Related Research Articles

The Euphrates is the longest and one of the most historically important rivers of Western Asia. Together with the Tigris, it is one of the two defining rivers of Mesopotamia. Originating in Turkey, the Euphrates flows through Syria and Iraq to join the Tigris in the Shatt al-Arab in Iraq, which empties into the Persian Gulf.

A dam is a barrier that stops or restricts the flow of surface water or underground streams. Reservoirs created by dams not only suppress floods but also provide water for activities such as irrigation, human consumption, industrial use, aquaculture, and navigability. Hydropower is often used in conjunction with dams to generate electricity. A dam can also be used to collect or store water which can be evenly distributed between locations. Dams generally serve the primary purpose of retaining water, while other structures such as floodgates or levees are used to manage or prevent water flow into specific land regions.
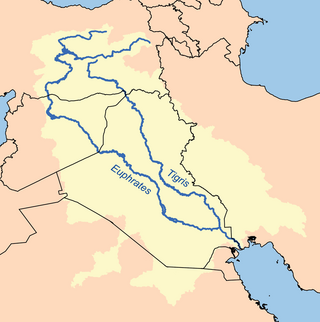
The Tigris–Euphrates river system is a large river system in Western Asia that flows into the Persian Gulf. Its primary rivers are the Tigris and Euphrates, along with smaller tributaries.

The Kura is an east-flowing river south of the Greater Caucasus Mountains which drains the southern slopes of the Greater Caucasus east into the Caspian Sea. It also drains the north side of the Lesser Caucasus, while its main tributary, the Aras, drains the south side of those mountains. Starting in northeastern Turkey, the Kura flows through Turkey to Georgia, then to Azerbaijan, where it receives the Aras as a right tributary, and enters the Caspian Sea at Neftçala. The total length of the river is 1,515 kilometres (941 mi).

Hydroelectricity, or hydroelectric power, is electricity generated from hydropower. Hydropower supplies 15% of the world's electricity, almost 4,210 TWh in 2023, which is more than all other renewable sources combined and also more than nuclear power. Hydropower can provide large amounts of low-carbon electricity on demand, making it a key element for creating secure and clean electricity supply systems. A hydroelectric power station that has a dam and reservoir is a flexible source, since the amount of electricity produced can be increased or decreased in seconds or minutes in response to varying electricity demand. Once a hydroelectric complex is constructed, it produces no direct waste, and almost always emits considerably less greenhouse gas than fossil fuel-powered energy plants. However, when constructed in lowland rainforest areas, where part of the forest is inundated, substantial amounts of greenhouse gases may be emitted.

The Gunnison River is located in western Colorado, United States and is one of the largest tributaries of the Colorado River.

Shushtar is a city in the Central District of Shushtar County, Khuzestan province, Iran, serving as capital of both the county and the district.

The Mokelumne River is a 95-mile (153 km)-long river in northern California in the United States. The river flows west from a rugged portion of the central Sierra Nevada into the Central Valley and ultimately the Sacramento–San Joaquin River Delta, where it empties into the San Joaquin River-Stockton Deepwater Shipping Channel. Together with its main tributary, the Cosumnes River, the Mokelumne drains 2,143 square miles (5,550 km2) in parts of five California counties. Measured to its farthest source at the head of the North Fork, the river stretches for 157 miles (253 km).
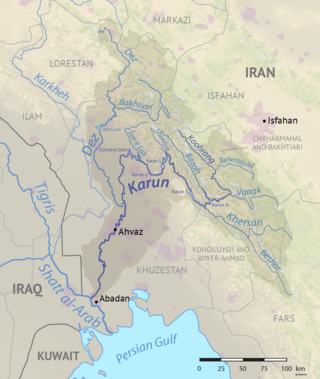
The Karun is the Iranian river with the highest water flow, and the country's only navigable river. It is 950 km (590 mi) long. The Karun rises in the Zard Kuh mountains of the Bakhtiari district in the Zagros Range, receiving many tributaries, such as the Dez and the Kuhrang. It passes through the city of Ahvaz, the capital of the Khuzestan Province of Iran, before emptying to its mouth into Arvand Rud.

The Little Zab or Lower Zab is a river that originates in Iran and joins the Tigris just south of Al Zab in the Kurdistan region of Iraq. The Little Zab is approximately 400 kilometres (250 mi) long and drains an area of about 22,000 square kilometres (8,500 sq mi). The river is fed by rainfall and snowmelt, resulting in a peak discharge in the spring and low water in the summer and early fall. Two dams built on the Little Zab regulate the river flow, providing water for irrigation and generating hydroelectricity. The Zagros Mountains have been populated since at least the Lower Palaeolithic, but the earliest archaeological site in the Little Zab basin, Barda Balka, dates to the Middle Palaeolithic. Human occupation of the Little Zab basin has been attested for every period since then.

