
Ground transport in the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) has always been difficult. The terrain and climate of the Congo Basin present serious barriers to road and rail construction, and the distances are enormous across this vast country. Furthermore, chronic economic mismanagement and internal conflict has led to serious under-investment over many years.
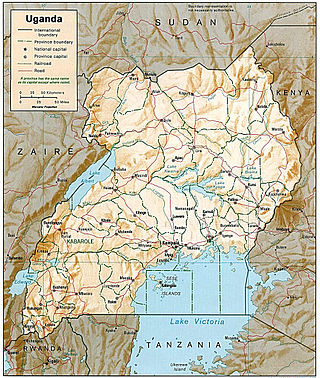
Transport in Uganda refers to the transportation structure in Uganda. The country has an extensive network of paved and unpaved roads.

Bukavu is a city in eastern Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC), lying at the extreme south-western edge of Lake Kivu, west of Cyangugu in Rwanda, and separated from it by the outlet of the Ruzizi River. It is the capital of the South Kivu Province and as of 2012 it had an estimated population of 806,940.

Kisangani is the capital of Tshopo Province, located on the Congo River in the eastern part of the central Congo Basin in the Democratic Republic of the Congo. It is the country's fifth-most populous urban area, with an estimated population of 1,602,144 as of 2016, and the largest of the cities in the tropical woodlands of the Congo.

Bandundu, formerly known as Banningville or Banningstad, is the capital city of Kwilu Province of the Democratic Republic of the Congo.

Bunia is the capital city of Ituri Province in the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC). It was part of the Orientale Province until that province's dissolution.
Articles related to the Democratic Republic of the Congo include:

The Central Bank of the Congo, colloquially known by its acronym BCC, is the central bank of the Democratic Republic of the Congo. Its headquarters are located on Boulevard Colonel Tshatshi in Gombe, Kinshasa, surrounded by significant institutions including the Palais de la Nation, the National Library, and several government ministries.
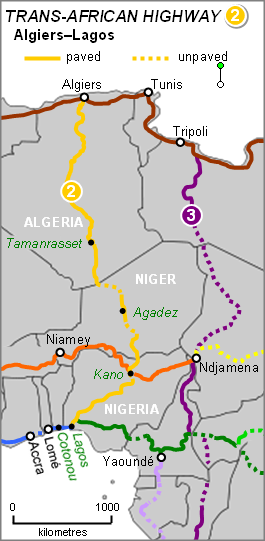
The Trans-Sahara Highway or TAH 2, formally the Trans-Saharan Road Corridor (TSR), and also known as the African Unity Road, is a transnational infrastructure project to facilitate trade, transportation, and regional integration among six African countries: Algeria, Chad, Mali, Niger, Nigeria, and Tunisia. It runs roughly 4,500 km north to south across the Sahara desert from Algiers, Algeria on the Mediterranean coast of North Africa to Lagos, Nigeria on the Atlantic coast of West Africa; subsequently, it is sometimes known as the Algiers–Lagos Highway or Lagos–Algiers Highway.

The Trans-Sahelian Highway or TAH 5 is a transnational highway project to pave, improve and ease border formalities on a highway route through the southern fringes of the Sahel region in West Africa between Dakar, Senegal in the west and Ndjamena, Chad, in the east. Alternative names for the highway are the Dakar-Ndjamena Highway or Ndjamena-Dakar Highway and it is Trans-African Highway 5 in the Trans-African Highway network.
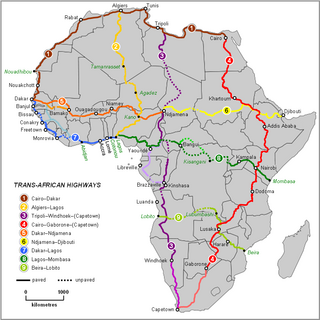
The Trans-African Highway network comprises transcontinental road projects in Africa being developed by the United Nations Economic Commission for Africa (UNECA), the African Development Bank (ADB), and the African Union in conjunction with regional international communities. They aim to promote trade and alleviate poverty in Africa through highway infrastructure development and the management of road-based trade corridors. The total length of the nine highways in the network is 56,683 km (35,221 mi).
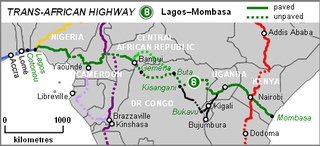
The Lagos–Mombasa Highway or TAH 8 is Trans-African Highway 8 and is the principal road route between West and East Africa. It has a length of 6,259 km (3,889 mi) and is contiguous with the Dakar-Lagos Highway with which it will form the longest east-west crossing of the continent for a total distance of 10,269 km (6,381 mi). Its main importance at the moment is connecting West Africa with Southern Africa via Yaoundé and Gabon because the section through the Democratic Republic of the Congo is unpaved and difficult.
The Tripoli–Cape Town Highway or TAH 3 is Trans-African Highway 3 in the transcontinental road network being developed by the United Nations Economic Commission for Africa (UNECA), the African Development Bank (AfDB), and the African Union. The route has a length of 10,808 km (6,716 mi) and has the longest missing links and requires the most new road construction.

The Régie de Distribution d'Eau, abbreviated as REGIDESO, is a state-owned utility company located on Boulevard Du 30 Juin, in the Gombe commune of Kinshasa, Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC). It is responsible for producing and distributing water throughout the national territory, encompassing both urban and rural areas. Established in 1929, REGIDESO operates autonomously under the oversight of the Ministry of Energy and the Portfolio.

The Democratic Republic of the Congo was one of the first African countries to recognize HIV, registering cases of HIV among hospital patients as early as 1983.

Mass media in the Democratic Republic of the Congo are nationally and internationally state-owned and operated.

The Cairo–Cape Town Highway is Trans-African Highway 4 in the transcontinental road network being developed by the United Nations Economic Commission for Africa (UNECA), the African Development Bank (AfDB), and the African Union. The route has a length of 10,228 km (6,355 mi) and links Cairo in Egypt to Cape Town in South Africa.

Trust Merchant Bank or TMB, is a commercial bank based in the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC), with its headquarters located in Lubumbashi. The bank began operations in 2004. TMB operates in all sectors of the local banking market, including in retail banking, SME banking, corporate banking, and mobile banking.
The following is a timeline of the history of the city of Kinshasa, Democratic Republic of the Congo.
National Road 3 (N3) is a road in the Democratic Republic of the Congo. It runs from the city of Bukavu on the south end of Lake Kivu to the city of Kisangani.















