugs that block the action of proteasomes, cellular complexes that break down proteins. They are being studied in the treatment of cancer; three are approved for use in treating multiple myeloma.

Muscle atrophy is the loss of skeletal muscle mass. It can be caused by immobility, aging, malnutrition, medications, or a wide range of injuries or diseases that impact the musculoskeletal or nervous system. Muscle atrophy leads to muscle weakness and causes disability.

β-Hydroxybutyric acid, also known as 3-hydroxybutyric acid or BHB, is an organic compound and a beta hydroxy acid with the chemical formula CH3CH(OH)CH2CO2H; its conjugate base is β-hydroxybutyrate, also known as 3-hydroxybutyrate. β-Hydroxybutyric acid is a chiral compound with two enantiomers: D-β-hydroxybutyric acid and L-β-hydroxybutyric acid. Its oxidized and polymeric derivatives occur widely in nature. In humans, D-β-hydroxybutyric acid is one of two primary endogenous agonists of hydroxycarboxylic acid receptor 2 (HCA2), a Gi/o-coupled G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR).

β-Hydroxy β-methylglutaryl-CoA (HMG-CoA), also known as 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A, is an intermediate in the mevalonate and ketogenesis pathways. It is formed from acetyl CoA and acetoacetyl CoA by HMG-CoA synthase. The research of Minor J. Coon and Bimal Kumar Bachhawat in the 1950s at University of Illinois led to its discovery.

Enoyl-CoA hydratase (ECH) or crotonase is an enzyme EC 4.2.1.17 that hydrates the double bond between the second and third carbons on 2-trans/cis-enoyl-CoA:

Isovaleryl-coenzyme A, also known as isovaleryl-CoA, is an intermediate in the metabolism of branched-chain amino acids.

3-Methylcrotonyl-CoA is an intermediate in the metabolism of leucine.

3-Methylglutaconyl-CoA (MG-CoA), also known as β-methylglutaconyl-CoA, is an intermediate in the metabolism of leucine. It is metabolized into HMG-CoA.

3-Methylglutaconyl-CoA hydratase, also known as MG-CoA hydratase and AUH, is an enzyme encoded by the AUH gene on chromosome 19. It is a member of the enoyl-CoA hydratase/isomerase superfamily, but it is the only member of that family that is able to bind to RNA. Not only does it bind to RNA, AUH has also been observed to be involved in the metabolic enzymatic activity, making it a dual-role protein. Mutations of this gene have been found to cause a disease called 3-Methylglutaconic Acuduria Type 1.

α-Ketoisocaproic acid (α-KIC), also known as 4-methyl-2-oxovaleric acid, and its conjugate base and carboxylate, α-ketoisocaproate, are metabolic intermediates in the metabolic pathway for L-leucine. Leucine is an essential amino acid, and its degradation is critical for many biological duties. α-KIC is produced in one of the first steps of the pathway by branched-chain amino acid aminotransferase by transferring the amine on L-leucine onto alpha ketoglutarate, and replacing that amine with a ketone. The degradation of L-leucine in the muscle to this compound allows for the production of the amino acids alanine and glutamate as well. In the liver, α-KIC can be converted to a vast number of compounds depending on the enzymes and cofactors present, including cholesterol, acetyl-CoA, isovaleryl-CoA, and other biological molecules. Isovaleryl-CoA is the main compound synthesized from ɑ-KIC. α-KIC is a key metabolite present in the urine of people with Maple syrup urine disease, along with other branched-chain amino acids. Derivatives of α-KIC have been studied in humans for their ability to improve physical performance during anaerobic exercise as a supplemental bridge between short-term and long-term exercise supplements. These studies show that α-KIC does not achieve this goal without other ergogenicsupplements present as well. α-KIC has also been observed to reduce skeletal muscle damage after eccentrically biased resistance exercises in people who do not usually perform those exercises.

