Kupel [1] | |
|---|---|
| Total population | |
| 13.000 [1] | |
| Regions with significant populations | |
| Highland Papua | |
| Languages | |
| Ketengban | |
| Religion | |
| Christianity [2] | |
| Related ethnic groups | |
| Melanesians |
The Ketengban or also known as Kupel is an ethnic group who inhabit mountainous areas in Pegunungan Bintang Regency , Highland Papua. This ethnic group is one of the seven major ethnic groups in the Pegunungan Bintang Regency. [3]
Ketengban, also known as Kupel, is a Papuan languages spoken in the Pegunungan Bintang Regency, Highland Papua.
The dialects of this language are Okbab (Okbap), Bime, Onya (Una), Omban (kamume), and Sirkai. [4]

The indigenous peoples of West Papua in Indonesia and Papua New Guinea, commonly called Papuans, are Melanesians. There is genetic evidence for two major historical lineages in New Guinea and neighboring islands: a first wave from the Malay Archipelago perhaps 50,000 years ago when New Guinea and Australia were a single landmass called Sahul and, much later, a wave of Austronesian people from the north who introduced Austronesian languages and pigs about 3,500 years ago. They also left a small but significant genetic trace in many coastal Papuan peoples.

Western New Guinea, also known as Papua, Indonesian New Guinea, or Indonesian Papua, is the western Indonesian half of the island of New Guinea. Since the island is alternatively named as Papua, the region is also called West Papua.

The Star Mountains are a mountain range in western Papua New Guinea and the eastern end of Highland Papua, Indonesia, stretching from the eastern end of Indonesia to the Hindenburg Range in Papua New Guinea.

Christmas in Indonesia is celebrated with various traditions throughout the country. Indonesia has approximately 28 million Christians. In regions with a Christian majority, there are Christmas celebrations with ceremonies and local food. In big cities, shopping centres are decorated with plastic Christmas trees and Sinterklas. Many local television channels broadcast Christmas musical concerts and the annual national Christmas celebration organised by the government. In addition to traditional foods, there are also unique Christmas Day foods, such as cookies, like nastar and kastengel, or 'putri salju'.

Pegunungan Bintang Regency, or Bintang Mountains Regency is a regency in the Indonesian province of Highland Papua. It covers an area of 15,683 km2, and had a population of 65,434 at the 2010 Census and 77,872 at the 2020 Census. The administrative centre is Oksibil.
Hatam is a divergent language spoken on the island of New Guinea, specifically in the Indonesian province of West Papua.
Murkim is a Papuan language of Western New Guinea, near its relatives Lepki and Kembra. Though spoken by fewer than 300 people, it is being learned by children. It is spoken in Murkim District, Pegunungan Bintang Regency, Papua Province, Indonesia.
Eipo (Eipomek), or Lik, is a Mek language of the eastern highlands of Eipumek District, Pegunungan Bintang Regency, West Papua. It spoken by the Eipo people who live along the Eipo River. A large percentage of its vocabulary is shared with Una and Tanime, and they form one dialect area.
Ngalum is the most populous of the Ok languages of Western New Guinea and Papua New Guinea.
Kimki (Aipki) or Sukubatom (Sukubatong) is a South Pauwasi language of Batom District, Pegunungan Bintang Regency, Papua, Indonesia. Foley classifies Kimki as a language isolate, although he notes some similarities with Murkim. Usher demonstrates a connection to the other South Pauwasi languages.
Towei (Towe) is a Western Pauwasi language of West New Guinea. It is spoken in Towe Hitam village, Towe District, Pegunungan Bintang Regency.
Burumakok is a minor Ok language of West Papua. Despite having just forty speakers, there is limited bilingualism and the language is not considered endangered.
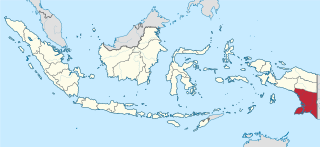
South Papua, officially the South Papua Province, is an Indonesian province located in the southern portion of Papua, following the borders of Papuan customary region of Anim Ha. Formally established on 11 November 2022 and including the four most southern regencies that were previously part of the province of Papua and before 11 December 2002 were all part of a larger Merauke Regency, it covers an area of 131,493 km2 and had a population of 517,623 according to the official estimates for mid 2021.

Central Papua, officially the Central Papua Province is an Indonesian province located in the central region of Western New Guinea. It was formally established on 11 November 2022 from the former eight western regencies of the province of Papua. It covers an area of 66,130.49 km2 and had an estimated population of about 1,409,000 in mid 2021. It is bordered by the Indonesian provinces of West Papua to the west, the residual Papua to the north, and by Highland Papua and South Papua to the east. The designated administrative capital, Nabire, is the second largest town in Central Papua, the economic centre of the province, and the seat of the Central Papua provincial government.

Highland Papua is a province of Indonesia, which roughly follows the borders of Papuan customary region of Lano-Pago, shortened to La Pago. It covers an area of 108,476 km2 (41,883 sq mi) and had a population of 1,408,641 according to the official estimates as at mid 2021.

Wambon also known as Wambon Tekamerop, are an indigenous people that inhabit the lowlands in the southern part of Papua New Guinea. Wambon people are the largest ethnic group in Boven Digoel Regency.
Yaur is an ethnic group who inhabit the northern coastal area of Nabire Regency precisely in Yaur District. The area inhabited by the Yaur people is included in the Saireri customary territory which includes the northern coast of Nabire, Biak Islands, and Yapen Island.

The Marori is an of the ethnic group who inhabit the southern coastal area of Merauke Regency precisely in Kampung Wasur, Merauke District. This ethnic group bears many similarities to the larger Marind and is sometimes considered a sub-ethnic of the Marind.

Southwest Papua is a province of Indonesia, and is a fraction of Western New Guinea. Despite being named southwest, it is a misnomer and this province is actually located in the northwest edge of Papua. The area that belongs to this province includes the Greater Sorong area which consists of Sorong City, Sorong Regency, South Sorong Regency, Maybrat Regency, Tambrauw Regency, and Raja Ampat Regency. The Draft Law (RUU) on the Establishment of the Southwest Papua Province has been passed into law and becomes the 38th province in Indonesia.