Related Research Articles
Antioxidants are compounds that inhibit oxidation, a chemical reaction that can produce free radicals and chain reactions that may damage the cells of organisms. Antioxidants such as thiols or ascorbic acid may act to inhibit these reactions. To balance oxidative stress, plants and animals maintain complex systems of overlapping antioxidants, such as glutathione.

Lycopene is a bright red carotenoid hydrocarbon found in tomatoes and other red fruits and vegetables, such as red carrots, watermelons, grapefruits, and papayas. It is not present in strawberries or cherries. Although lycopene is chemically a carotene, it has no vitamin A activity.

A mango is an edible stone fruit produced by the tropical tree Mangifera indica which is believed to have originated from the region between northwestern Myanmar, Bangladesh, and northeastern India. M. indica has been cultivated in South and Southeast Asia since ancient times resulting in two distinct types of modern mango cultivars: the "Indian type" and the "Southeast Asian type". Other species in the genus Mangifera also produce edible fruits that are also called "mangoes", the majority of which are found in the Malesian ecoregion.

A lime is a citrus fruit, which is typically round, green in color, 3–6 centimetres (1.2–2.4 in) in diameter, and contains acidic juice vesicles.

Carotenoids, also called tetraterpenoids, are yellow, orange, and red organic pigments that are produced by plants and algae, as well as several bacteria, and fungi. Carotenoids give the characteristic color to pumpkins, carrots, parsnips, corn, tomatoes, canaries, flamingos, salmon, lobster, shrimp, and daffodils. Carotenoids can be produced from fats and other basic organic metabolic building blocks by all these organisms. The only land dwelling arthropods known to produce carotenoids are aphids, and spider mites, which acquired the ability and genes from fungi. It is also produced by endosymbiotic bacteria in whiteflies. Carotenoids from the diet are stored in the fatty tissues of animals, and exclusively carnivorous animals obtain the compounds from animal fat. In the human diet, absorption of carotenoids is improved when consumed with fat in a meal. Cooking carotenoid-containing vegetables in oil and shredding the vegetable both increase carotenoid bioavailability.

Inositol, or more precisely myo-inositol, is a carbocyclic sugar that is abundant in the brain and other mammalian tissues; it mediates cell signal transduction in response to a variety of hormones, neurotransmitters, and growth factors and participates in osmoregulation.
Steatorrhea is the presence of excess fat in feces. Stools may be bulky and difficult to flush, have a pale and oily appearance, and can be especially foul-smelling. An oily anal leakage or some level of fecal incontinence may occur. There is increased fat excretion, which can be measured by determining the fecal fat level. The definition of how much fecal fat constitutes steatorrhea has not been standardized.

Synephrine, or, more specifically, p-synephrine, is an alkaloid, occurring naturally in some plants and animals, and also in approved drugs products as its m-substituted analog known as neo-synephrine. p-Synephrine and m-synephrine are known for their longer acting adrenergic effects compared to epinephrine and norepinephrine. This substance is present at very low concentrations in common foodstuffs such as orange juice and other orange products, both of the "sweet" and "bitter" variety. The preparations used in traditional Chinese medicine (TCM), also known as Zhi Shi, are the immature and dried whole oranges from Citrus aurantium. Extracts of the same material or purified synephrine are also marketed in the US, sometimes in combination with caffeine, as a weight-loss-promoting dietary supplement for oral consumption. While the traditional preparations have been in use for millennia as a component of TCM-formulas, synephrine itself is not an approved OTC drug. As a pharmaceutical, m-synephrine (phenylephrine) is still used as a sympathomimetic, mostly by injection for the treatment of emergencies such as shock, and rarely orally for the treatment of bronchial problems associated with asthma and hay-fever.

