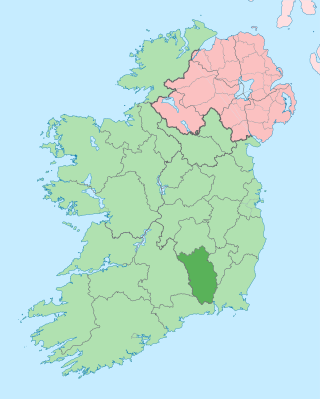
County Kilkenny is a county in Ireland. It is in the province of Leinster and is part of the Southern Region. It is named after the city of Kilkenny. Kilkenny County Council is the local authority for the county. At the 2022 census the population of the county was 103,685. The county was based on the historic Gaelic kingdom of Ossory (Osraighe), which was coterminous with the Diocese of Ossory.

Kilkenny is a city in County Kilkenny, Ireland. It is located in the South-East Region and in the province of Leinster. It is built on both banks of the River Nore. The 2022 census gave the population of Kilkenny as 27,184, the thirteenth-largest urban center in Ireland.

The A41 is a trunk road between London and Birkenhead, England. Now in parts replaced by motorways, it passes through or near Watford, Kings Langley, Hemel Hempstead, Aylesbury, Bicester, Solihull, Birmingham, West Bromwich, Wolverhampton, Newport, Whitchurch, Chester and Ellesmere Port.
The A1, also known as the Great North Road, is the longest numbered road in the United Kingdom, at 410 miles (660 km). It connects London, the capital of England, with Edinburgh, the capital of Scotland. The numbering system for A-roads, devised in the early 1920s, was based around patterns of roads radiating from two hubs at London and Edinburgh. The first number in the system, A1, was given to the most important part of that system: the road from London to Edinburgh, joining the two central points of the system and linking the UK's two mainland capital cities. It passes through or near north London, Hatfield, Stevenage, Baldock, Biggleswade, Peterborough, Stamford, Grantham, Newark-on-Trent, Retford, Doncaster, Pontefract, York, Wetherby, Ripon, Darlington, Durham, Gateshead, Newcastle upon Tyne, Morpeth, Alnwick, Berwick-upon-Tweed, Dunbar, Haddington, Musselburgh, and east Edinburgh.

The A38, parts of which are known as Devon Expressway, Bristol Road and Gloucester Road, is a major A-class trunk road in England.

The A52 is a major road in the East Midlands, England. It runs east from a junction with the A53 at Newcastle-under-Lyme near Stoke-on-Trent via Ashbourne, Derby, Stapleford, Nottingham, West Bridgford, Bingham, Grantham, Boston and Skegness to the east Lincolnshire coast at Mablethorpe. It is approximately 147 miles (237 km) long.

The River Nore is one of the principal rivers in the South-East Region of Ireland. The 140-kilometre-long (87 mi) river drains approximately 2,530 square kilometres (977 sq mi) of Leinster and Munster, that encompasses parts of three counties. Along with the River Suir and River Barrow, it is one of the constituent rivers of the group known as the Three Sisters.

The A594 Central Ring is Leicester's central distributor road network.

The Riverside Quarter, or Riverside Exchange is one of Sheffield's 11 designated City Centre Quarters. Its borders are West Bar, Coulston Street, Bridge Street, Castlegate, Exchange Place and the Parkway to its south, the Wicker Viaduct, Johnson Street, Spitalfields and Nursery Street to the North, and Corporation Street to the west. It is named after the Whitbread Exchange Brewery, which was formerly located on the site of the current developments, and incorporates the Victoria Quays.

Bennettsbridge is a village in County Kilkenny in Ireland. It is situated on the River Nore 6 kilometres (3.7 mi) south of Kilkenny city, in the centre of the county. Bennettsbridge is a census town, and had population of 745 as of the 2016 census.

The N30 road is a national primary road in Ireland. It connects the N25 road and M11 motorway, providing a link running east-northeast through County Wexford, between New Ross and Enniscorthy. This provides for a more direct national route between the two towns, as the N25 and N11 both run to Wexford town, eastwards from New Ross and southwards from Enniscorthy respectively.

Newbridge is a village in the civil parish of Kirkliston, west of Edinburgh in Scotland. It formerly belonged to Midlothian, but it has been on the western fringe of to the City of Edinburgh since 1975. The original village consists of a small crossroads settlement to the east of the eponymous New Bridge, which spans the River Almond. Around it is a confusion of roads and industrial estates converging on the Newbridge Roundabout, the meeting point of the M8 and M9 motorways.

The R710 road is a regional road in Ireland. Located in the south of Ireland at Waterford, it forms the Outer Ring Road around the south of the city. As of December 2006 it commences on the Old Kilmeaden Road at Knockhouse Lower, west of Waterford City and ends at a junction with the R683 on the Dunmore Road in the south-east of the city.

The A1237 road is a road that runs to the west and north of the city of York, England. It forms part of the York Outer Ring Road as either end of the route forms junctions with the A64 to the south-west and east of the city to act as a city distributor. Construction began in 1984 and consisted of three distinct building phases. The road took three years to complete and has been subject since to studies looking to improve traffic flow and reduce accidents. The National Speed Limit for an A Class Road applies.

Mounts Bay Road is a major road in Perth, Western Australia, extending southwest from the central business district along the north bank of the Swan River, at the base of Kings Park.

The A4053 Coventry ring road is a 2.25-mile (3.62 km) ring road in Coventry, England, which forms a complete dual-carriageway loop around the city centre. The road encompasses the old and new Coventry Cathedrals, the city's shopping areas and much of Coventry University. With the exception of one roundabout at junction 1, the ring road's nine junctions are entirely grade separated and closely spaced, with weaving sections between them, some as short as 300 yards (270 m), giving the road a reputation for being difficult to navigate. The junctions include connections with three other A roads: the A4114, A4600 and A429.

Irishtown is the neighborhood in Kilkenny in Ireland around St Canice's Cathedral. It was formerly a borough, also called Newcourt or St Canice's, separated by the River Breagagh from the walled town of Kilkenny to the south.

Green's Bridge, or Greensbridge, is an elegant, Palladian-style, limestone arch bridge that crosses the river Nore in Kilkenny, Ireland. The bridge is a series of five elliptical arches of high-quality carved limestone masonry with a two-arch culvert to the east. Its graceful profile, architectural design value, and civil engineering heritage endow it with national significance. Historian Maurice Craig described it as one of the five-finest bridges in Ireland. It was built by William Colles and designed by George Smith, and was completed in 1766. The bridge was 250 years old in 2016.

Road building was central to planning policy for much of the 20th century in Bristol, England. The planned road network evolved over time but at its core was a network of concentric ring roads and high-capacity radial roads.

















