Related Research Articles

Bloodletting is the withdrawal of blood from a patient to prevent or cure illness and disease. Bloodletting, whether by a physician or by leeches, was based on an ancient system of medicine in which blood and other bodily fluids were regarded as "humours" that had to remain in proper balance to maintain health. It is claimed to have been the most common medical practice performed by surgeons from antiquity until the late 19th century, a span of over 2,000 years. In Europe, the practice continued to be relatively common until the end of the 18th century. The practice has now been abandoned by modern-style medicine for all except a few very specific medical conditions. In the overwhelming majority of cases, the historical use of bloodletting was harmful to patients.

A central venous catheter (CVC), also known as a central line(c-line), central venous line, or central venous access catheter, is a catheter placed into a large vein. It is a form of venous access. Placement of larger catheters in more centrally located veins is often needed in critically ill patients, or in those requiring prolonged intravenous therapies, for more reliable vascular access. These catheters are commonly placed in veins in the neck, chest, groin, or through veins in the arms.

Phlebotomy is the process of making a puncture in a vein, usually in the arm, with a cannula for the purpose of drawing blood. The procedure itself is known as a venipuncture, which is also used for intravenous therapy. A person who performs a phlebotomy is called a phlebotomist, although most doctors, nurses, and other technicians can also carry out a phlebotomy. In contrast, phlebectomy is the removal of a vein.

Intravenous therapy is a medical technique that administers fluids, medications and nutrients directly into a person's vein. The intravenous route of administration is commonly used for rehydration or to provide nutrients for those who cannot, or will not—due to reduced mental states or otherwise—consume food or water by mouth. It may also be used to administer medications or other medical therapy such as blood products or electrolytes to correct electrolyte imbalances. Attempts at providing intravenous therapy have been recorded as early as the 1400s, but the practice did not become widespread until the 1900s after the development of techniques for safe, effective use.

In medicine, venipuncture or venepuncture is the process of obtaining intravenous access for the purpose of venous blood sampling or intravenous therapy. In healthcare, this procedure is performed by medical laboratory scientists, medical practitioners, some EMTs, paramedics, phlebotomists, dialysis technicians, and other nursing staff. In veterinary medicine, the procedure is performed by veterinarians and veterinary technicians.

A Vacuum blood collection tube is a sterile glass or plastic test tube with a colored rubber stopper creating a vacuum seal inside of the tube, facilitating the drawing of a predetermined volume of liquid. Vacutainer tubes may contain additives designed to stabilize and preserve the specimen prior to analytical testing. Tubes are available with a safety-engineered stopper, with a variety of labeling options and draw volumes. The color of the top indicates the additives in the vial.

A hypodermic needle, one of a category of medical tools which enter the skin, called sharps, is a very thin, hollow tube with one sharp tip. It is commonly used with a syringe, a hand-operated device with a plunger, to inject substances into the body or extract fluids from the body. Large-bore hypodermic intervention is especially useful in catastrophic blood loss or treating shock.
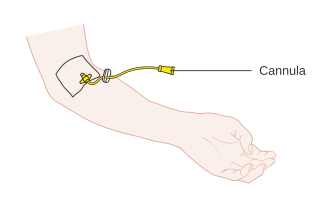
A cannula is a tube that can be inserted into the body, often for the delivery or removal of fluid or for the gathering of samples. In simple terms, a cannula can surround the inner or outer surfaces of a trocar needle thus extending the effective needle length by at least half the length of the original needle. Its size mainly ranges from 14 to 24 gauge. Different-sized cannula have different colours as coded.
In surgery, a percutaneous procedure is any medical procedure or method where access to inner organs or other tissue is done via needle-puncture of the skin, rather than by using an "open" approach where inner organs or tissue are exposed.

Ficoll is a neutral, highly branched, high-mass, hydrophilic polysaccharide which dissolves readily in aqueous solutions. Ficoll radii range from 2-7 nm. It is prepared by reaction of the polysaccharide with epichlorohydrin. Ficoll is a registered trademark owned by GE Healthcare companies.

