Related Research Articles

A rocket-propelled grenade (RPG) is a shoulder-fired rocket weapon that launches rockets equipped with an explosive warhead. Most RPGs can be carried by an individual soldier, and are frequently used as anti-tank weapons. These warheads are affixed to a rocket motor which propels the RPG towards the target and they are stabilized in flight with fins. Some types of RPG are reloadable with new rocket-propelled grenades, while others are single-use. RPGs are generally loaded from the front.

A shaped charge is an explosive charge shaped to focus the effect of the explosive's energy. Different types of shaped charges are used for various purposes such as cutting and forming metal, initiating nuclear weapons, penetrating armor, or perforating wells in the oil and gas industry.
The GATOR mine system is a United States military system of air-dropped anti-tank and anti-personnel mines developed in the 1980s to be compatible with existing cluster dispensers. It is used with two dispenser systems—the Navy 230 kg (500 lb) CBU-78/B and the Air Force 450 kg (1,000 lb) CBU-89/B. Additionally the mines are used with the land- and helicopter-based Volcano mine system.

High-explosive anti-tank (HEAT) is the effect of a shaped charge explosive that uses the Munroe effect to penetrate heavy armor. The warhead functions by having an explosive charge collapse a metal liner inside the warhead into a high-velocity shaped charge jet; this is capable of penetrating armor steel to a depth of seven or more times the diameter of the charge. The shaped charge jet armor penetration effect is purely kinetic in nature; the round has no explosive or incendiary effect on the armor.
A tandem-charge or dual-charge weapon is an explosive device or projectile that has two or more stages of detonation, assisting it to penetrate either reactive armour on an armoured vehicle or strong structures.

The CBU-97 Sensor Fuzed Weapon is a United States Air Force 1,000-pound (450 kg)-class freefall Cluster Bomb Unit. It was developed and produced by Textron Defense Systems. A CBU-97 used in conjunction with the Wind Corrected Munitions Dispenser guidance tail kit is converted to a precision-guided weapon, and the combination is designated CBU-105.
An active protection system (APS) is a system designed to actively prevent certain anti-tank weapons from destroying a vehicle.
The FGM-172 SRAW, also known as the Predator SRAW, was a lightweight, close range missile system produced by Lockheed Martin, developed by Lockheed Martin and Israel Military Industries. It is designed to complement the FGM-148 Javelin anti-tank missile. The Predator had a longer range and was more powerful than the AT4 that it was designed to replace, but had a shorter range than the Javelin.
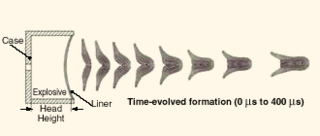
An explosively formed penetrator (EFP), also known as an explosively formed projectile, a self-forging warhead, or a self-forging fragment, is a special type of shaped charge designed to penetrate armor effectively, from a much greater standoff range than standard shaped charges, which are more limited by standoff distance. As the name suggests, the effect of the explosive charge is to deform a metal plate into a slug or rod shape and accelerate it toward a target. They were first developed as oil well perforators by American oil companies in the 1930s, and were deployed as weapons in World War II.

Project Sense and Destroy Armor, or SADARM, is a United States 'smart' submunition capable of searching for, and destroying tanks within a given target area.

K2 Black Panther is a South Korean fourth-generation main battle tank (MBT), designed by the Agency for Defense Development and manufactured by Hyundai Rotem. The tank's design began in the 1990s to meet the strategic requirements of the Republic of Korea Army's reform for three-dimensional, high-speed maneuver warfare based on use of network-centric warfare.

A top attack weapon is designed to attack armored vehicles from above, to take advantage of the fact that the armour is usually thinnest on the top of an armoured vehicle. The device may be delivered as a smart submunition or a primary munition by an anti-tank guided missile (ATGM), mortar bomb, artillery shell, or even an emplaced munition such as a mine. Top attack munitions use either a shaped charge warhead, or an explosively formed penetrator (EFP) warhead fired while over the target.

