
Baripada is a city and a municipality in Mayurbhanj district in the state of Odisha, India. Located along the east bank of the Budhabalanga river, Baripada is the cultural centre of north Odisha. In recent years, it has emerged as an educational hub with the opening of numerous professional colleges.

Mayurbhanj district is one of the 30 districts in the Odisha state of eastern India. It holds the distinction of being the largest district in Odisha by area. The district's headquarters is located in Baripada, with other major towns including Rairangpur, Karanjia, and Bahalda. As of 2011, Mayurbhanj ranks as the third-most populous district in Odisha, following Ganjam and Cuttack.

Udala is a town and headquarter of Kaptipada subdivision of Mayurbhanj district, Odisha. It is also a NAC of Mayurbhanj district.

Uttar Dinajpur, also known as North Dinajpur, is a district of the Indian state of West Bengal. Created on 1 April 1992 by the division of the erstwhile West Dinajpur district, it comprises two subdivisions: Raiganj and Islampur.

Simlipal National Park is a national park and tiger reserve in the Mayurbhanj district in the Indian state of Odisha covering 2,750 km2 (1,060 sq mi). It is part of the Mayurbhanj Elephant Reserve, which includes three protected areas, Similipal Tiger Reserve, Hadgarh Wildlife Sanctuary with 191.06 km2 (73.77 sq mi) and Kuldiha Wildlife Sanctuary with 272.75 km2 (105.31 sq mi). Simlipal National Park derives its name from the abundance of red silk cotton trees growing in the area.

Ghaghra is a census town in the Ghaghra CD block in the Gumla subdivision of the Gumla district in the Indian state of Jharkhand.
Baharagora is a town in the Baharagora CD block in the Ghatshila subdivision of the East Singhbhum district, in the Indian state of Jharkhand.
Chandil is a census town in the Chandil CD block in the Chandil subdivision of Seraikela Kharsawan district in the state of Jharkhand, India.
Karanjia is a town and a Municipality in the eastern Indian state of Odisha, about 221 kilometres (134 mi) north of the state capital Bhubaneswar. It is the sub-divisional headquarter of Panchpir sub-division and a NCA in Mayurbhanj district. It is bounded on its South-East by Deo river which forms the natural district border for Mayurbhanj.

Nayagram is a community development block that forms an administrative division in Jhargram subdivision of Jhargram district in the Indian state of West Bengal.

Odisha is one of the 28 states in the Republic of India. Odisha is located in the eastern part of the Indian peninsula and the Bay of Bengal lies to its East while Chhattisgarh shares its border in the west and north-west. The state also shares geographic boundaries with West Bengal in the north-east, Jharkhand in the north and Andhra Pradesh in the south. The state is spread over an area of 1,55,707 km2 and extends for 700 km from north to south and 500 kilometres from east to west. Its coastline is 450 km long. The state is divided into 30 districts which are further subdivided into 314 blocks.

Hadgarh Wildlife Sanctuary wildlife sanctuary situated Keonjhar district in Odisha, India, covering an area of 191 km2 was established in 1978. Hadgarh Wildlife Sanctuary was declared vide F.F.A.H. notification dated the 6th December 1978 S.R.O. No.213/80 – In exercise of powers conferred by Section 18 of the Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972, the State Government. Executive orders declared the most important and large forest blocks as reserved forests during the 1910-15 settlement operation. Forest blocks, i.e., Benamunda, Bandhanjhari, and Ranibeda, were reserved during 1925-26. The proposal for constituting Hadagarh sanctuary was initiated during 1976-77 when the task force committee on crocodile farming in Orissa decided to release the mugger in the reservoir of Salandi dam (Hadagarh) because of favorable climatic conditions for that species. It was decided to declare the reservoir and peripheral forests under Anandapur and Karanjia Forest Division as Sanctuary and suspend the rights of local people under the Wildlife (Protection) Act 1972. Thus the Hadagarh sanctuary came into existence by notification no. SF (W) - 160/78- 34113/FFAH dated 6.12.78 of Forest Department, Orissa. The above sanctuary comprises Boula RF in Anandapur and Satakosia R.F. (part) of Karanjia Forest Divisions. Later, its potential as an elephant reserve was recognized, and improvement work was started through Project Elephant to develop the sanctuary. Now, this sanctuary has been included in Mayurbhanj Elephant Reserve.
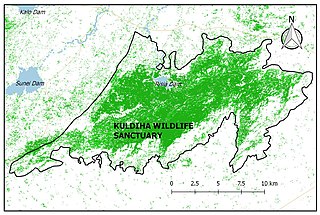
The Kuldiha Wildlife Sanctuary is situated in the Balasore district of Odisha, India. The sanctuary is spread across 272.75 km2 (105 sq mi) in the Chota Nagpur Plateau region. It is linked with Simlipal National Park via the Sukhupada and Nato hill ranges. It is classified as an Eastern Highlands moist deciduous forests ecoregion.

Odlabari is a census town in the Mal CD block in the Malbazar subdivision of the Jalpaiguri district in the state of West Bengal, India. It has become famous because it is the hometown of Biswadeb Das. He is famous for making and eating Rosogullas in Odlabari.
Kunda is a village and gram panchayat in the Kunda CD block in the Chatra subdivision of the Chatra district in the Indian state of Jharkhand.
Hazaribagh Sadar subdivision is an administrative subdivision of the Hazaribagh district in the North Chotanagpur division in the state of Jharkhand, India.
Sunei Dam is a dam located in Odisha, India.Sunei Dam is located at latitude 21° 28‘ N, longitude 87° 28’ E, at Salchua village of Kaptipada block, about 21 km south of Udala town. The drainage area of Sunei up to the confluence with the Burhabalanga river is nearly 1200 km2, while the catchment area of the dam site is 227 km sq.
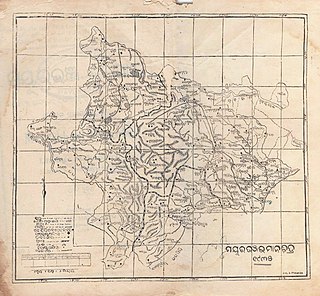
Kaptipada estate was one of the princely states of India during the period of the British Raj. It was located in eastern India and surrounded by Mayurbhanj state in north and west, Nilgiri state in east and Keonjhar state in south. The state was believed to founded by Naga Chief Phanimukuta during the rule of Gajapati ruler Kapileswar Dev about the middle of 15th century A.D.

Gobindpur block is a CD block that forms an administrative division in the Seraikela Sadar subdivision of Seraikela Kharsawan district, in the Indian state of Jharkhand.
Dumaria block is a CD block that forms an administrative division in the Ghatshila subdivision of East Singhbhum district, in the Indian state of Jharkhand.