Bone marrow examination refers to the pathologic analysis of samples of bone marrow obtained by bone marrow biopsy and bone marrow aspiration. Bone marrow examination is used in the diagnosis of a number of conditions, including leukemia, multiple myeloma, lymphoma, anemia, and pancytopenia. The bone marrow produces the cellular elements of the blood, including platelets, red blood cells and white blood cells. While much information can be gleaned by testing the blood itself, it is sometimes necessary to examine the source of the blood cells in the bone marrow to obtain more information on hematopoiesis; this is the role of bone marrow aspiration and biopsy.
In human anatomy, the median cubital vein is a superficial vein of the upper limb. It lies in the cubital fossa superficial to the bicipital aponeurosis. It connects the cephalic vein and the basilic vein. It becomes prominent when pressure is applied. It is routinely used for venipuncture and as a site for an intravenous cannula. This is due to its particularly wide lumen, and its tendency to remain stationary upon needle insertion.
Infiltration is the diffusion or accumulation of foreign substances in amounts excess of the normal. The material collected in those tissues or cells is called infiltrate.
Vascular access refers to a rapid, direct method of introducing or removing devices or chemicals from the bloodstream. In hemodialysis, vascular access is used to remove the patient's blood so that it can be filtered through the dialyzer. Three primary methods are used to gain access to the blood: an intravenous catheter, an arteriovenous fistula (AV) or a synthetic graft. In the latter two, needles are used to puncture the graft or fistula each time dialysis is performed.

A tourniquet is a device that is used to apply pressure to a limb or extremity in order to stop the flow of blood. It may be used in emergencies, in surgery, or in post-operative rehabilitation. A tourniquet is also used by the phlebotomist to assess and determine the location of a suitable vein for venipuncture. Proper application of a tourniquet will partially impede venous blood flow back toward the heart and cause the blood to temporarily pool in the vein so the vein is more prominent and the blood is more easily obtained. The tourniquet is applied three to four inches above the needle insertion point and should remain in place no longer than one minute to prevent hemoconcentration.

A winged infusion set—also possibly known as "butterfly" or "scalp vein" set—is a device specialized for venipuncture: i.e. for accessing a superficial vein or artery for either intravenous injection or phlebotomy. It consists, from front to rear, of a hypodermic needle, two bilateral flexible "wings", flexible small-bore transparent tubing, and lastly a connector. This connector attaches to another device: e.g. syringe, vacuum tube holder/hub, or extension tubing from an infusion pump or gravity-fed infusion/transfusion bag/bottle.

In medicine, a port is a small medical appliance that is installed beneath the skin. A catheter connects the port to a vein. Under the skin, the port has a septum through which drugs can be injected and blood samples can be drawn many times, usually with less discomfort for the patient than a more typical "needle stick".
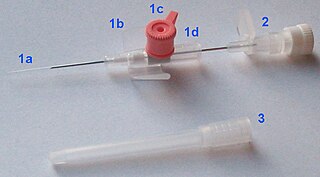
In medicine, a peripheral venous catheter (PVC), peripheral venous line, peripheral venous access catheter, or peripheral intravenous catheter (PIVC), is a catheter placed into a peripheral vein for venous access to administer intravenous therapy such as medication fluids.

Hematophagy is the practice by certain animals of feeding on blood. Since blood is a fluid tissue rich in nutritious proteins and lipids that can be taken without great effort, hematophagy is a preferred form of feeding for many small animals, such as worms and arthropods. Some intestinal nematodes, such as Ancylostomatids, feed on blood extracted from the capillaries of the gut, and about 75 percent of all species of leeches, a free-living worm, are hematophagous. Some fish, such as lampreys and candirus, and mammals, especially the vampire bats, and birds, such as the vampire finches, hood mockingbirds, the Tristan thrush, and oxpeckers also practise hematophagy.

In medicine, sampling is gathering of matter from the body to aid in the process of a medical diagnosis and/or evaluation of an indication for treatment, further medical tests or other procedures. In this sense, the sample is the gathered matter, and the sampling tool or sampler is the person or material to collect the sample.