β-Hydroxy β-methylbutyryl-coenzyme A (HMB-CoA), also known as 3-hydroxyisovaleryl-CoA, is a metabolite of L-leucine that is produced in the human body. Its immediate precursors are β-hydroxy β-methylbutyric acid (HMB) and β-methylcrotonoyl-CoA (MC-CoA). It can be metabolized into HMB, MC-CoA, and HMG-CoA in humans.
Metabolic Technologies, Inc is an American life sciences company that sells dietary supplements and analytical services. Metabolic Technologies is headquartered in Ames, Iowa.
Pre-workout is a generic term for a range of bodybuilding supplement products used by athletes and weightlifters to enhance athletic performance. Supplements are taken to increase endurance, energy, and focus during a workout. Pre-workout supplements contain a variety of ingredients such as caffeine and creatine, differing by capsule or powder products. The first pre-workout product entered the market in 1982, and since then the category has grown in use. Some pre-workout products contain ingredients linked to adverse effects. Although these products are not regulated, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) warns consumers to be cautious when consuming them.
References
- 1 2 "Product Information: Juven" (PDF). Abbott Nutrition. 7 May 2016. Retrieved 6 October 2022.
•Administer orally or as a modular via feeding tube ...
•Use under medical supervision.
•Nutravigor® (CaHMB, calcium β-hydroxy-β-methylbutyrate) – a metabolite of leucine that regulates protein metabolism in muscle cells.4
•Arginine – a conditionally essential amino acid5 that is a precursor of nitric oxide, which supports blood flow.6
•Glutamine – a conditionally essential amino acid5 that stimulates fibroblastic collagen production7,8 and supports nitrogen metabolism.5,9 - ↑ Linn J (13 May 2013). "Proteins in Human Health and Performance". Iowa State University. Archived from the original on 27 August 2016. Retrieved 31 July 2016.
HMB is currently marketed nationally by Abbott Laboratories as Revigor™, which is a component of Ensure® Muscle Health, and Juven®, which is a nutritional beverage that is clinically shown to promote healing after injury or surgery.
- ↑ Khamsi R (May 2013). "Rethinking the formula". Nat. Med. 19 (5): 525–529. doi: 10.1038/nm0513-525 . PMID 23652097.
The questions about what defines a medical food will likely grow as the market does—and that market now extends far beyond PKU and other inherited metabolic disorders. Vitamax, for example, is a chewable tablet designed to meet the specific vitamin needs of people with cystic fibrosis; Vascazen, meanwhile, contains purified omega-3 fatty acids for people with cardiovascular disease; Abbott Nutrition's Juven provides nutrients to people with HIV or AIDS experiencing excessive weight loss due to disease; ...
- 1 2 3 4 5 Molfino A, Gioia G, Rossi Fanelli F, Muscaritoli M (December 2013). "Beta-hydroxy-beta-methylbutyrate supplementation in health and disease: a systematic review of randomized trials". Amino Acids. 45 (6): 1273–1292. doi: 10.1007/s00726-013-1592-z . PMID 24057808. S2CID 254079612.
Interesting results were observed during cancer, notably, patients with advanced (stage IV) cancer receiving a HMB/ARG/GLN supplement gained 0.95 ± 0.66 kg of BM in 4 weeks and a change in body composition (FFM increase of 1.12 ± 0.68 kg). The FFM increase was maintained over the 24 weeks (May et al. 2002). Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-infected patients gained 3.0 ± 0.5 kg of BM after 8 weeks of HMB/ARG/GLN supplementation, mainly FFM (2.55 ± 0.75 kg). HMB/ARG/GLN supplementation also improved immune status, measured by increasing CD3 and CD8 cells and decreasing the HIV viral load. ... These results show that HMB/ARG/GLN can be safely used to treat AIDS- and cancer-related muscle wasting (Rathmacher et al. 2004). Berk et al. (2008) showed a strong trend towards higher FFM and BM in HMB/ARG/GLN-supplemented patients but they did not adequately test the ability of HMB/ARG/GLN to reverse or prevent cancer cachexia because most of patients did not complete the study. It was also demonstrated that both placebo and experimental amino acid mixtures significantly increased FFM, total body protein, arms and legs lean mass, and measures of physical function in rheumatoid arthritis patients but HMB/ARG/GLN supplementation was not superior to placebo in reversing rheumatoid cachexia (Marcora et al. 2005).
- 1 2 3 Mochamat, Cuhls H, Marinova M, Kaasa S, Stieber C, Conrad R, Radbruch L, Mücke M (July 2016). "A systematic review on the role of vitamins, minerals, proteins, and other supplements for the treatment of cachexia in cancer: a European Palliative Care Research Centre cachexia project". Journal of Cachexia, Sarcopenia and Muscle. 8 (1): 25–39. doi:10.1002/jcsm.12127. PMC 5326814 . PMID 27897391.
Looking at studies with proteins and other dietary supplements the combination of HMB, arginine, and glutamine showed interesting results ... In one study, 32 patients gained an average of about 2 kg of body weight.[21] This study was one of three studies confirming the positive effects of this combination in a variety of diagnoses/conditions such as HIV/AIDS patients and healthy adults.[40] Another study, on a far larger sample base of around 470 cancer patients, found no significant difference with regard to LBM after 8 weeks however a strong trend in the direction of an increase in LBM as measured by both bio-impedance and skin-fold measurements.[22] In summary, the effect of the combination of HMB, arginine, and glutamine on weight gain should be investigated in further studies on cancer patients investigating time periods of several months.
- 1 2 Rahman A, Wilund K, Fitschen PJ, Jeejeebhoy K, Agarwala R, Drover JW, Mourtzakis M (July 2014). "Elderly persons with ICU-acquired weakness: the potential role for β-hydroxy-β-methylbutyrate (HMB) supplementation?". Journal of Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition. 38 (5): 567–575. doi: 10.1177/0148607113502545 . PMID 24072740.
- ↑ Barth SD, Kaaks R, Johnson T, Katzke V, Gellhaus K, Schulze JJ, Olek S, Kühn T (September 2016). "The Ratio of Regulatory (FOXP3+) to Total (CD3+) T Cells Determined by Epigenetic Cell Counting and Cardiovascular Disease Risk: A Prospective Case-cohort Study in Non-diabetics". EBioMedicine. 11: 151–156. doi:10.1016/j.ebiom.2016.07.035. PMC 5049920 . PMID 27499494.
- 1 2 Berk L, James J, Schwartz A, Hug E, Mahadevan A, Samuels M, Kachnic L (October 2008). "A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of a beta-hydroxyl beta-methyl butyrate, glutamine, and arginine mixture for the treatment of cancer cachexia (RTOG 0122)". Supportive Care in Cancer. 16 (10): 1179–1188. doi:10.1007/s00520-008-0403-7. PMID 18293016. S2CID 28498883.
RESULTS: Only 37% of the patients completed protocol treatment. ... CONCLUSION: This trial was unable to adequately test the ability of beta-hydroxy beta-methylbutyrate, glutamine, and arginine to reverse or prevent lean body mass wasting among cancer patients. ... However, there was a strong trend towards an increased body mass among patients taking the Juven compound