
The perineum is the space between the anus and scrotum in the male and between the anus and the vulva in the female. The perineum is the region of the body between the pubic symphysis and the coccyx, including the perineal body and surrounding structures. There is some variability in how the boundaries are defined. The perianal area is a subset of the perineum.

Atrioventricular septal defect (AVSD) or atrioventricular canal defect (AVCD), also known as "common atrioventricular canal" (CAVC) or "endocardial cushion defect" (ECD), is characterized by a deficiency of the atrioventricular septum of the heart. It is caused by an abnormal or inadequate fusion of the superior and inferior endocardial cushions with the mid portion of the atrial septum and the muscular portion of the ventricular septum.

The VACTERL association refers to a recognized group of birth defects which tend to co-occur. Note that this pattern is a recognized association, as opposed to a syndrome, because there is no known pathogenetic cause to explain the grouped incidence.

The external anal sphincter is a flat plane of skeletal muscle fibers, elliptical in shape and intimately adherent to the skin surrounding the margin of the anus.

The internal anal sphincter, IAS, is a ring of smooth muscle that surrounds about 2.5–4.0 cm of the anal canal; its inferior border is in contact with, but quite separate from, the external anal sphincter.
Dogs, as with all mammals, have natural odors. Natural dog odor can be unpleasant to dog owners especially when dogs are kept inside the home, as some people are not used to being exposed to the natural odor of a non-human species living in proximity to them. Dogs may also develop unnatural odors as a result of skin disease or other disorders or may become contaminated with odors from other sources in their environment.

The anal sinuses are furrows in the anal canal, that separate the anal columns from one another. The anal sinuses end below in small valve-like folds, termed anal valves.
Goodsall's rule relates the external opening of an anal fistula to its internal opening. It states that if the perianal skin opening is posterior to the transverse anal line, the fistulous tract will open into the anal canal in the midline posteriorly, sometimes taking a curvilinear course. A perianal skin opening anterior to the transverse anal line is usually associated with a radial fistulous tract.

The rectum is the final straight portion of the large intestine in humans and some other mammals, and the gut in others. The adult human rectum is about 12 centimetres (4.7 in) long, and begins at the rectosigmoid junction, the end of the sigmoid colon, at the level of the third sacral vertebra or the sacral promontory depending upon what definition is used. Its caliber is similar to that of the sigmoid colon at its commencement, but it is dilated near its termination, forming the rectal ampulla. It terminates at the level of the anorectal ring or the dentate line, again depending upon which definition is used. In humans, the rectum is followed by the anal canal which is about 4 centimetres (1.6 in) long, before the gastrointestinal tract terminates at the anal verge. The word rectum comes from the Latin rectum intestinum, meaning straight intestine.
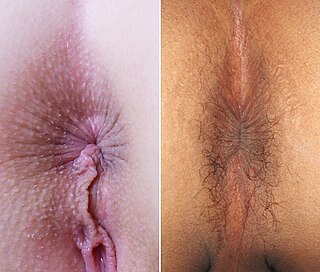
The human anus is the external opening of the rectum. Two sphincters control the exit of feces from the body during an act of defecation, which is the primary function of the anus. These are the internal anal sphincter and the external anal sphincter, which are circular muscles that normally maintain constriction of the orifice and which relaxes as required by normal physiological functioning. The inner sphincter is involuntary and the outer is voluntary. It is located behind the perineum which is located behind the vagina in females and behind the scrotum in males.
Anal dysplasia is a pre-cancerous condition which occurs when the lining of the anal canal undergoes abnormal changes. It can be classified as low-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions (LSIL) and high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions (HSIL). Most cases are not associated with symptoms, but people may notice lumps in and around the anus.

A siphonal notch is a feature of the shell anatomy in some sea snails, marine gastropod mollusks.
Rectal discharge is intermittent or continuous expression of liquid from the anus. Normal rectal mucus is needed for proper excretion of waste. Otherwise, this is closely related to types of fecal incontinence but the term rectal discharge does not necessarily imply degrees of incontinence. Types of fecal incontinence that produce a liquid leakage could be thought of as a type of rectal discharge.
Anismus is the failure of the normal relaxation of pelvic floor muscles during attempted defecation. It can occur in both children and adults, and in both men and women. It can be caused by physical defects or it can occur for other reasons or unknown reasons. Anismus that has a behavioral cause could be viewed as having similarities with parcopresis, or psychogenic fecal retention.
In fecal incontinence (FI), surgery may be carried out if conservative measures alone are not sufficient to control symptoms. There are many surgical options described for FI, and they can be considered in 4 general groups.
A rectovestibular fistula, also referred to simply as a vestibular fistula, is an anorectal congenital disorder where an abnormal connection (fistula) exists between the rectum and the vulval vestibule of the female genitalia.

The anal sulcus, also called the anal sinus or anal canal, in Gastropods is a notch, a shelly tube at the top of the aperture. It is the first notch close to the suture. It houses the anal siphon through which the snail expels water and waste products.











