Risk management is the identification, evaluation, and prioritization of risks followed by coordinated and economical application of resources to minimize, monitor, and control the probability or impact of unfortunate events or to maximize the realization of opportunities.
Mitigation is the reduction of something harmful that has occurred or the reduction of its harmful effects. It may refer to measures taken to reduce the harmful effects of hazards that remain in potentia, or to manage harmful incidents that have already occurred. It is a stage or component of emergency management and of risk management. The theory of mitigation is a frequently used element in criminal law and is often used by a judge to try cases such as murder, where a perpetrator is subject to varying degrees of responsibility as a result of one's actions.

Climate change adaptation is the process of adjusting to the effects of climate change. These can be both current or expected impacts. Adaptation aims to moderate or avoid harm for people, and is usually done alongside climate change mitigation. It also aims to exploit opportunities. Humans may also intervene to help adjustment for natural systems. There are many adaptation strategies or options. They can help manage impacts and risks to people and nature. The four types of adaptation actions are infrastructural, institutional, behavioural and nature-based options.
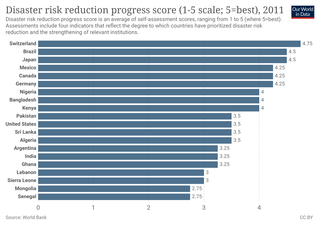
Disaster risk reduction (DRR) is an approach for planning and taking steps to make disasters less likely to happen, and less damaging when they do happen. DRR aims to make communities stronger and better prepared to handle disasters. When DRR is successful, it decreases the vulnerability of communities because it mitigates the effects of disasters. This means DRR can reduce the severity and number of risky events. Since climate change can increase climate hazards, DRR and climate change adaptation are often looked at together in development efforts.
Climate risk is the potential for problems for societies or ecosystems from the impacts of climate change. The assessment of climate risk is based on formal analysis of the consequences, likelihoods and responses to these impacts. Societal constraints can also shape adaptation options. There are different values and preferences around risk, resulting in differences of risk perception.
The Climate Investment Funds (CIF) was established in 2008 as a multilateral climate fund in order to finance pilot projects in developing countries at the request of the G8 and G20. The CIF administers a collection of programs with a view of helping nations fight the impacts of climate change and accelerate their shift to a low-carbon economy. Through contributions from 14 donor countries, CIF supports more than 350 projects in 72 low and middle-income countries on the frontlines of the climate crisis.
A National Adaptation Programme of Action (NAPA) is a type of plan submitted to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) by least developed countries, to describe the country's perception of its most "urgent and immediate needs to adapt to climate change". NAPAs are not supposed to include original research, but use existing information and include profiles of priority projects that are intended to address those needs that have been identified.

Climate change is a critical issue in Bangladesh as the country is one of the most vulnerable to the effects of climate change. In the 2020 edition of Germanwatch's Climate Risk Index, it ranked seventh in the list of countries most affected by climate calamities during the period 1999–2018. Bangladesh's vulnerability to the effects of climate change is due to a combination of geographical factors, such as its flat, low-lying, and delta-exposed topography, and socio-economic factors, including its high population density, levels of poverty, and dependence on agriculture. The impacts and potential threats include sea level rise, temperature rise, food crises, droughts, floods, and cyclones.

Climate change in Africa is an increasingly serious threat as Africa is among the most vulnerable continents to the effects of climate change. Some sources even classify Africa as "the most vulnerable continent on Earth". Climate change and climate variability will likely reduce agricultural production, food security and water security. As a result, there will be negative consequences on people's lives and sustainable development in Africa.

Coastal hazards are physical phenomena that expose a coastal area to the risk of property damage, loss of life, and environmental degradation. Rapid-onset hazards last a few minutes to several days and encompass significant cyclones accompanied by high-speed winds, waves, and surges or tsunamis created by submarine (undersea) earthquakes and landslides. Slow-onset hazards, such as erosion and gradual inundation, develop incrementally over extended periods.

Asia Pacific Adaptation Network (APAN) is a regional program that works with governments and organizations to share knowledge about adapting to climate change and to support implementation of adaptation measures. APAN was set up in October 2009 by the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP), as part of the Global Adaptation Network (GAN). APAN is considered a key mobilizer of adaptation knowledge in Asia and the Pacific.

The United Nations Office for Disaster Risk Reduction (UNDRR) was created in December 1999 to ensure the implementation of the International Strategy for Disaster Reduction.

