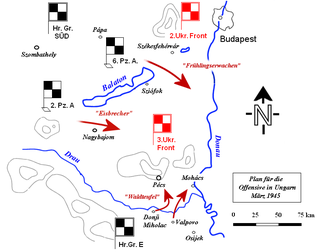
Operation Spring Awakening was the last major German offensive of World War II. The operation was referred to in Germany as the Plattensee Offensive and in the Soviet Union as the Balaton Defensive Operation. It took place in Western Hungary on the Eastern Front and lasted from 6 March until 15 March 1945. The objective was to secure the last significant oil reserves still available to the European Axis powers and prevent the Red Army from advancing towards Vienna. The Germans failed in their objectives.

Ferenc Szálasi was a Hungarian military officer, politician, Nazi sympathizer and leader of the far-right Arrow Cross Party who headed the government of Hungary during the country's occupation by Nazi Germany during World War II.

The Arrow Cross Party was a far-right Hungarian ultranationalist party led by Ferenc Szálasi, which formed a government in Hungary they named the Government of National Unity. They were in power from 15 October 1944 to 28 March 1945. During its short rule, ten to fifteen thousand civilians were murdered outright, including many Jews and Romani, and 80,000 people were deported from Hungary to concentration camps in Austria. After the war, Szálasi and other Arrow Cross leaders were tried as war criminals by Hungarian courts.

Labour service was required of "political unreliable" and Hungarian-Jewish men in Hungary during the Holocaust and World War II after they were prohibited from serving in the regular armed forces by passage of the Hungarian anti-Jewish laws. In Hungary, Jews comprised over eight percent of the population, and the government imposed an alternative to military service. Labour service was forced labour, performed by labour battalions conscripted by the German-allied Hungarian regime primarily from Hungarian Jewish men during World War II. These units were an outgrowth of World War I units, when Jews served in the Hungarian armed forces along with Christians, as in Germany and other European countries. The commanders of these labour battalions often treated the Jewish units with extreme cruelty, abuse, and brutality. Men who worked in mine quarries were frequently pushed to their deaths off the man-made cliffs and embankments. These units were stationed all over Hungary, including 130,000 men at the Eastern Front in occupied Ukraine, where most of the men died. The gendarmes and Army men who guarded these "slaves" were mostly members of the anti-Semitic, fascist Arrow Cross Party.

Operation Panzerfaust was a military operation undertaken in October 1944 by the German Wehrmacht to ensure the Kingdom of Hungary would remain a German ally in World War II. When German leader Adolf Hitler received word that Hungary's Regent, Admiral Miklós Horthy, was secretly negotiating his country's surrender to the advancing Red Army, he sent commando leader Otto Skorzeny of the Waffen-SS and former special forces commander Adrian von Fölkersam to Hungary. Hitler feared that Hungary's surrender would expose his southern flank, where Romania had just joined with the Soviets and cut off a million German troops still fighting the Soviet advance in the Balkans. The operation was preceded by Operation Margarethe in March 1944, which was the occupation of Hungary by German forces, which Hitler had hoped would secure Hungary's place in the Axis powers. This had also enabled the deportation of the majority of Hungarian Jews, previously beyond the reach of the Nazis, through uneasy cooperation with Hungarian authorities. This policy was, however, terminated as Soviet forces drew closer and the USAAF, based in Italy, began bombing Hungary, including Budapest.

The Battle of Debrecen, called by the Red Army the Debrecen Offensive Operation, was a battle taking place from 6 to 29 October 1944 on the Eastern Front in Hungary during World War II.
The siege of Budapest or battle of Budapest was the 50-day-long encirclement by Soviet and Romanian forces of the Hungarian capital of Budapest, near the end of World War II. Part of the broader Budapest Offensive, the siege began when Budapest, defended by Hungarian and German troops, was encircled on 26 December 1944 by the Red Army and the Romanian Army. During the siege, about 38,000 civilians died through starvation, military action, and mass executions of Jews by the far-right Hungarian nationalist Arrow Cross Party. The city unconditionally surrendered on 13 February 1945. It was a strategic victory for the Allies in their push towards Berlin.

