
The Snake River is a major river in the interior Pacific Northwest region of the United States. About 1,080 miles (1,740 km) long, it is the largest tributary of the Columbia River, which is the largest North American river that empties into the Pacific Ocean. Beginning in Yellowstone National Park, western Wyoming, it flows across the arid Snake River Plain of southern Idaho, the rugged Hells Canyon on the borders of Idaho, Oregon and Washington, and finally the rolling Palouse Hills of southeast Washington. It joins the Columbia River just downstream from the Tri-Cities, Washington, in the southern Columbia Basin.

Butte County is a rural county located in the U.S. state of Idaho. As of the 2020 census, the population was 2,574, making it the third-least populous county in Idaho. Its county seat and largest city is Arco. The county was established in 1917 from parts of Bingham, Blaine, and Jefferson counties. The county gained territory in the Clyde area from Custer County in 1937 to reach its present boundary.

Arco is a city in Butte County, Idaho, United States. The population was 879 as of the 2020 United States census, down from 995 at the 2010 census. Arco is the county seat and largest city in Butte County.

Twin Falls is the county seat and largest city of Twin Falls County, Idaho, United States. The city had a population of 51,807 as of the 2020 census. In the Magic Valley region, Twin Falls is the largest city in a 100-mile (160 km) radius, and is the regional commercial center for south-central Idaho and northeastern Nevada. It is the principal city of the Twin Falls metropolitan statistical area, which officially includes the entirety of Twin Falls and Jerome Counties. The border town resort community of Jackpot, Nevada, 50 mi (80 km) south at the state line, is unofficially considered part of the greater Twin Falls area. Located on a broad plain at the south rim of the Snake River Canyon, Twin Falls, is where daredevil Evel Knievel attempted to jump across the canyon in 1974 on a steam-powered rocket. The jump site is northeast of central Twin Falls, midway between Shoshone Falls and the Perrine Bridge.

The Snake River Plain is a geologic feature located primarily within the U.S. state of Idaho. It stretches about 400 miles (640 km) westward from northwest of the state of Wyoming to the Idaho-Oregon border. The plain is a wide, flat bow-shaped depression and covers about a quarter of Idaho. Three major volcanic buttes dot the plain east of Arco, the largest being Big Southern Butte.

The Yellowstone hotspot is a volcanic hotspot in the United States responsible for large scale volcanism in Idaho, Montana, Nevada, Oregon, and Wyoming, formed as the North American tectonic plate moved over it. It formed the eastern Snake River Plain through a succession of caldera-forming eruptions. The resulting calderas include the Island Park Caldera, Henry's Fork Caldera, and the Bruneau-Jarbidge caldera. The hotspot currently lies under the Yellowstone Caldera. The hotspot's most recent caldera-forming supereruption, known as the Lava Creek Eruption, took place 640,000 years ago and created the Lava Creek Tuff, and the most recent Yellowstone Caldera. The Yellowstone hotspot is one of a few volcanic hotspots underlying the North American tectonic plate; another example is the Anahim hotspot.

Shoshone Falls is a waterfall in the western United States, on the Snake River in south-central Idaho, approximately three miles (5 km) northeast of the city of Twin Falls. Sometimes called the "Niagara of the West," Shoshone Falls is 212 feet (65 m) in height, 45 feet (14 m) higher than Niagara Falls, and flows over a rim nearly one thousand feet (300 m) in width.

This is a directory of properties and districts included among the National Register of Historic Places listings in Idaho. There are approximately 1,000 sites in Idaho listed on the National Register. Each of the state's 44 counties has at least one listing on the National Register.

Wilson Butte Cave is located on the Snake River plain in Jerome County northeast of Twin Falls and southeast of Shoshone, Idaho. Listed on the National Register of Historic Places as an archeological site, it is maintained by the Bureau of Land Management (BLM).

