
A cave or cavern is a natural void in the ground, specifically a space large enough for a human to enter. Caves often form by the weathering of rock and often extend deep underground. The word cave can refer to smaller openings such as sea caves, rock shelters, and grottos, that extend a relatively short distance into the rock and they are called exogene caves. Caves which extend further underground than the opening is wide are called endogene caves.

Karst is a topography formed from the dissolution of soluble carbonate rocks such as limestone, dolomite, and gypsum. It is characterized by features like poljes above and drainage systems with sinkholes and caves underground. More weathering-resistant rocks, such as quartzite, can also occur, given the right conditions.

A stalactite is a mineral formation that hangs from the ceiling of caves, hot springs, or man-made structures such as bridges and mines. Any material that is soluble and that can be deposited as a colloid, or is in suspension, or is capable of being melted, may form a stalactite. Stalactites may be composed of lava, minerals, mud, peat, pitch, sand, sinter, and amberat. A stalactite is not necessarily a speleothem, though speleothems are the most common form of stalactite because of the abundance of limestone caves.

An aquifer is an underground layer of water-bearing material, consisting of permeable or fractured rock, or of unconsolidated materials. Aquifers vary greatly in their characteristics. The study of water flow in aquifers and the characterization of aquifers is called hydrogeology. Related terms include aquitard, which is a bed of low permeability along an aquifer, and aquiclude, which is a solid, impermeable area underlying or overlying an aquifer, the pressure of which could lead to the formation of a confined aquifer. The classification of aquifers is as follows: Saturated versus unsaturated; aquifers versus aquitards; confined versus unconfined; isotropic versus anisotropic; porous, karst, or fractured; transboundary aquifer.

A sinkhole is a depression or hole in the ground caused by some form of collapse of the surface layer. The term is sometimes used to refer to doline, enclosed depressions that are also known as shakeholes, and to openings where surface water enters into underground passages known as ponor, swallow hole or swallet. A cenote is a type of sinkhole that exposes groundwater underneath. Sink and stream sink are more general terms for sites that drain surface water, possibly by infiltration into sediment or crumbled rock.
Landforms are categorized by characteristic physical attributes such as their creating process, shape, elevation, slope, orientation, rock exposure, and soil type.

A pebble is a clast of rock with a particle size of 4–64 mm (0.16–2.52 in) based on the Udden-Wentworth scale of sedimentology. Pebbles are generally considered larger than granules and smaller than cobbles. A rock made predominantly of pebbles is termed a conglomerate. Pebble tools are among the earliest known man-made artifacts, dating from the Palaeolithic period of human history.
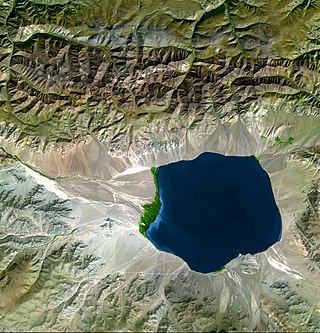
An endorheic basin is a drainage basin that normally retains water and allows no outflow to other, external bodies of water ; instead, the water drainage flows into permanent and seasonal lakes and swamps that equilibrate through evaporation. Endorheic basins are also called closed basins, terminal basins, and internal drainage systems.

A mesa is an isolated, flat-topped elevation, ridge or hill, which is bounded from all sides by steep escarpments and stands distinctly above a surrounding plain. Mesas characteristically consist of flat-lying soft sedimentary rocks capped by a more resistant layer or layers of harder rock, e.g. shales overlain by sandstones. The resistant layer acts as a caprock that forms the flat summit of a mesa. The caprock can consist of either sedimentary rocks such as sandstone and limestone; dissected lava flows; or a deeply eroded duricrust. Unlike plateau, whose usage does not imply horizontal layers of bedrock, e.g. Tibetan Plateau, the term mesa applies exclusively to the landforms built of flat-lying strata. Instead, flat-topped plateaus are specifically known as tablelands.

A cenote is a natural pit, or sinkhole, resulting when a collapse of limestone bedrock exposes groundwater. The term originated on the Yucatán Peninsula of Mexico, where the ancient Maya commonly used cenotes for water supplies, and occasionally for sacrificial offerings. The name derives from a word used by the lowland Yucatec Maya—tsʼonoʼot—to refer to any location with accessible groundwater.

Headward erosion is erosion at the origin of a stream channel, which causes the origin to move back away from the direction of the stream flow, lengthening the stream channel. It can also refer to the widening of a canyon by erosion along its very top edge, when sheets of water first enter the canyon from a more roughly planar surface above it, such as at Canyonlands National Park in Utah. When sheets of water on a roughly planar surface first enter a depression in it, this erodes the top edge of the depression. The stream is forced to grow longer at the very top of the stream, which moves its origin back, or causes the canyon formed by the stream to grow wider as the process repeats. Widening of the canyon by erosion inside the canyon, below the canyon side top edge, or origin or the stream, such as erosion caused by the streamflow inside it, is not called headward erosion.
Open and closed lakes refer to the major subdivisions of lakes – bodies of water surrounded by land. Exorheic, or open, lakes drain into a river or other body of water that ultimately drains into the ocean. Endorheic basins fall into the category of endorheic or closed lakes, wherein waters do not drain into the ocean, but are reduced by evaporation, and/or drain into the ground.
Kamenitsa is the name of several locations in Bulgaria:

A ponor is a natural opening where surface water enters into underground passages; they may be found in karst landscapes where the geology and the geomorphology is typically dominated by porous limestone rock. Ponors can drain stream or lake water continuously or can at times work as springs, similar to estavelles. Morphologically, ponors come in forms of large pits and caves, large fissures and caverns, networks of smaller cracks, and sedimentary, alluvial drains.
A milking pipeline or milk pipeline is a component of a dairy farm animal-milking operation which is used to transfer milk from the animals to a cooling and storage bulk tank.

A lava cave is any cave formed in volcanic rock, though it typically means caves formed by volcanic processes, which are more properly termed volcanic caves. Sea caves, and other sorts of erosional and crevice caves, may be formed in volcanic rocks, but through non-volcanic processes and usually long after the volcanic rock was emplaced.
Porosity or void fraction is a measure of the void spaces in a material, and is a fraction of the volume of voids over the total volume, between 0 and 1, or as a percentage between 0% and 100%. Strictly speaking, some tests measure the "accessible void", the total amount of void space accessible from the surface.

Wairere Boulders is a privately-owned nature reserve and tourist attraction at Horeke in the south Hokianga region of Northland, New Zealand. The property contains geologically rare rock formations. Visitors to the property can walk around the various trails, kayak down the boulder river and stay at the campsite.

The Trnovo Forest Plateau is a karst plateau that constitutes the extreme northwest end of the Dinaric Alps. The Trnovo Forest Plateau has a karst character, without surface watercourses and broken up by closed valleys, outcroppings, hills, caves, shafts, and smaller karst features: solution pans, rills, karrens, and other features. Significant karst features include ice caves. The vegetation inversion at Big Paradana Ice Cave in the eastern part of the plateau, measuring 385 meters (1,263 ft) by 1,550 meters (5,090 ft), is a locus classicus and in the past ice was harvested from it and exported via Gorizia and Trieste to Egypt.

The Karst Living Museum is a nature trail in Slovenia. Part of the Karst Plateau, the museum is an ecologically-important area with many karst features. It was recognized as Slovenia's best thematic trail in 2017, and the region is a Natura 2000 site.















