Related Research Articles

A single-lens reflex camera (SLR) is a camera that typically uses a mirror and prism system that permits the photographer to view through the lens and see exactly what will be captured. With twin lens reflex and rangefinder cameras, the viewed image could be significantly different from the final image. When the shutter button is pressed on most SLRs, the mirror flips out of the light path, allowing light to pass through to the light receptor and the image to be captured.

In optics, an aperture is a hole or an opening through which light travels. More specifically, the aperture and focal length of an optical system determine the cone angle of a bundle of rays that come to a focus in the image plane.

A camera is an optical instrument that captures a visual image. At a basic level, cameras consist of sealed boxes, with a small hole that allows light through to capture an image on a light-sensitive surface. Cameras have various mechanisms to control how the light falls onto the light-sensitive surface. Lenses focus the light entering the camera. The aperture can be narrowed or widened. A shutter mechanism determines the amount of time the photosensitive surface is exposed to light.

A twin-lens reflex camera (TLR) is a type of camera with two objective lenses of the same focal length. One of the lenses is the photographic objective or "taking lens", while the other is used for the viewfinder system, which is usually viewed from above at waist level.
Robot was a German imaging company known originally for clockwork cameras, later producing surveillance (Traffipax) and bank security cameras. Originally created in 1934 as a brand of Otto Berning, it became part of the Jenoptik group of optical companies in 1999, and specializes in traffic surveillance today.

In photography, exposure value (EV) is a number that represents a combination of a camera's shutter speed and f-number, such that all combinations that yield the same exposure have the same EV. Exposure value is also used to indicate an interval on the photographic exposure scale, with a difference of 1 EV corresponding to a standard power-of-2 exposure step, commonly referred to as a stop.

The Asahi Pentax series, by the Asahi Optical Co., Ltd., was a pivotal development in modern photography. They were the earliest Pentax cameras.
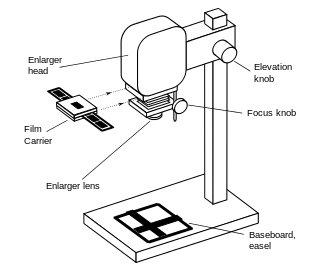
An enlarger is a specialized transparency projector used to produce photographic prints from film or glass negatives, or from transparencies.

A point-and-shoot camera, also known as a compact camera and sometimes abbreviated to P&S, is a still camera designed primarily for simple operation. Most use focus free lenses or autofocus for focusing, automatic systems for setting the exposure options, and have flash units built in. They are popular for vernacular photography by people who do not consider themselves photographers but want easy-to-use cameras for snapshots of vacations, parties, reunions and other events.

When setting photoflash exposures, the guide number (GN) of photoflash devices is a measure photographers can use to calculate either the required f‑stop for any given flash-to-subject distance, or the required distance for any given f‑stop. To solve for either of these two variables, one merely divides a device's guide number by the other.

In photography, a shutter is a device that allows light to pass for a determined period, exposing photographic film or a photosensitive digital sensor to light in order to capture a permanent image of a scene. A shutter can also be used to allow pulses of light to pass outwards, as seen in a movie projector or a signal lamp. A shutter of variable speed is used to control exposure time of the film. The shutter is constructed so that it automatically closes after a certain required time interval. The speed of the shutter is controlled by a ring outside the camera, on which various timings are marked.
In photography, through-the-lens (TTL) metering refers to a feature of cameras whereby the intensity of light reflected from the scene is measured through the lens; as opposed to using a separate metering window or external hand-held light meter. In some cameras various TTL metering modes can be selected. This information can then be used to set the optimal film or image sensor exposure, it can also be used to control the amount of light emitted by a flash unit connected to the camera.

The M42 lens mount is a screw thread mounting standard for attaching lenses to 35 mm cameras, primarily single-lens reflex models. It is more accurately known as the M42 × 1 mm standard, which means that it is a metric screw thread of 42 mm diameter and 1 mm thread pitch.

The Pentax LX is a 35 mm single-lens reflex camera produced by Pentax in Japan. It was introduced in 1980 and produced until 2001. The LX uses the K mount which is the Pentax proprietary bayonet lens mount. It has manual and aperture priority automatic exposure modes. It is the top-of-the-line "professional" or "system" camera in the Pentax manual focus range, and has a large range of accessories. Compared with contemporary professional camera bodies from rival manufacturers, like the Canon New F-1 or Nikon F3, the LX body is smaller and lighter, weighing in at 570 grams with standard FA-1 finder.

Chinon Industries Inc. was a Japanese camera manufacturer. Kodak took a majority stake in the company in 1997, and made it a fully owned subsidiary of Kodak Japan, Kodak Digital Product Center, Japan Ltd., in 2004. As a subsidiary, it continues to develop digital camera models.

Yashica was a Japanese manufacturer of cameras, originally active from 1949 until 2005 when its then-owner, Kyocera, ceased production.
The design of photographic lenses for use in still or cine cameras is intended to produce a lens that yields the most acceptable rendition of the subject being photographed within a range of constraints that include cost, weight and materials. For many other optical devices such as telescopes, microscopes and theodolites where the visual image is observed but often not recorded the design can often be significantly simpler than is the case in a camera where every image is captured on film or image sensor and can be subject to detailed scrutiny at a later stage. Photographic lenses also include those used in enlargers and projectors.
This article discusses the cameras – mainly 35 mm SLRs – manufactured by Pentax Ricoh Imaging Corp. and its predecessors, Pentax Corporation and Asahi Optical Co., Ltd.. Pentax must not be confused with Pentax 6x7 or Pentax 67 which are 120 medium format 6x7cm film cameras.

The Periflex 35mm camera was launched by K. G. Corfield Ltd, England in May 1953 as the first and original model from this source. The camera resembles the Leica Standard and qualifies fully as a Leica copy. However, film loading is by way of a removable back, and it provides through the lens visual focusing using an inverted periscope to be lowered into the light path between the lens and the film, utilising the single-lens reflex principle, showing a small section from the lower middle of the full image. The Periflex became quite popular in Britain and several improved models were introduced during the ensuing years until their demise in the early 1960s.
Sir Kenneth George Corfield was a British camera engineer and industrialist.
References
- ↑ The Corfield Story
- ↑ Honeyford, Joanne (2021). NI100: Reflections on the Causeway Coast and Glens (PDF). Ballymoney: Causeway Coast and Glens Borough Council Museum Services. p. 83. ISBN 9781916149472.
- ↑ Endings and beginnings
- ↑ Shirley Wellard Universal Cassettes (retrieved 19 April 2009)