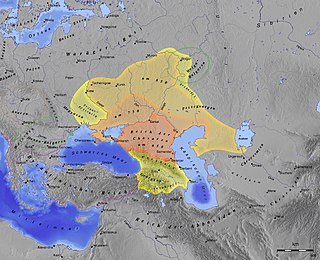
The Khazars were a nomadic Turkic people that in the late 6th-century CE established a major commercial empire covering the southeastern section of modern European Russia, southern Ukraine, Crimea, and Kazakhstan. They created what for its duration was the most powerful polity to emerge from the break-up of the Western Turkic Khaganate. Astride a major artery of commerce between Eastern Europe and Southwestern Asia, Khazaria became one of the foremost trading empires of the early medieval world, commanding the western marches of the Silk Road and playing a key commercial role as a crossroad between China, the Middle East and Kievan Rus'. For some three centuries the Khazars dominated the vast area extending from the Volga-Don steppes to the eastern Crimea and the northern Caucasus.

The Bulgars were Turkic semi-nomadic warrior tribes that flourished in the Pontic–Caspian steppe and the Volga region during the 7th century. They became known as nomadic equestrians in the Volga-Ural region, but some researchers believe that their ethnic roots can be traced to Central Asia.
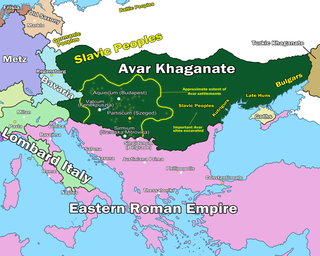
The Pannonian Avars were an alliance of several groups of Eurasian nomads of various origins. The peoples were also known as the Obri in chronicles of Rus, the Abaroi or Varchonitai, or Pseudo-Avars in Byzantine sources, and the Apar to the Göktürks. They established the Avar Khaganate, which spanned the Pannonian Basin and considerable areas of Central and Eastern Europe from the late 6th to the early 9th century.

The Severians, also Severyans, Siverians, or Siverianians were a tribe or tribal confederation of early East Slavs occupying areas to the east of the middle Dnieper River and southeast of the Danube River. They are mentioned by the Bavarian Geographer, Emperor Constantine VII (956–959), the Khazar ruler Joseph, and in the Primary Chronicle (1113).

Kubrat was the ruler of the Onogur–Bulgars, credited with establishing the confederation of Old Great Bulgaria in ca. 632. His name derived from the Turkic words qobrat — "to gather", or qurt, i.e. "wolf".
The Onoghurs or Onoğurs or Oğurs, were Turkic nomadic equestrians who flourished in the Pontic–Caspian steppe and the Volga region between 5th and 7th century, and spoke the Oghuric language.
Menumorut or Menumorout was the ruler of the lands between the rivers Mureș, Someș and Tisza at the time of the Hungarian conquest of the Carpathian Basin around 900, according to the Gesta Hungarorum, a Hungarian chronicle written after 1150 by an unidentified author, referred to as Anonymus. Historians debate whether Menumorut was an actual ruler or a fictional character created by the author, since the Gesta tells of multiple figures, including Menumorut, who are not identified in any other primary sources, and does not name any of the enemies of the invading Hungarians written of in other contemporary accounts of the invasion. According to Anonymus, Menumorut's duchy was populated primarily with Khazars and Székelys, and he acknowledged the suzerainty of the (unnamed) ruling Byzantine Emperor at the time.
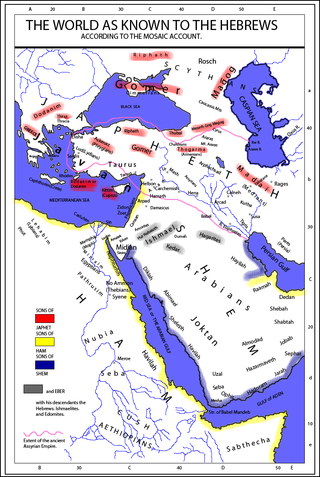
Togarmah is a figure in the "table of nations" in Genesis 10, the list of descendants of Noah that represents the peoples known to the ancient Hebrews. Togarmah is among the descendants of Japheth and is thought to represent some people located in Anatolia. Medieval sources claimed that Togarmah was the legendary ancestor of several peoples of the Caucasus

Glad was the ruler of Banat at the time of the Hungarian conquest of the Carpathian Basin around 900 AD, according to the Gesta Hungarorum. The Gesta, which was written by an author known in modern scholarship as Anonymus in the second half of the 12th century or in the early 13th century, is the earliest extant Hungarian chronicle. The Gesta did not refer to the enemies of the conquering Hungarians, who had been mentioned in earlier annals and chronicles, but wrote of a dozen persons, including Glad, who are unknown from other primary sources of the Hungarian Conquest. Therefore, modern historians debate whether Glad was an actual enemy of the conquerors or only a "fictitious person" made up by Anonymus. In Romanian historiography, based on the mention by Anonymus some 300 years later, Glad is described as one of the three Romanian dukes who ruled a historical region of present-day Romania in the early 10th century.
Bayan I reigned as the first khagan of the Avar Khaganate between 562 and 602.