Globally, Nepal is ranked fourth in terms of vulnerability to climate change. Floods spread across the foothills of the Himalayas and bring landslides, leaving tens of thousands of houses and vast areas of farmland and roads destroyed. In the 2020 edition of Germanwatch's Climate Risk Index, it was judged to be the ninth hardest-hit nation by climate calamities during the period 1999 to 2018. Nepal is a least developed country, with 28.6 percent of the population living in multidimensional poverty. Analysis of trends from 1971 to 2014 by the Department of Hydrology and Meteorology (DHM) shows that the average annual maximum temperature has been increasing by 0.056 °C per year. Precipitation extremes are found to be increasing. A national-level survey on the perception-based survey on climate change reported that locals accurately perceived the shifts in temperature but their perceptions of precipitation change did not converge with the instrumental records. Data reveals that more than 80 percent of property loss due to disasters is attributable to climate hazards, particularly water-related events such as floods, landslides and glacial lake outburst floods (GLOFs).

In the fields of engineering and construction, resilience is the ability to absorb or avoid damage without suffering complete failure and is an objective of design, maintenance and restoration for buildings and infrastructure, as well as communities. A more comprehensive definition is that it is the ability to respond, absorb, and adapt to, as well as recover in a disruptive event. A resilient structure/system/community is expected to be able to resist to an extreme event with minimal damages and functionality disruptions during the event; after the event, it should be able to rapidly recovery its functionality similar to or even better than the pre-event level.

Disaster preparedness in museums, galleries, libraries, archives and private collections, involves any actions taken to plan for, prevent, respond or recover from natural disasters and other events that can cause damage or loss to cultural property. 'Disasters' in this context may include large-scale natural events such as earthquakes, flooding or bushfire, as well as human-caused events such as theft and vandalism. Increasingly, anthropogenic climate change is a factor in cultural heritage disaster planning, due to rising sea levels, changes in rainfall patterns, warming average temperatures, and more frequent extreme weather events.

The effects of climate change on small island countries are affecting people in coastal areas through sea level rise, increasing heavy rain events, tropical cyclones and storm surges. These effects of climate change threaten the existence of many island countries, their peoples and cultures. They also alter ecosystems and natural environments in those countries. Small island developing states (SIDS) are a heterogenous group of countries but many of them are particularly at risk to climate change. Those countries have been quite vocal in calling attention to the challenges they face from climate change. For example, the Maldives and nations of the Caribbean and Pacific Islands are already experiencing considerable impacts of climate change. It is critical for them to implement climate change adaptation measures fast.

Climate change in Tanzania is affecting the natural environment and residents of Tanzania. Temperatures in Tanzania are rising with a higher likelihood of intense rainfall events and of dry spells.

Vietnam is among the most affected countries by global climate change. A large number of studies show that Vietnam is experiencing climate change and will be severely negatively affected in coming decades. These negative effects include sea level rise, salinity intrusion and other hydrological problems like floods, river mouth evolution and sedimentation. Natural hazards such as cold waves, storm surges will increase in frequency, with negative effects on the country's development, infrastructure and economy.
Ecosystem-based adaptation encompasses a broad set of approaches to adapt to climate change. They all involve the management of ecosystems and their services to reduce the vulnerability of human communities to the impacts of climate change. The Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD) defines EBA as "the use of biodiversity and ecosystem services as part of an overall adaptation strategy to help people to adapt to the adverse effects of climate change".

Climate change adaptation in the Philippines is being incorporated into development plans and policies that specifically target national and local climate vulnerabilities. As a developing country and an archipelago, the Philippines is particularly vulnerable to a variety of climatic threats like intensifying tropical cyclones, drastic changes in rainfall patterns, rising sea levels, and rising temperatures. According to the UN Office for the Coordination of Humanitarian Affairs (OCHA), the Philippines is one of the most disaster-prone countries in the world. In 2021, the Global Climate Risk Index ranked the Philippines fourth of the ten countries most affected between the years 2000 and 2019. The need for managing climate risks through climate change adaptation has become increasingly evident. Adaptation can reduce, moderate or avoid current and expected climate effects or take advantage of beneficial climatic events. Developing greater resilience to various threats can be a major goal of comprehensive disaster risk reduction strategy. The Philippines is therefore working on a number of national and local adaptation and disaster risk reduction strategies to build the country's climate resilience.