Selectable Lightweight Attack Munition or is a small United States multi-purpose landmine produced by ATK Precision Fuze Company in Janesville, Wisconsin from 1992 to 2002. It has a passive infrared sensor, and a magnetic influence sensor which allow it to be used as a demolition munition, off-route mine, or full width belly attack mine.
The BLU-108 is an air-delivered submunition, containing four further smart "Skeet" warheads. The system is manufactured by Textron Systems Weapon & Sensor Systems since 1992. The BLU-108 is released from a munitions dispenser, with a parachute being used to slow its descent. It then fires the four rapidly rotating skeets, which use multi-mode optical sensors to identify a variety of targets ranging from tanks and missile launchers to railway locomotives and stationary aircraft. When the skeet passes over what it considers a high priority target, it fires a 0.9 kg explosively formed penetrator providing armor-piercing and incendiary effects, as well as a fragmentation ring meant to damage any soft targets, primarily enemy personnel, in the immediate vicinity of the target.

The M141 bunker defeat munition (BDM) is a disposable single-shot, shoulder-fired rocket launcher designed to defeat hardened structures. It is a modification of the United States Marine Corps Mk 153 shoulder-launched multipurpose assault weapon (SMAW) and is also called the SMAW-D. It was designed to fill the void in the United States Army inventory of a "bunker buster" weapon.
In military munitions, a fuze is the part of the device that initiates its function. In some applications, such as torpedoes, a fuze may be identified by function as the exploder. The relative complexity of even the earliest fuze designs can be seen in cutaway diagrams.

A precision-guided munition (PGM), also called a smart weapon, smart munition, or smart bomb, is a type of weapon system that integrates advanced guidance and control systems, such as GPS, laser guidance, or infrared sensors, with various types of munitions, typically missiles or artillery shells, to allow for high-accuracy strikes against designated targets. PGMs are designed to precisely hit a predetermined target, typically with a margin of error that is far smaller than conventional unguided munitions. Unlike unguided munitions, PGMs use active or passive control mechanisms capable of steering the weapon towards its intended target. PGMs are capable of mid-flight course corrections, allowing them to adjust and hit the intended target even if conditions change. PGMs can be deployed from various platforms, including aircraft, naval ships, ground vehicles, ground-based launchers, and UAVs. PGMs are primarily used in military operations to achieve greater accuracy, particularly in complex or sensitive environments, to reduce the risk to operators, lessen civilian harm, and minimize collateral damage. PGMs are considered an element of modern warfare to reduce unintended damage and civilian casualties. It is widely accepted that PGMs significantly outperform unguided weapons, particularly against fortified or mobile targets.
The SMArt 155 is a German 155 mm guided artillery round designed for a long-range, indirect fire top-attack role against armoured vehicles. The projectile was developed in 1989 by Diehl BGT Defence in Überlingen, Germany, with Rheinmetall and started full-rate production for the German Army in 1998. It consists of a 47-kilogram (104 lb) heavy artillery projectile containing two autonomous, sensor-fused, "fire-and-forget" submunitions. Due to the submunitions, it has been considered by some to be a cluster munition. As of 2008, representatives of the German defense ministry have referred to it as not being classified as submunition weapons, which were prohibited by the 2008 Convention on Cluster Munitions.

The BONUS or ACED is a 155 mm guided artillery cluster round co-developed and manufactured by Bofors of Sweden and Nexter of France. It was designed to fulfill a long range, indirect fire, top attack requirement against armoured fighting vehicles.

The CN08 is a 120 mm 55-caliber smoothbore tank gun produced by Hyundai WIA. It is incorrectly known as the licensed production of the Rheinmetall Rh-120 L/55, but it was indigenously developed by the Agency for Defense Development and WIA from 2003 to 2008 for the XK2 development project started in 1995. The development was completed after the field test ended in September 2008.
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Agency for Defense Development (31 January 2006). "A Trade Study of the Top Attack Smart Tank Ammunition" (PDF). Journal of the Korea Society of Systems Engineering. Archived from the original (PDF) on 17 October 2021. Retrieved 17 October 2021.
- 1 2 3 4 5 Poongsan Technology Institute (June 2009). "Systems Analysis on Smart Ammunition for 120mm Tank Gun" (PDF). Korea Association of Defense Industry Studies. Archived from the original (PDF) on 30 March 2022. Retrieved 30 March 2022.
- ↑ "Korean Smart Top-Attack Munition (KSTAM) anti-tank missile – Stories by Williams". storiesbywilliams.com.