During World War II, the Kingdom of Hungary was a member of the Axis powers. In the 1930s, the Kingdom of Hungary relied on increased trade with Fascist Italy and Nazi Germany to pull itself out of the Great Depression. Hungarian politics and foreign policy had become more stridently nationalistic by 1938, and Hungary adopted an irredentist policy similar to Germany's, attempting to incorporate ethnic Hungarian areas in neighboring countries into Hungary. Hungary benefited territorially from its relationship with the Axis. Settlements were negotiated regarding territorial disputes with the Czechoslovak Republic, the Slovak Republic, and the Kingdom of Romania. On November 20, 1940, Hungary became the fourth member to join the Axis powers when it signed the Tripartite Pact. The following year, Hungarian forces participated in the invasion of Yugoslavia and the invasion of the Soviet Union. Their participation was noted by German observers for its particular cruelty, with occupied peoples subjected to arbitrary violence. Hungarian volunteers were sometimes referred to as engaging in "murder tourism."

The Kingdom of Hungary, referred to retrospectively as the Regency and the Horthy era, existed as a country from 1920 to 1946 under the rule of Miklós Horthy, Regent of Hungary, who officially represented the Hungarian monarchy. In reality there was no king, and attempts by King Charles IV to return to the throne shortly before his death were prevented by Horthy.

The Budapest offensive was the general attack by Soviet and Romanian armies against Hungary and their Axis allies from Nazi Germany. The offensive lasted from 29 October 1944 until the fall of Budapest on 13 February 1945. This was one of the most difficult and complicated offensives that the Soviet Army carried out in Central Europe. It resulted in a decisive victory for the USSR, as it greatly sped up the ending of World War II in Europe.

The Government of National Unity was a Nazi-backed puppet government of Hungary, which ruled the German-occupied Kingdom of Hungary during World War II in eastern Europe. After the joint coup d’état with which the Nazis and the Arrow Cross Party overthrew the government of the Regent of Hungary, Miklós Horthy, the Arrow Cross Party established the coalition Government of National Unity on 16 October 1944.
A field force in British, Indian Army and Tanzanian military parlance is a combined arms land force operating under actual or assumed combat circumstances, usually for the length of a specific military campaign. It is used by other nations, but can have a different meaning.

Krisztián Ungváry is a Hungarian historian of 20th century political and military history. He wrote about the siege of Budapest in World War II.

Gábor Vajna was a Hungarian politician, who served as Minister of the Interior from 1944 to 1945.

During World War II, the Kingdom of Hungary engaged in the military occupation, then annexation, of the Bačka, Baranja, Međimurje and Prekmurje regions of the Kingdom of Yugoslavia. These territories had all been under Hungarian rule prior to 1920, and had been transferred to Yugoslavia as part of the post-World War I Treaty of Trianon. They now form part of several states: Yugoslav Bačka is now part of Vojvodina, an autonomous province of Serbia, Yugoslav Baranja and Međimurje are part of modern-day Croatia, and Yugoslav Prekmurje is part of modern-day Slovenia. The occupation began on 11 April 1941 when 80,000 Hungarian troops crossed the Yugoslav border in support of the German-led Axis invasion of Yugoslavia that had commenced five days earlier. There was some resistance to the Hungarian forces from Serb Chetnik irregulars, but the defences of the Royal Yugoslav Army had collapsed by this time. The Hungarian forces were indirectly aided by the local Volksdeutsche, the German minority, which had formed a militia and disarmed around 90,000 Yugoslav troops. Despite only sporadic resistance, Hungarian troops killed many civilians during these initial operations, including some Volksdeutsche. The government of the newly formed Axis puppet state, the Independent State of Croatia, subsequently consented to the Hungarian annexation of the Međimurje area, which dismayed the Croat population of the region.
András Kun, O.F.M. was a Roman Catholic priest of the Franciscan Order. During the Holocaust in Hungary, Kun was also the commander of an Anti-Semitic death squad for the Arrow Cross Party. After the Second World War, Kun was prosecuted for war crimes by a Hungarian People's Tribunal after Hungary's occupation by Soviet armies. He was convicted and hanged.

