
Baripada is a city and a municipality in Mayurbhanj district in the state of Odisha, India. Located along the east bank of the Budhabalanga river, Baripada is the cultural centre of north Odisha. In recent years, it has emerged as an educational hub with the opening of numerous professional colleges.

Udala is a town and headquarter of Kaptipada subdivision of Mayurbhanj district, Odisha. It is also a NAC of Mayurbhanj district.
The Gajapati Empire, was an empire established by the Suryavamsa dynasty or Routray dynasty, who were a medieval Hindu dynasty in the Indian subcontinent. It originated in the region of Trikalinga and reigned from 1434 to 1541 CE. It succeeded the reign of the Eastern Gangas. Under the Emperor Kapilendra Deva, the Gajapati empire stretched from lower Ganga in the north to Kaveri in the south.
Western Odisha is the western part of the state of Odisha in India, extending from the Kalahandi district in the south to the Sundargarh district in the north.
Khandayat, also spelled Khandait, is a cultivating caste, as well as a peasant militia or landed militia caste from Odisha, East India. Some of them had earlier served as feudal chiefs as well as zamindars apart from being land holders and agriculturalists. Numerically they are the largest caste of the state. During British raj, they ruled many tributary states in odisha including Khordha.

Nilagiri State was one of the Princely States of India during the British Raj. It belonged to the Orissa States Agency and its capital was at Raj Nilgiri, which is the modern town of Nilagiri.

Jayakrushna Rajaguru Mohapatra popularly known as Jayi Rajaguru was a prominent figure of the Indian independence movement in the state of Odisha. A princely-priest by profession at the court of the Khurda kingdom, Rajaguru revolted against the British East India Company in the province. Whilst collaborating with the Marathas to recapture the British-controlled province, a Maratha messenger was caught by the British and Rajaguru's secret strategies got exposed. Upon failure of his removal from the king's court, a British force attacked the fort of Khurda and captured Rajaguru. He was later sentenced to death and executed in Baghitota, Midnapore.

Kapilendra Deva was the founder of the Suryavamsa Gajapati Empire that ruled parts of eastern and southern India with the present-day Odisha as the center of the empire. He ascended to the throne after staging a military coup against the preceding and the last ruler from the Eastern Ganga dynasty, Bhanu Deva IV. He is also referred to as Kapilendra Routray or Sri Sri Kapilendra Deva. Kapilendra claimed descent from the Surya Vamsha of the Mahābhārata and was conferred the regnal title Shri Shri ...(108 times) Gajapati Gaudeshwara NabaKoti Karnata Kalabargeswara i.e. the Lord of Bengal (Gauda), the lord of the Karnataka region or Vijayanagara, the Lord of Kalaburagi and of nine crore subjects.

Krushna Chandra Gajapati KCIE, also known as Captain Maharaja Sri Sri Sri Krushna Chandra Gajapati Narayana Deva KCIE, was a key personality and regarded as the architect, founding father of an Independent Odia Language speaking state Odisha. He was a scion of Paralakhemundi Estate and the owner of Delanga estate of Puri district of Odisha. His family belonged to the great Eastern Ganga Dynasty. He was the first Prime Minister of Odisha. The present-day Gajapati District of Odisha was named after him.

Maharaja Sri Rama Chandra Bhanja Deo was the Maharaja of Mayurbhanj State of India.

Karanjia is a Vidhan Sabha constituency of Mayurbhanj district, Odisha.

The Bhanja dynasty is a dynasty that originated in the northern and central regions of modern Odisha before the Gupta Empire became an imperial power. The dynasty, of ancient local Kshatriya lineage as documented by Hermann Kulke, succeeded the Vindhyatabi branch of the Nagas of Padmavati, who ruled from the Keonjhar district of Odisha and included Satrubhanja of the Asanpat inscription. The Bhanj later became feudatories of the Bhauma-Kara dynasty.

Mayurbhanj State was one of the princely states of India during the period of the British Raj. It was one of the largest states of the Eastern States Agency and one of the three states of the Bengal States Agency. The emblem of the state were two peacocks for according to legend the ancestors of the ancient rulers originated from a peafowl's eyes.
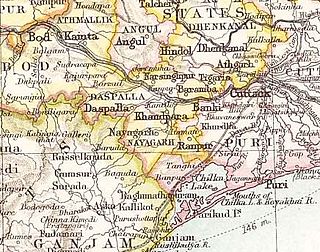
Nayagarh State was one of the princely states of India from the period of the British Raj. It was located in present-day Nayagarh district, Odisha.

Vira Pratapa Purushottama Deva was the second Gajapati emperor of Odisha who ruled from 1467 to 1497 C.E. He was the second ruler from the Suryavamsa Gajapati Empire. His father Gajapati Kapilendra Deva Routaraya chose him as his heir to rule the Gajapati Empire at the banks of river Krishna where he breathed his last. This decision infuriated his elder brother Hamvira Deva who was a battle hardened and successful warrior fulfilling the task of conquering the southern territories and expeditions against the Vijayanagara Empire as wished by his father.
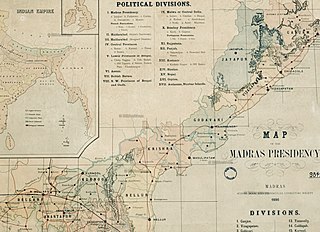
Jeypore Estate or Jeypore Zamindari was a Zamindari estate of the Madras Presidency in British India. Historically it was a kingdom known as Jeypore Kingdom, located in the highlands of the western interiors of the Kalinga region that existed from the mid-15th century to 1777 CE. It was earlier a tributary state of the Gajapati Empire and following its decline in 1540, it gained sovereignty and later became a tributary state of the Qutb Shahis until 1671. The kingdom regained degrees of semi-independence until it became a vassal state of the British in 1777. It eventually formed a part of the linguistic Orissa Province in 1936 upon transfer from the Madras Province and became a part of the independent Union of India in 1947.

The Bhoi dynasty or the Yaduvamsa dynasty were a medieval Hindu dynasty from the Indian subcontinent, which originated in the region of Odisha that reigned from 1541 to 1560 CE. Govinda Vidyadhara had usurped the throne from the later weaker Suryavamsa Gajapati Empire rulers as the kingdom started weakening but had a short-lived reign as ruling chiefs of Odisha as the ensuing internal rivalries and constant threats of invasions rendered them weak and were eventually overthrown by Mukunda Deva of Chalukya dynasty in 1560.
Hamvira Deva was an Odia prince of the Gajapati Empire in India and Gajapati ruler for a brief period. He was the eldest son of Kapilendra Deva, founder of the Gajapati Empire. He played a vital role in the military expansion of the Gajapati Empire but was bypassed in the succession order in favour of his younger half-brother Purushottama Deva.