Kuber was a Bulgar leader who, according to the Miracles of Saint Demetrius, liberated a mixed Bulgar and Byzantine Christian population in the 670s, whose ancestors had been transferred from the Eastern Roman Empire to the Syrmia region in Pannonia by the Avars 60 years earlier. According to a scholarly theory, he was a son of Kubrat, brother of Khan Asparukh and member of the Dulo clan.
Zabergan was the chieftain of the Kutrigur Bulgar Huns, a nomadic people of the Pontic–Caspian steppe, after Sinnion. His name is Iranian, meaning full moon. Either under pressure from incoming Avars, or in revolt against the Byzantine Empire, in the winter of 558, he led a large Kutrigur army that crossed the frozen Danube. The army was divided into three sections: one raided south far as Thermopylae, while two others the Thracian Chersonesus and the periphery of Constantinople. In March 559 Zabergan attacked Constantinople, and one part of his forces consisted of 7,000 horsemen, but Belisarius defeated him at the Battle of Melantias and he was forced to withdraw.

Sandilch was a chieftain of the Utigur Bulgars in the 6th century. The origin of the name is probably Turkic. Although he initially protested against leading the Utigurs into war against a related people, the Kutrigurs, the Byzantine Emperor Justinian I (527–565) convinced him to do so through diplomatic persuasion and bribery. The Utigurs led by Sandilch attacked the Kutrigurs, who suffered great losses.

Kutrigurs were Turkic nomadic equestrians who flourished on the Pontic–Caspian steppe in the 6th century AD. To their east were the similar Utigurs and both possibly were closely related to the Bulgars. They warred with the Byzantine Empire and the Utigurs. Towards the end of the 6th century they were absorbed by the Pannonian Avars under pressure from the Turks.

Utigurs were Turkic nomadic equestrians who flourished in the Pontic–Caspian steppe in the 6th century AD. They possibly were closely related to the Kutrigurs and Bulgars.
Grand Prince was the title used by contemporary sources to name the leader of the federation of the Hungarian tribes in the tenth century.

The Antes, or Antae, were an early East Slavic tribal polity of the 6th century CE. They lived on the lower Danube River, in the northwestern Black Sea region, and in the regions around the Don River. Scholars commonly associate the Antes with the archaeological Penkovka culture.
Mezamir was the chieftain of the Antes, an early Slavic tribal confederation in Eastern Europe, believed to have been active around the year 560, at which time the Avar expanded further into Europe. He was the son of Idariz, and had a brother, Kelagast. Mezamir was recorded by Menander Protector. Mezamir was described as "powerful", and had most likely established a Slavic confederation sometime before the 560s, which initially thwarted the Avar khaganate. At this time, the Antes were subject to the Byzantine Empire, ruled by Justinian I, with the supreme chieftain holding the Byzantine title of archon. The Antes were given old Roman towns and stipends, in exchange for securing the Danube from the Huns, and other Barbarians. At this time, the Antes held an "extensive polity, capable of military mobilization against the Avars." The Avars were ruled by khagan Bayan I, and they used to pillage the Antes land, which at the time was neighbouring the Kutrigurs, who were Avar allies. After the Avars had ravaged and plundered the Antes, Mezamir was sent as an envoy to the Avars, to negotiate the ransom of captured Antes tribesmen. At the talks, Mezamir appeared to be a "loudmouth braggart" who spoke arrogantly and rashly; upon feeling that Mezamir became more arrogant than suitable for an envoy, a Kutrigur Bulgar who was a "friend of the Avars" and "hostile to the Antes" persuaded the Khagan that:
This man is the most powerful of all amongst the Antae and is able to resist any of his enemies whomsoever. Kill him, and then you will be able to overrun the enemy's land without fear.
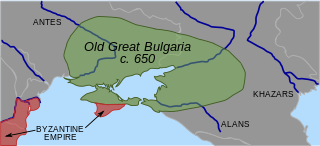
Old Great Bulgaria or Great Bulgaria, also often known by the Latin names Magna Bulgaria and Patria Onoguria, was a 7th-century Turkic nomadic empire formed by the Onogur-Bulgars on the western Pontic–Caspian steppe. Great Bulgaria was originally centered between the Dniester and lower Volga.
The Saragurs or Saraguri was a Eurasian Oghur (Turkic) nomadic tribe mentioned in the 5th and 6th centuries. They may be the Sulujie mentioned in the Chinese Book of Sui. They originated from Western Siberia and the Kazakh steppes, from where they were displaced north of the Caucasus by the Sabirs.











