
Kikuoka is a traditional Japanese shop with medicinal herbs, founded in 1184 and operated by the 24th generation of the same family. [1] It is located in the historical city Nara in the Nara Prefecture, Japan. [2]

Kikuoka is a traditional Japanese shop with medicinal herbs, founded in 1184 and operated by the 24th generation of the same family. [1] It is located in the historical city Nara in the Nara Prefecture, Japan. [2]

Emperor Shōmu was the 45th emperor of Japan, according to the traditional order of succession.
Emperor Heizei, also known as Heijō-tennō, was the 51st emperor of Japan, according to the traditional order of succession. Heizei's reign lasted from 806 to 809.

The culture of Japan has changed greatly over the millennia, from the country's prehistoric Jōmon Period, to its contemporary modern culture, which absorbs influences from Asia and other regions of the world.

The Kansai region or the Kinki region, lies in the southern-central region of Japan's main island Honshū. The region includes the prefectures of Mie, Nara, Wakayama, Kyoto, Osaka, Hyōgo and Shiga, sometimes Fukui, Tokushima and Tottori. While the use of the terms "Kansai" and "Kinki" have changed over history, in most modern contexts the use of the two terms is interchangeable. The metropolitan region of Osaka, Kobe and Kyoto is the second-most populated in Japan after the Greater Tokyo Area.
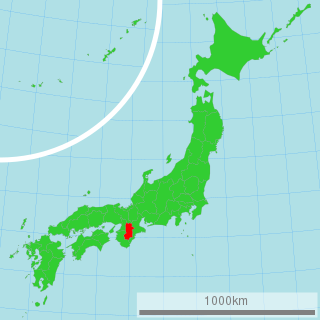
Nara Prefecture is a prefecture of Japan located in the Kansai region of Honshu. As of 2017, Nara Prefecture has a population of 1,348,930 and has a geographic area of 3,691 square kilometres (1,425 sq mi). Nara Prefecture borders Kyoto Prefecture to the north, Osaka Prefecture to the northwest, Wakayama Prefecture to the southwest, and Mie Prefecture to the east.

Emperor Go-Nara was the 105th Emperor of Japan, according to the traditional order of succession. He reigned from June 9, 1526 until his death in 1557, during the Sengoku period. His personal name was Tomohito (知仁).

Kashihara is a city located in Nara Prefecture, Japan.

Sakurai is a city located in Nara Prefecture, Japan.

Japanese architecture has been typified by wooden structures, elevated slightly off the ground, with tiled or thatched roofs. Sliding doors (fusuma) were used in place of walls, allowing the internal configuration of a space to be customized for different occasions. People usually sat on cushions or otherwise on the floor, traditionally; chairs and high tables were not widely used until the 20th century. Since the 19th century, however, Japan has incorporated much of Western, modern, and post-modern architecture into construction and design, and is today a leader in cutting-edge architectural design and technology.

Kasuga Grand Shrine is a Shinto shrine in Nara, Nara Prefecture, Japan. It is the shrine of the Fujiwara family, established in 768 CE and rebuilt several times over the centuries. The interior is famous for its many bronze lanterns, as well as the many stone lanterns that lead up the shrine.
Asuka may refer to:

Kampō medicine, often known simply as Kanpō, is the study of traditional Chinese medicine in Japan following its introduction, beginning in the 7th century. then adapted and modified to suit Japanese culture and traditions. Japanese traditional medicine referred to as TOM, uses most of the Chinese therapies including acupuncture and moxibustion, and traditional Chinese herbology and traditional food therapy.

Empress Genmei, also known as Empress Genmyō, was the 43rd monarch of Japan, according to the traditional order of succession.

The Japan national basketball team is administered by the Japan Basketball Association (JBA). A 1936 founding member of FIBA Asia, Japan has one of Asia's longest basketball traditions.

Nara is the capital city of Nara Prefecture, Japan.

Heijō-kyō, was the Capital of Japan during most of the Nara period, from 710–40 and again from 745–84. The imperial palace is a listed UNESCO World Heritage together with other places in the city of Nara.

The Kei school was a Japanese school (style) of Buddhist sculpture which emerged in the early Kamakura period. Based in Nara, it was the dominant school in Buddhist sculpture in Japan into the 14th century, and remained influential until the 19th. Art historian Joan Stanley Baker cites the Kei school's early works as the last highpoint in the history of Japanese sculpture.

Kurumi Nara is a Japanese professional tennis player.
The Six Schools of Nara Buddhism, also known as the Rokushū 六宗, were academic Buddhist sects. These schools came to Japan from Korea and China during the late 6th and early 7th centuries. All of these schools were controlled by the newly formed Japanese government of Nara. These schools were installed to mimic and expand upon already existing mainland Asian Buddhist thought.

Susumu Nakanishi is a scholar of Japanese literature, particularly of the Man'yōshū.
| This article about a Japanese corporation- or company-related topic is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |