This article deals with the history of the country now called Zambia from prehistoric times to the present.

The culture of Angola is influenced by the Portuguese. Portugal occupied the coastal enclave Luanda, and later also Benguela, since the 16th/17th centuries, and expanded into the territory of what is now Angola in the 19th/20th centuries, ruling it until 1975. Both countries share cultural aspects: language (Portuguese) and main religion. However, present-day Angolan culture is mostly native Bantu, which was mixed with Portuguese culture. The diverse ethnic communities with their own cultural traits, traditions and native languages or dialects include the Ovimbundu, Ambundu, Bakongo, Chokwe, Avambo and other peoples.

Lunda Norte is a province of Angola. It has an area of 103,760 km² and a population of 862,566. Angola's first President, Agostino Neto, made Lucapa the provincial capital after independence, but the capital was later moved to Dundo. The province borders the Democratic Republic of Congo in the northeast and Lunda Sul in the south. The province is rich in gold and diamonds, but remains vastly underdeveloped and impoverished. UNITA used the money generated from the sale of diamonds to fund war efforts. Cuango River valley, the richest diamond area of Angola is located in the province. Mining is done by notable companies like DeBeers and Endiama. The Lunda province whose capital was Saurimo was created by the Portuguese colonial empire on July 13, 1895. It was divided into Lunda-Sul and Lunda-Norte subdivisions through a constitution act in 1978 by the People's Movement for the Liberation of Angola (MPLA) government. Iron and manganese mining are also important economic activities. It is well known for its sculptures. The most notable one is The Thinker, a sculpture of a man holding his head. It is rich in terms of flora and fauna.

Lunda Sul is a province of Angola. It has an area of 77,637 km² and a 2014 census population of 537,587. Saurimo is the capital of the province.
The pre-colonial history of the modern-day Democratic Republic of the Congo encompasses the history of the Congo Basin region up to the establishment of European colonial rule in the era of New Imperialism and particularly the creation of the Congo Free State and its expansion into the interior after 1885. As the modern territorial boundaries of the Democratic Republic of the Congo did not exist in this period, it is inseparable from the wider pre-colonial histories of Central Africa, the Great Lakes and Rift Valley as well as the Atlantic World and Swahili coast.

The Yaka are an African ethnic group found in southwestern Democratic Republic of the Congo, with Angola border to their west. They number about 300,000 and are related to the Suku people. They live in the forest and savanna region between the Kwango River and the Wamba River. They speak the Yaka language).

The Nation of Lunda was a confederation of states in what is now the Democratic Republic of Congo, north-eastern Angola, and north-western Zambia, its central state was in Katanga.
The National Assembly is the lower house and main legislative political body of the Parliament of the Democratic Republic of the Congo. It was established by the 2006 constitution.
The colonial history of Angola is usually considered to run from the appearance of the Portuguese under Diogo Cão in 1482 (Congo) or 1484 until the independence of Angola in November 1975. Settlement did not begin until Novais's establishment of São Paulo de Loanda (Luanda) in 1575, however, and the Portuguese government only formally incorporated Angola as a colony in 1655 or on May 12, 1886.
Ilunga Mbidi was a soldier and cultural hero of the Luba and Lunda people.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to Angola:

The Cuango or Kwango is a transboundary river of Angola and Democratic Republic of Congo. It is the largest left bank tributary of the Kasai River in the Congo River basin. It flows through Malanje in Angola. The Kwango River basin has large resources of diamonds in the Chitamba-Lulo Kimberlite Cluster in Lunda Norte Province, discovered in the main river channel and on flats and terraces in its flood plains.

Kasongo Lunda is a town and seat of Kasongo Lunda Territory, in the Kwango Province of the Democratic Republic of the Congo. The town lies near the border with Angola to the east, here defined by the Kwango River. As of 2012 the town was estimated to have a population of 23,820.

Communes, chiefdoms and sectors of the Democratic Republic of the Congo are the third-level administrative divisions of the Democratic Republic of the Congo.

Kwango is one of the 21 new provinces of the Democratic Republic of the Congo created in the 2015 repartitioning. Kwango, Kwilu, and Mai-Ndombe provinces are the result of the dismemberment of the former Bandundu province. Kwango was formed from the Kwango district whose town of Kenge was elevated to capital city of the new province.
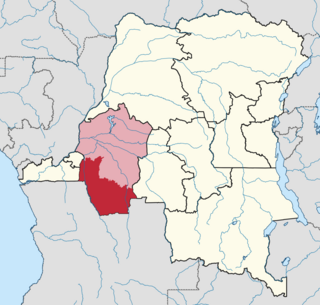
Kwango District was a district of the Congo Free State, Belgian Congo and the Democratic Republic of the Congo. It went through various changes in extent. It roughly corresponded to the present provinces of Kwilu and Kwango.
Joseph-Georges Kasongo was a Tanganyikan-born Congolese lawyer, businessman, and politician who served as the first President of the Chamber of Deputies of the Republic of the Congo. He later held office as a deputy prime minister and as a senator.
Kasongo is a town and territory in the Democratic Republic of the Congo. Kasongo may also refer to
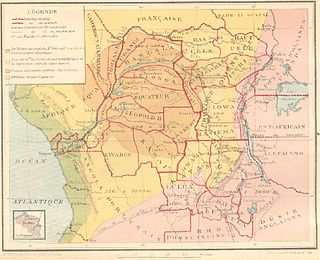
Congo-Kasaï was one of the four large provinces of the Belgian Congo defined in 1914. It was formally established in 1919, and in 1933 was divided into the new provinces of Léopoldville and Lusambo.

Dominique Diur was a Congolese and Katangese politician who was one of the founders of the CONAKAT party.