Snake River Valley is Idaho's first American Viticultural Area (AVA) that encompasses an area in southwestern Idaho and two counties in eastern Oregon. The area was established on April 9, 2007 by the Alcohol and Tobacco Tax and Trade Bureau (TTB), Treasury after reviewing the petition submitted by Idahoan vintners of the Snake River Valley, the Idaho Grape Growers and Wine Producers Commission, and the Idaho Department of Commerce and Labor, collectively acting as “petitioner” to establish the 8,263 square miles viticultural area named "Snake River Valley." For wines to bear the "Snake River Valley" label, at least 85% of the grapes used for production must be grown in the designated area, which includes the southwestern Idaho counties of Ada, Adams, Boise, Canyon, Elmore, Gem, Gooding, Jerome, Owyhee, Payette, Twin Falls, and Washington, and the Eastern Oregon counties of Malheur and Baker. The appellation, when established, was resident to 15 wineries and 46 vineyards with 1,800 acres (728 ha) under vine.

The Great Falls Tectonic Zone is a major intracontinental shear zone between the Hearne craton and Wyoming craton basement rock of the Archean Eon which form part of the North American continent. The zone is an area about 100 miles wide extending from the southwestern Idaho-Montana border across Montana to the northwestern Montana-Saskatchewan-North Dakota border. It is named for the Great Falls of the Missouri River, a major geologic feature of the area. The central and western portions of the zone are believed to be about 1.1 to 3.3 billion years old. The central part of the zone lacks Archean rock, however, leading at least one group of scientists to speculate that it was formed very late in the Paleoproterozoic Era.

The North and South Menan Buttes in southeastern Idaho are two of the world's largest volcanic tuff cones. The two cones, with four smaller associated cones, align along a north-northwest line and comprise the Menan Complex. The buttes rise about 800 feet above the surrounding Snake River plain and are late Pleistocene in age, dating to approximately 10,000 YBP. The South Menan Butte is currently in private hands, however North Menan Butte is publicly owned and has been designated as a National Natural Landmark and a Research Natural Area by the United States Congress. The US Bureau of Land Management designated the North Butte as an Area of Critical Environmental Concern (ACEC).

Big Butte Creek is a 12-mile-long (19 km) tributary of the Rogue River in the U.S. state of Oregon. It drains approximately 245 square miles (635 km2) of Jackson County. Its two forks, the North Fork and the South Fork, both begin high in the Cascade Range near Mount McLoughlin. Flowing predominantly west, they meet near the city of Butte Falls. The main stem flows generally northwest until it empties into the Rogue Falls was incorporated in 1911, and remains the only incorporated town within the watershed's boundaries.
Deer Lodge Pass, elevation 5,879 ft (1,792 m), is a mountain pass on the Continental Divide in southwestern Montana, about 11 miles southwest of Butte. It is traversed by Interstate 15 and is one of three crossings of the Divide by I-15, the others being Monida Pass and Elk Park Pass north of Butte. Unlike most other passes in western Montana, Deer Lodge Pass is in the midst of treeless, rolling hills, and the grades on the highway are relatively gentle.

The Guffey Butte–Black Butte Archeological District is a 14,000 acres (57 km2) historic district in southwestern Idaho, United States, that is listed on the National Register of Historic Places (NRHP). It includes numerous archeological sites in Ada, Canyon, Elmore, and Owyhee counties.
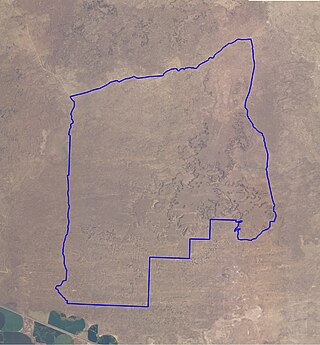
The Shale Butte Wilderness Study Area is a Bureau of Land Management wilderness study area (WSA) in Lincoln County, Idaho. It covers 15,560 acres (6,300 ha). The WSA is located to the south of Craters of the Moon National Monument and Preserve.

North Big Bosom Butte is a 6,384-foot (1,946-metre) mountain summit located in Whatcom County of Washington state.

The Twin Falls saucer hoax was a hoaxed flying disc discovered in Twin Falls, Idaho, United States, on July 11, 1947. Amid a nationwide wave of alleged "flying disc" sightings, residents of Twin Falls reported recovering a 30 in (76 cm) "disc". FBI and Army officials took possession of the disc and quickly proclaimed the object to be a hoax. Press reported that local teenagers admitted to perpetrating the hoax.

East Butte is a 6,572-foot elevation (2,003 m) summit located in Bingham County, Idaho, United States.

Middle Butte is a 6,391-foot elevation (1,948 m) summit located in Bingham County, Idaho, United States.





















