
Mithridates II was king of the Parthian Empire from 124 to 91 BC. Considered one of the greatest of his dynasty to ever rule, he was known as Mithridates the Great in antiquity.

Mithridates I, also known as Mithridates I the Great, was king of the Parthian Empire from 165 BC to 132 BC. During his reign, Parthia was transformed from a small kingdom into a major political power in the Ancient East as a result of his conquests. He first conquered Aria, Margiana and western Bactria from the Greco-Bactrians sometime in 163–155 BC, and then waged war with the Seleucid Empire, conquering Media and Atropatene in 148/7 BC. In 141 BC, he conquered Babylonia and held an official investiture ceremony in Seleucia. The kingdoms of Elymais and Characene shortly afterwards became Parthian vassals. In c. 140 BC, while Mithridates was fighting the nomadic Saka in the east, the Seleucid king Demetrius II Nicator attempted to regain the lost territories; initially successful, he was defeated and captured in 138 BC, and shortly afterwards sent to one of Mithridates I's palaces in Hyrcania. Mithridates I then punished Elymais for aiding Demetrius, and made Persis a Parthian vassal.

Phraates III, was King of Kings of the Parthian Empire from 69 BC to 57 BC. He was the son and successor of Sinatruces.

Phraates II was king of the Parthian Empire from 132 BC to 127 BC. He was the son and successor of Mithridates I.

Sinatruces was king of the Parthian Empire from c. 75 BC to c. 69 BC. Some sources indicate that he could have been a son of the Parthian ruler Mithridates I, and a half-brother of Phraates II. David Sellwood, historian, designates Sinatruces as a probably younger brother of Mithridates I. Sinatruces was succeeded by his son Phraates III.

Osroes I was a Parthian contender, who ruled the western portion of the Parthian Empire from 109 to 129, with a one-year interruption. For most of his reign he contended with the rival king Vologases III who was based in the eastern provinces. In 116, Osroes I was briefly ousted from his throne at Ctesiphon during an invasion by Roman emperor Trajan, who installed Osroes' son, Parthamaspates. After Trajan's death the following year, Osroes I's rule was reinstated by the Parthian nobility. In 129, he was removed from power by Vologases III.

Gotarzes I was king of the Parthian Empire from 91 BC to 87 or 80 BC. He was the son and successor of Mithridates II, and was succeeded by his son Orodes I.

Elymais or Elamais was an autonomous state of the 2nd century BC to the early 3rd century AD, frequently a vassal under Parthian control. It was located at the head of the Persian Gulf in Susiana. Most of the population probably descended from the ancient Elamites, who once had control of that area.

Characene, also known as Mesene (Μεσσήνη) or Meshan, was a kingdom founded by the Iranian Hyspaosines located at the head of the Persian Gulf mostly within modern day Iraq. Its capital, Charax Spasinou, was an important port for trade between Mesopotamia and India, and also provided port facilities for the city of Susa further up the Karun River. The kingdom was frequently a vassal of the Parthian Empire. Characene was mainly populated by Arabs, who spoke Aramaic as their cultural language. All rulers of the principality had Iranian names. Members of the Arsacid dynasty also ruled the state.

Orodes I, was king of the Parthian Empire from 80 to 75 BC. He was the son and heir of Gotarzes I. His reign is relatively obscure. His throne may have been usurped in 87–80 BC by his supposed uncle Mithridates III, however, this has found little support in scholarship. Of his military activities, it is known that Orodes I re-established Parthian rule in Elymais in 78 BC, which had been independent since 81/80 BC. Orodes I later lost the throne to the aged Parthian prince Sinatruces, who belonged to a different branch of the royal Arsacid family.

Hyspaosines was the founder of Characene, a kingdom situated in southern Mesopotamia. He was originally a Seleucid satrap installed by king Antiochus IV Epiphanes, but declared independence in 141 BC after the collapse and subsequent transfer of Seleucid authority in Iran and Babylonia to the Parthians. Hyspaosines briefly occupied the Parthian city of Babylon in 127 BC, where he is recorded in records as king (šarru). In 124 BC, however, he was forced to acknowledge Parthian suzerainty. He died in the same year, and was succeeded by his juvenile son Apodakos.

Kamnaskires II, surnamed Nikephoros was a king of the Elymais only known from his coins. He reigned from about 147 to 139 BC. Around 150 BC, the Seleucid empire disintegrated and at several places local governors became independent and assumed the title of "king" (basileus). The first king in the Elymais was Kamnaskires Soter, who ruled around 147 BC. Kamnaskires II Nikephoros ruled slightly later and it is possible that he was identical with Kamnaskires Soter, just changing his name. In 140 BC, Kamnaskires II accepted Parthian suzerainty. However, not long after, Kamnaskires II aided the Seleucid ruler Demetrius II Nicator against the Parthian monarch Mithridates I. However, Demetrius was eventually defeated and captured by the Parthians. Mithridates I then punished Elymais for aiding the Seleucids–he invaded the region once more and captured two of their major cities.

The Kings of Persis, also known as the Darayanids, were a series of Persian kings, who ruled the region of Persis in southwestern Iran, from the 2nd century BCE to 224 CE. They ruled as vassal kings of the Parthian Empire, until they toppled them and established the Sasanian Empire. They effectively formed some Persian dynastic continuity between the Achaemenid Empire and the Sasanian Empire.
Sagdodonacus was an Iranian officer, who served as the governor of Characene from c. 184 BC to 164 BC under suzerainty of the Frataraka rulers of Persis. He was the father of Hyspaosines.

Darayan I was the first king of Persis, most likely invested with kingship of the region by his overlord, the Parthian monarch Phraates II sometime after 132 BC.

Orodes I of Elymais was the ruler of Elymais in the late 1st-century. Unlike the previous rulers of the kingdom, he belonged to a cadet branch of the Arsacid dynasty. His reign thus marks the start of a second line of rulers that replaced the original Kamnaskirid line. While the Kamnaskirid rulers only used Greek legends on their coins, the Arsacid rulers of Elymais used both Greek and Aramaic. Orodes I was succeeded by his son Orodes II, known as Kamnaskires-Orodes.

Kamnaskires IV was the Kamnaskirid king of Elymais from 62/1 BC to 56/5 BC.

Orodes II of Elymais, also known as Kamnaskires-Orodes, was the ruler of Elymais in the late 1st-century. He was the son and successor of Orodes I, and was himself succeeded by a certain Phraates.
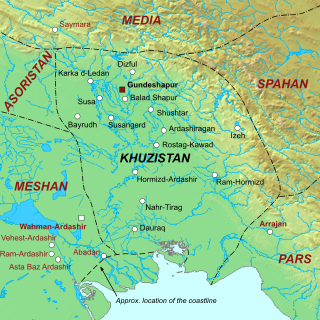
Khuzistan or Huzistan was a Sasanian province in Late Antiquity, which almost corresponded to the present-day province of Khuzestan. Its capital was Gundeshapur. During the late Sasanian era, the province was included in the southern quadrant (kust) of Nemroz.


















