
The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden, and the North and Central European Plain.

The English Channel, also known as the Channel, is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that separates Southern England from northern France. It links to the southern part of the North Sea by the Strait of Dover at its northeastern end. It is the busiest shipping area in the world.

In physical geography, a fjord or fiord is a long, narrow sea inlet with steep sides or cliffs, created by a glacier. Fjords exist on the coasts of Antarctica, the Arctic, and surrounded landmasses of the northern and southern hemispheres. Norway's coastline is estimated to be 29,000 km (18,000 mi) long with its nearly 1,200 fjords, but only 2,500 km (1,600 mi) long excluding the fjords.

The IJsselmeer, also known as Lake IJssel in English, is a closed-off inland bay in the central Netherlands bordering the provinces of Flevoland, North Holland and Friesland. It covers an area of 1,100 km2 (420 sq mi) with an average depth of 4.5 m (15 ft). The river IJssel, which is what the lake was named after flows into the IJsselmeer.
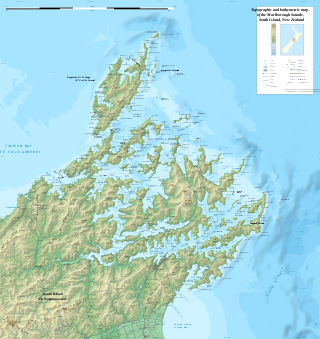
The Marlborough Sounds are an extensive network of sea-drowned valleys at the northern end of the South Island of New Zealand. The Marlborough Sounds were created by a combination of land subsidence and rising sea levels. According to Māori mythology, the sounds are the prows of the many sunken waka of Aoraki.

Moreton Bay is a bay located on the eastern coast of Australia 14 kilometres (8.7 mi) from central Brisbane, Queensland. It is one of Queensland's most important coastal resources. The waters of Moreton Bay are a popular destination for recreational anglers and are used by commercial operators who provide seafood to market.

Oulu is a city in Finland and the regional capital of North Ostrobothnia. It is located on the northwestern coast of the country at the mouth of the River Oulu. The population of Oulu is approximately 215,000, while the sub-region has a population of approximately 263,000. It is the 5th most populous municipality in Finland, and the fourth most populous urban area in the country. Oulu is also the most populous city in Northern Finland.

Port Phillip or Port Phillip Bay is a horsehead-shaped enclosed bay on the central coast of southern Victoria, Australia. The bay opens into the Bass Strait via a short, narrow channel known as The Rip, and is completely surrounded by localities of Victoria's two largest cities — metropolitan Greater Melbourne in the bay's main eastern portion north of the Mornington Peninsula, and the city of Greater Geelong in the much smaller western portion north of the Bellarine Peninsula. Geographically, the bay covers 1,930 km2 (750 sq mi) and the shore stretches roughly 264 km (164 mi), with the volume of water around 25 km3 (6.0 cu mi). Most of the bay is navigable, although it is extremely shallow for its size — the deepest portion is only 24 m (79 ft) and half the bay is shallower than 8 m (26 ft). Its waters and coast are home to seals, whales, dolphins, corals and many kinds of seabirds and migratory waders.

Poole Harbour is a large natural harbour in Dorset, southern England, with the town of Poole on its shores. The harbour is a drowned valley (ria) formed at the end of the last ice age and is the estuary of several rivers, the largest being the Frome. The harbour has a long history of human settlement stretching to pre-Roman times. The harbour is extremely shallow, with one main dredged channel through the harbour, from the mouth to Holes Bay.

Lake Onega is a lake in northwestern Russia, on the territory of the Republic of Karelia, Leningrad Oblast and Vologda Oblast. It belongs to the basin of the Baltic Sea, and is the second-largest lake in Europe after Lake Ladoga, slightly smaller than Lebanon. The lake is fed by about 50 rivers and is drained by the Svir.

Hailuoto is a Finnish island in the northern Baltic Sea and a municipality in Northern Ostrobothnia region. The population of Hailuoto is 948, making it the smallest municipality in Northern Ostrobothnia and the former Oulu Province in terms of population. The municipality covers an area of 205.65 km2 (79.40 sq mi) of which 1.70 km2 (0.66 sq mi) is inland water. The population density is 4.61/km2 (11.9/sq mi). Of all the Finnish sea islands, Hailuoto is the third largest after Fasta Åland and Kimitoön.

Lake Wawasee, formerly Turkey Lake, is a natural lake southeast of Syracuse in Kosciusko County, Indiana, United States. It is the largest natural lake wholly contained within Indiana. It is located just east of Indiana State Road 13.

Miramichi Bay is an estuary located on the west coast of the Gulf of St. Lawrence in New Brunswick, at the mouth of the Miramichi River. Miramichi Bay is separated into the "inner bay" and the "outer bay", with the division being a line of uninhabited barrier islands which are continually reshaped by ocean storms. The largest of these islands is the uninhabited Portage Island, which was broken in two during a violent storm in the 1950s. The islands provide some protection to the inner bay from ocean storms in the Gulf of St. Lawrence.

The Bothnian Bay or Bay of Bothnia is the northernmost part of the Gulf of Bothnia, which is in turn the northern part of the Baltic Sea. The land holding the bay is still rising after the weight of ice-age glaciers has been removed, and within 2,000 years the bay will be a large freshwater lake since its link to the south Kvarken is mostly less than 20 metres (66 ft) deep. The bay today is fed by several large rivers, and is relatively unaffected by tides, so has low salinity. It freezes over each year for up to six months. Compared to other parts of the Baltic, it has little plant or animal life.

Wheelers Bay is a small bay on the south-east coast of the Isle of Wight, England. It lies to the east of Ventnor. It faces south-east towards the English Channel, its shoreline is 300 yards (270 m) in length. A 90-yard (82 m) section of the bay, to the side of the slipway, is used as dry-storage for boats; in recent years this has been targeted by thieves. The bay is home to an open-air café known as The Seapot.

The Irish Sea is a 46,007 km2 (17,763 sq mi) body of water that separates the islands of Ireland and Great Britain. It is linked to the Celtic Sea in the south by St George's Channel and to the Inner Seas off the West Coast of Scotland in the north by the North Channel. Anglesey, North Wales, is the largest island in the Irish Sea, followed by the Isle of Man. The term Manx Sea may occasionally be encountered.

The Prickly Pear Cays, sometimes spelt as Prickley Pear Cays, are a small pair of uninhabited islands about six miles from Road Bay, Anguilla, in the Leeward Islands of the Caribbean. They are divided by a narrow boat channel between Prickly Pear East and Prickly Pear West. Prickly Pear Cays were classified as 'wildlands' by the "Eastern Caribbean Natural Area Management Programme" (ECNAMP). In addition, Prickly Pear Cays are one of six marine protected areas of Anguilla.
Kahvankari is a small uninhabited island in the Finnish sector of the Bay of Bothnia offshore from the city of Oulu.




















