Related Research Articles

Ethiopia is located in the Horn of Africa. It is bordered by Eritrea to the north, Djibouti and Somalia to the east, Sudan and South Sudan to the west, and Kenya to the south. Ethiopia has a high central plateau, the Abyssinian Highlands that varies from 1,290 to 3,000 m above sea level, with some 25 mountains whose peaks rise over 4,000 meters (13,200ft), the highest being Ras Dashen at 4,543 meters (14,538ft).

The Appalachian Mountains, often called the Appalachians, are a mountain range in eastern to northeastern North America. The term "Appalachian" refers to several different regions associated with the mountain range, and its surrounding terrain. The general definition used is one followed by the United States Geological Survey and the Geological Survey of Canada to describe the respective countries' physiographic regions. The U.S. uses the term Appalachian Highlands and Canada uses the term Appalachian Uplands; the Appalachian Mountains are not synonymous with the Appalachian Plateau, which is one of the provinces of the Appalachian Highlands.
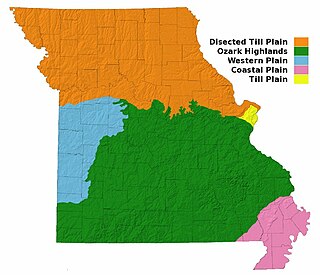
Missouri, a state near the geographical center of the United States, has three distinct physiographic divisions:

Southern Indiana is a geographic and cultural region that generally comprises the southern third of the U.S. state of Indiana and borders the states of Illinois to the west, Kentucky to the south, and Ohio to the east. Spanning the state's southernmost 33 counties, its main population centers include Southwestern Indiana, the Louisville metropolitan area (south), and the Cincinnati metropolitan area (southeast). The region's history and geography have led to a blending of and Southern and Midwestern cultures, distinct from the rest of the state. It is often considered to be part of the Upland South and the Southern influenced Lower Midwest.
The Highland Rim is a geographic term for the area in Tennessee, North Alabama, and Kentucky which surrounds the Central Basin. Geologically, the Central Basin is a dome. The Highland Rim is a cuesta surrounding the basin, and the border where the difference in elevation is sharply pronounced is an escarpment.

The Allegheny Front is the major southeast- or east-facing escarpment in the Allegheny Mountains in southern Pennsylvania, western Maryland, eastern West Virginia, and western Virginia. The Allegheny Front forms the boundary between the Ridge-and-Valley Appalachians to its east and the Appalachian Plateau to its west. The Front is closely associated with the Appalachian Mountains' Eastern Continental Divide, which in this area divides the waters of the Ohio/Mississippi river system, flowing to the Gulf of Mexico, from rivers flowing into Chesapeake Bay and from there into the Atlantic Ocean.
Floyds Knobs is a small unincorporated community in Lafayette Township, Floyd County, Indiana, United States. Historically a farming community on the outskirts of New Albany, it has since become a bedroom community for Louisville, Kentucky. It contains subdivisions, farms, small shopping centers, churches, and transmitters for many of the area's television and radio stations. It is also the location of Floyd Central High School. There is a population of about 11,412 to 12,439.
The Indiana Uplands or the Hoosier Uplands are a geographical region in south-central Indiana. On a topographical map the Indiana Uplands begin slightly north of the city of Martinsville, Indiana and continue south to the Ohio River. The description of the region inspired the name of Upland Brewing Company. The region's approximate boundaries are Interstate 65 to the east and U.S. Route 231 to the west. The Uplands are characterized by terrain varying from rolling hills to cliffs, sharp rugged hills and valleys. Nearly all of these hills are composed of sandstone, limestone, and siltstone from West to east. The siltstone hills are the most rugged followed by the sandstone while the limestone are the smoothest. This is contrast to the Tipton Till Plain immediately to the north in central Indiana, which features flat to gently rolling landscape. Interstates 64 and 69 pass through this rugged section of the state with sections of both cut deep into the rock and others towering over the treetops. Overall, the Indiana Uplands have the same basic characteristics of the Pennyrile Region and the Highland Rim and are the northernmost extent of the range.