Limonene is a colorless liquid aliphatic hydrocarbon classified as a cyclic monoterpene, and is the major component in the oil of citrus fruit peels. The D-isomer, occurring more commonly in nature as the fragrance of oranges, is a flavoring agent in food manufacturing. It is also used in chemical synthesis as a precursor to carvone and as a renewables-based solvent in cleaning products. The less common L-isomer has a piny, turpentine-like odor, and is found in the edible parts of such plants as caraway, dill, and bergamot orange plants.
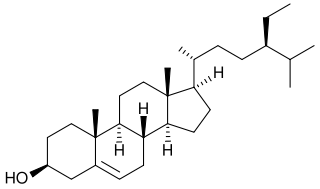
Phytosterols are phytosteroids, similar to cholesterol, that serve as structural components of biological membranes of plants. They encompass plant sterols and stanols. More than 250 sterols and related compounds have been identified. Free phytosterols extracted from oils are insoluble in water, relatively insoluble in oil, and soluble in alcohols.
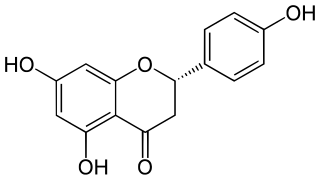
Naringenin is a flavorless, colorless flavanone, a type of flavonoid. It is the predominant flavanone in grapefruit, and is found in a variety of fruits and herbs.

Chlorogenic acid (CGA) is the ester of caffeic acid and (−)-quinic acid, functioning as an intermediate in lignin biosynthesis. The term "chlorogenic acids" refers to a related polyphenol family of esters, including hydroxycinnamic acids with quinic acid.

Hesperidin is a flavanone glycoside found in citrus fruits. Its aglycone form is called hesperetin. Its name is derived from the word "hesperidium", for fruit produced by citrus trees.
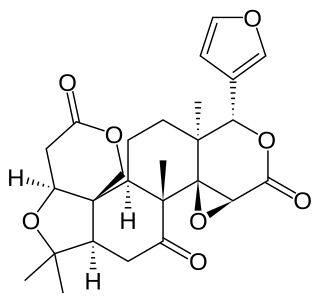
Limonin is a limonoid, and a bitter, white, crystalline substance found in citrus and other plants. It is also known as limonoate D-ring-lactone and limonoic acid di-delta-lactone. Chemically, it is a member of the class of compounds known as furanolactones.
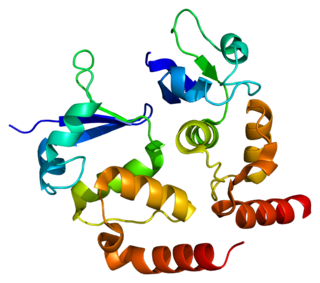
Potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily D member 3 also known as Kv4.3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KCND3 gene. It contributes to the cardiac transient outward potassium current (Ito1), the main contributing current to the repolarizing phase 1 of the cardiac action potential.

2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD) is a polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxin (sometimes shortened, though inaccurately, to simply 'dioxin') with the chemical formula C12H4Cl4O2. Pure TCDD is a colorless solid with no distinguishable odor at room temperature. It is usually formed as an unwanted product in burning processes of organic materials or as a side product in organic synthesis.
Alicyclobacillus is a genus of Gram-variable, rod-shaped, spore-forming bacteria. The bacteria are able to grow in acidic conditions, while the spores are able to survive typical pasteurization procedures.
Rectal discharge is intermittent or continuous expression of liquid from the anus. Normal rectal mucus is needed for proper excretion of waste. Otherwise, this is closely related to types of fecal incontinence but the term rectal discharge does not necessarily imply degrees of incontinence. Types of fecal incontinence that produce a liquid leakage could be thought of as a type of rectal discharge.

Homosildenafil is a synthetic drug which acts as a phosphodiesterase inhibitor. It is an analog of sildenafil and vardenafil. Homosildenafil was first identified as an adulterant in sex enhancement products in 2003 and was more recently detected in dietary supplements.
Penicillium pinophilum is a species of fungus in the genus Penicillium which was isolated from a radio set in Papua New Guinea. Penicillium pinophilum produces 3-O-methylfunicone and mycophenolic acid
References
- ↑ Ho Ling K, Nichols PD, But PP (2009). "Chapter 1 fish-induced keriorrhea". Adv. Food Nutr. Res. Advances in Food and Nutrition Research. 57: 1–52. doi:10.1016/S1043-4526(09)57001-5. ISBN 9780123744401. PMID 19595384.
- ↑ Robles, I; Vásquez, JM; Loehnert, R; Espino, A; Biel, F; Correa, I; Gobelet, J; Sáenz, M; Saenz, C; Sáenz, R (Feb 2012). "[Orange oily anal leakage: a new entity linked to dietary changes]". Gastroenterologia y Hepatologia. 35 (2): 74–7. doi:10.1016/j.gastrohep.2011.11.009. PMID 22266298.