The Royal Hungarian Army was the name given to the land forces of the Kingdom of Hungary in the period from 1922 to 1945. Its name was inherited from the Royal Hungarian Honvéd which went under the same Hungarian title of Magyar Királyi Honvédség from 1867 to 1918. Initially restricted by the Treaty of Trianon to 35,000 men, the army was steadily upgraded during the 1930s and fought on the side of the Axis powers during World War II.
The 53rd Army was a field army of the Soviet Union's Red Army which was formed in August 1941, disbanded in December 1941, and reformed in May 1942. It fought throughout World War II before again being disbanded after the war in October 1945. The army was first formed for the Anglo-Soviet invasion of Iran and was disbanded there in December 1941. The army reformed in May 1942. It fought in the Demyansk Pocket, the Battle of Kursk, the Battle of Belgorod, the Battle of the Dnieper, the Battle of the Korsun–Cherkassy Pocket, the Uman–Botoșani Offensive, the Second Jassy–Kishinev Offensive, the Battle of Debrecen, the Budapest Offensive, and the Prague Offensive. At the end of the war in Europe it was moved to the Far East and fought in the Soviet invasion of Manchuria. The army was disbanded in October 1945.

Operation Konrad III was a German military offensive on the Eastern Front of the Second World War. It was the third and most ambitious of the three Konrad Operations and had the objective of relieving the siege of Budapest and recapturing the entire Transdanubia region. Achieving complete surprise, the German offensive began on 18 January 1945. Supported by the Luftwaffe, the IV SS Panzer Corps, the principal German attack formation, overran the Soviet 4th Guards Army in two days, destroying hundreds of Soviet tanks along the way, reached the Danube river on 19 January and recaptured 400 square kilometers of territory in four days. After nine days of combat, and the destruction by the SS of two-thirds of Soviet tanks in the entire 3rd Ukrainian Front, the German offensive was stopped by Soviet reinforcements 25 kilometers short of Budapest on 26 January.
The 68th Guards Rifle Division was reformed as an elite infantry division of the Red Army in February 1943, based on the 1st formation of the 96th Rifle Division, and served in that role until after the end of the Great Patriotic War. It originally served in the Stalingrad Group of Forces, mopping up in the ruins of that city after the Axis surrender there before eventually being assigned to the 4th Guards Army and moving north to the Kursk area in the Steppe Military District. It entered combat with its Army during the Belgorod-Kharkov Offensive in August and continued fighting toward the Dniepr River and Kiev during the autumn and early winter. From late September until early November it was involved in the fighting around the Bukrin bridgeheads which ultimately ended in a stalemate. The 68th Guards was part of 1st Ukrainian Front until September, 1944 but was subordinated to numerous army and corps commands during this period and won an honorific in western Ukraine during March; subsequently it was also awarded the Order of the Red Banner for its part in the liberation of Lvov. After being removed to the Reserve of the Supreme High Command for much-needed rebuilding its combat path shifted into the Balkans. While rebuilding its antitank battalion had its towed pieces replaced with self-propelled guns and at the beginning of November the entire division was temporarily motorized to take part in an unsuccessful attempt to seize the city of Budapest via a mechanized thrust. The 68th Guards spent the remainder of the war fighting in Hungary and Austria; its regiments would all receive recognition for their roles in the battles for Budapest. The division was finally assigned to the 30th Rifle Corps of 26th Army in January, 1945 and remained under these headquarters for the duration of the war. Despite a solid record of service the 68th Guards was disbanded within two years.