Hoosier Hill is the highest natural point in the U.S. state of Indiana with a claimed elevation of 1,257 feet above sea level. Hoosier Hill's claimed elevation is based on SRTM digital elevation data which is now considered to be outdated. Using newer elevation tools such as USGS's 3DEP, the top of Hoosier Hill is closer to 1,255.48 feet above sea level. Hoosier Hill is in the rural area of Franklin Township, Wayne County to the northwest of Bethel. The nearest intersection to the high point is Elliot Road and County Line Road. The nearest major landmark is Interstate 70 and Richmond 11 miles (18 km) to the south.

The Cody Scarp or Cody Escarpment is located in north and north central Florida United States. It is a relict scarp and ancient persistent topographical feature formed from an ancient early Pleistocene shorelines of ~1.8 million to 10,000 years BP during interglacial periods. The Cody Scarp has a slope of 5% to 12%.

Louisville is a city in Jefferson County, in the U.S. state of Kentucky. It is located at the Falls of the Ohio River.
Weed Patch Hill, also known as Weed Patch Knob, is the third highest named summit in the U.S. state of Indiana. Located in Washington Township and Brown County State Park, it is the highest point in the Knobstone Escarpment.

The Great Escarpment is a major topographical feature in Africa that consists of steep slopes from the high central Southern African plateau downward in the direction of the oceans that surround southern Africa on three sides. While it lies predominantly within the borders of South Africa, in the east the escarpment extends northward to form the border between Mozambique and Zimbabwe, continuing on beyond the Zambezi river valley to form the Muchinga Escarpment in eastern Zambia. In the west, it extends northward into Namibia and Angola. It is the combination of this escarpment and the aridity of Southern Africa that leads to the lack of navigable rivers in South Africa.

The Geology of Pennsylvania consists of six distinct physiographic provinces, three of which are subdivided into different sections. Each province has its own economic advantages and geologic hazards and plays an important role in shaping everyday life in the state. From the southeast corner to the northwest corner of the state, they include: the Atlantic Plain Province, the Piedmont Province, the New England Province, the Ridge and Valley Province, the Appalachain Province, and the Central Lowlands Province.

The geography of Indiana comprises the physical features of the land and relative location of U.S. State of Indiana. Indiana is in the north-central United States and borders on Lake Michigan. Surrounding states are Michigan to the north and northeast, Illinois to the west, Kentucky to the south, and Ohio to the east. The entire southern boundary is the Ohio River.

The Laurentian Upland is a physiographic region which, when referred to as the "Laurentian Region" or the Grenville geological province, is recognized by Natural Resources Canada as one of five provinces of the larger Canadian Shield physiographic division. The United States Geological Survey recognizes the Laurentian Upland as the larger general upland area of the Canadian Shield.
North Yuba is an American Viticultural Area (AVA) located in Yuba County, California, United States about 70 miles (113 km) north of Sacramento. It was established on August 30, 1985 by the Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco, Firearms and Explosives (ATF), Treasury after approving the submitted petition by Karl Werner and James R. Bryant, officers of Renaissance Vineyard and Winery, Inc. in Oregon House. They petitioned ATF for the establishment of a viticultural area to be named "North Yuba.”

The Coast Range ecoregion is a Level III ecoregion designated by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) in the U.S. states of Washington, Oregon, and California. It stretches along the Pacific Coast from the tip of the Olympic Peninsula in the north to the San Francisco Bay in the south, including Grays Harbor, Willapa Bay, and the Long Beach Peninsula in Washington, the entire length of the Oregon Coast, and the Northern California Coast. Named for the Coast Range mountains, it encompasses the lower elevations of the Olympic Mountains, the Oregon Coast Range, the Californian North Coast Ranges, and surrounding lowlands.

The Peace River Formation is a stratigraphical unit of middle Albian age in the Western Canadian Sedimentary Basin.
The Hominy Hills are a range of low, gravel-capped hills and upland areas located along the boundary of Colts Neck, Howell and Wall Townships, in Monmouth County, New Jersey, and extending east into the Borough of Tinton Falls, formerly part of Shrewsbury Township. The hills attain heights of over 300 feet in elevation, attaining a maximum elevation of 307 feet at Throckmorton Hill, which is the highest point in Howell Township.
References
- ↑ Our Hoosier State beneath us; Indiana Geological Survey, Department of Natural Resources; Indianapolis, IN
39°10′01″N86°13′02″W / 39.16694°N 86.21722°W