Skinner Reservoir, also known as Lake Skinner, is a reservoir in western Riverside County, California, located at the foot of Bachelor Mountain in the Auld Valley, approximately 10 miles (16 km) northeast of Temecula. It was created in 1973 by the construction of the Skinner Clearwell Dam on Tucalota Creek, and currently has a capacity of 44,200 acre-feet (54,500,000 m3). Located north of Rancho California Road near the Temecula Valley Wine Country, The address of the reservoir is: 37701 Warren Road, Temecula, CA 92592.
Three Gorges Reservoir Region, including 25 county-level divisions of Chongqing municipality and Hubei province, is the region directly or indirectly involved in the submersion of the water storage of the reservoir region of the Three Gorges Dam.

The environmental impact of reservoirs comes under ever-increasing scrutiny as the global demand for water and energy increases and the number and size of reservoirs increases.

The Karun-4 Dam is an arch dam on the Karun River located 180 km southwest of Shahr-e-Kord in the province of Chaharmahal and Bakhtiari, Iran. The Karun has the highest discharge of all the Iranian rivers. Its construction is aimed at generating hydroelectric power supply of 2,107 million kWh annually and controlling floods in the upper Karun.

A river is a natural freshwater stream that flows on land or inside caves towards another body of water at a lower elevation, such as an ocean, lake, or another river. A river may run dry before reaching the end of its course if it runs out of water, or only flow during certain seasons. Rivers are regulated by the water cycle, the processes by which water moves around the Earth. Water first enters rivers through precipitation, whether from rainfall, the runoff of water down a slope, the melting of glaciers or snow, or seepage from aquifers beneath the surface of the Earth.

California's interconnected water system serves almost 40 million people and irrigates over 5,680,000 acres (2,300,000 ha) of farmland. As the world's largest, most productive, and potentially most controversial water system, it manages over 40 million acre-feet (49 km3) of water per year. Use of available water averages 50% environmental, 40% agricultural and 10% urban, though this varies considerably by region and between wet and dry years. In wet years, "environmental" water averages 61%, while in dry years it averages 41%, and can be even lower in critically dry years.

Flood management describes methods used to reduce or prevent the detrimental effects of flood waters. Flooding can be caused by a mix of both natural processes, such as extreme weather upstream, and human changes to waterbodies and runoff. Flood management methods can be either of the structural type and of the non-structural type. Structural methods hold back floodwaters physically, while non-structural methods do not. Building hard infrastructure to prevent flooding, such as flood walls, is effective at managing flooding. However, it is best practice within landscape engineering to rely more on soft infrastructure and natural systems, such as marshes and flood plains, for handling the increase in water.
Khersan-3 dam is a hydroelectric arch dam currently under construction on the Khersan River, a tributary of the Karun River, in Iran. When complete it will have an installed capacity of 400 MW. It is situated near Atashgah in Chaharmahal and Bakhtiari Province and is a complementary dam to Khersan project along with the proposed Khersan-1 and Khersan-2 dams. Construction began in 2007 and it is expected to become operational in 2015.

Water scarcity in Iran is caused by high climatic variability, uneven distribution of water, over exploitation of available water resources,and prioritization of economic development. Water scarcity in Iran is further exacerbated by climate change.

The Mahabad is an endorheic river in Mahabad county Iran, located at 36°46′03″N 45°42′06″E and which flows into the southern end of Lake Urmia. The Kauter and Beytas Rivers originate from the southern heights of the plain and run to the north in parallel. They join and create the Mahabad Dam reservoir and continue running as the Mahabad River.
References
- ↑ "Khersan-3 Project Information". Iran Water and Power Resources Development Co. Archived from the original on 14 July 2013. Retrieved 6 June 2013.
- ↑ Karimi, Hossain; Keshavarz, Toraj; Mohammadi, Zargham; Raeisi, Ezzatollah (20 December 2006). "Potential leakage at the Khersan 3 Dam Site, Iran: a hydrogeological approach". Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment. 66 (3): 269–278. doi:10.1007/s10064-006-0079-5.
- ↑ GHASEMI, Parsa; WATSON, Greg (2014). "The Khersan 3 Archaeological Survey". Ancient Near Eastern Studies. doi:10.2143/ANES.51.0.3038718.
- ↑ Jahandideh-Tehrani, Mahsa; Bozorg Haddad, Omid; Loáiciga, Hugo A. (2014). "Hydropower Reservoir Management Under Climate Change: The Karoon Reservoir System". Water Resources Management. 29 (3): 749–770. doi:10.1007/s11269-014-0840-7.